接着上一篇继续分析Rewriter::Rewriter()构造函数中完成的逻辑。在构造函数中会调用make_constant_pool_cache()函数,不过在先介绍这个函数之前,需要介绍一下ConstantPoolCache与ConstantPoolCacheEntry。这两个类都定义在cpCache.hpp文件中。
1、ConstantPoolCache类
ConstantPoolCache类保存了连接过程中的一些信息,从而让程序在解释执行的过程中避免重复执行连接的过程。这个类的定义如下:
// A constant pool cache is a runtime data structure set aside to a constant pool. The cache
// holds interpreter runtime information for all field access and invoke bytecodes. The cache
// is created and initialized before a class is actively used (i.e., initialized), the individual
// cache entries are filled at resolution (i.e., "link") time (see also: rewriter.*).
class ConstantPoolCache: public MetaspaceObj {
private:
int _length;
ConstantPool* _constant_pool; // the corresponding constant pool
// Constructor
ConstantPoolCache(int length,
const intStack& inverse_index_map,
const intStack& invokedynamic_inverse_index_map,
const intStack& invokedynamic_references_map) :
_length(length),
_constant_pool(NULL) {
initialize( inverse_index_map,
invokedynamic_inverse_index_map,
invokedynamic_references_map);
}
private:
static int header_size() {
return sizeof(ConstantPoolCache) / HeapWordSize; // 2个字,一个字包含有8字节
}
static int size(int length) { // 返回的是字数量
// ConstantPoolCache加上length个ConstantPoolCacheEntry的大小
// in_words(ConstantPoolCacheEntry::size())=4
return align_object_size(header_size() + length * in_words(ConstantPoolCacheEntry::size()));
}
public:
int size() const {
return size(length());
}
private:
ConstantPoolCacheEntry* base() const {
// 这就说明在ConstantPoolCache之后紧接着的是ConstantPoolCacheEntry项
return (ConstantPoolCacheEntry*)(
(address)this + in_bytes(base_offset())
);
}
public:
// Fetches the entry at the given index.
// In either case the index must not be encoded or byte-swapped in any way.
ConstantPoolCacheEntry* entry_at(int i) const {
assert(0 <= i && i < length(), "index out of bounds");
return base() + i;
}
// Code generation
static ByteSize base_offset() {
return in_ByteSize(sizeof(ConstantPoolCache));
}
static ByteSize entry_offset(int raw_index) {
int index = raw_index;
return (base_offset() + ConstantPoolCacheEntry::size_in_bytes() * index);
}
};
如上类删除了一些实现简单或不太重要的方法,保留了属性及重要方法的定义。这个类中定义了2个属性_length及_constant_pool,_length表示,而_constant_pool表示这是保存的哪个常量池连接的信息存,通常缓存具体的信息通过ConstantPoolCacheEntry来表示,它们在内存中的布局就是一个ConstantPoolCache后紧跟着数个ConstantPoolCacheEntry。这样size()及base()等方法的实现就不难简单了。
ConstantPoolCache主要用于缓存某些字节码指令所需的解析好的常量项,例如给[get|put]static、[get|put]field、invoke[static|special|virtual|interface|dynamic]等指令对应的常量池项使用。
2、ConstantPoolCacheEntry类
ConstantPoolCacheEntry类及重要属性的定义如下:
class ConstantPoolCacheEntry VALUE_OBJ_CLASS_SPEC {
private:
volatile intx _indices; // constant pool index & rewrite bytecodes
volatile Metadata* _f1; // entry specific metadata field
volatile intx _f2; // entry specific int/metadata field
volatile intx _flags; // flags
// ...
}
这4个属性能够表示非常多的信息。这4个字段表示的信息如下图所示。
这4个字段长度相同,以32为操作系统为例来介绍这4个字段。如果当前的ConstantPoolCacheEntry表示的是字段入口,则几个字段的信息如下图所示。
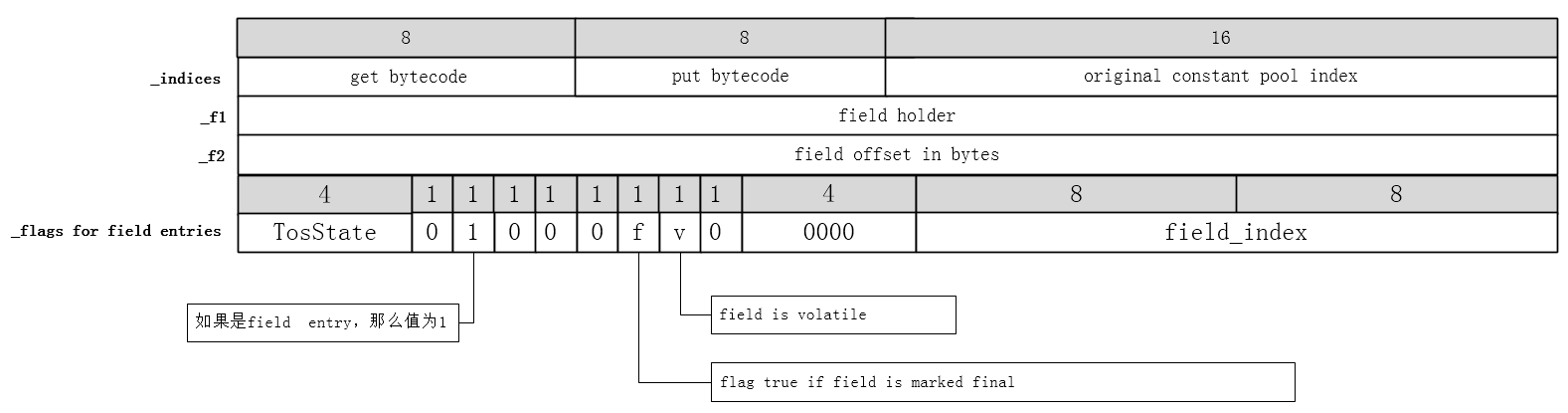
如果当前的ConstantPoolCacheEntry表示的是方法入口,则几个字段的信息如下图所示。
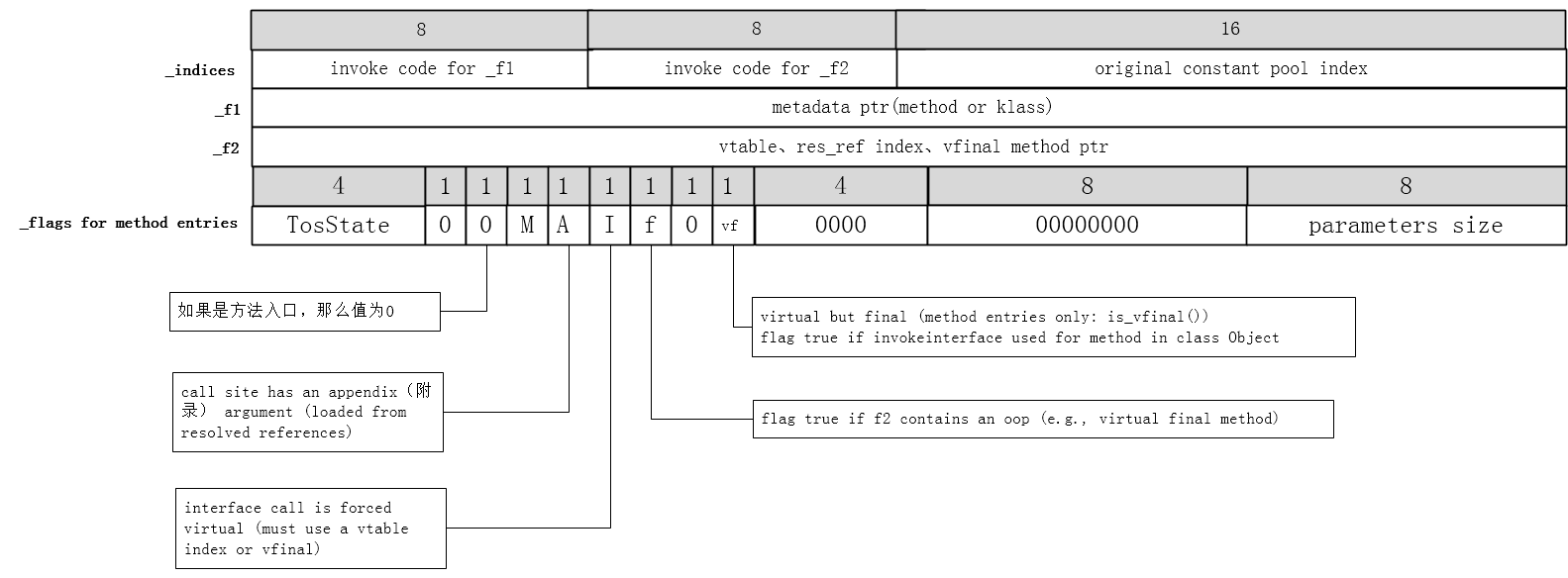
字节码调用方法的指令主要有如下几个:
(1)invokevirtual,通过vtable进行方法分发
- _f1:没有使用
- _f2:调用非final的virtual方法,_f2字段中则存放目标方法在vtable中的索引编号。如果是virtual final方法,_f2字段也直接指向目标方法的Method。
(2)invokeinterface,通过itable进行方法分发
- _f1:_f1字段指向对应接口的Klass
- _f2:存放的则是方法位于itable表中的索引编号
(3)invokespecial,调用private和构造方法,不需要分发机制
- _f1:_f1字段表示指向目标方法Method(用它可以定位Java方法在内存中的具体位置,从而实现方法调用)
- _f2:没有使用
(4)invokestatic,调用静态方法,不需要分发机制
- _f1:_f1字段表示指向目标方法Method(用它可以定位Java方法在内存中的具体位置,从而实现方法调用)
- _f2:没有使用
Note: invokevirtual & invokespecial bytecodes can share the same constant pool entry and thus the same constant pool cache entry. All invoke
bytecodes but invokevirtual use only _f1 and the corresponding b1 bytecode, while invokevirtual uses only _f2 and the corresponding
b2 bytecode. The value of _flags is shared for both types of entries.
在invokevirtual、invokespecial等字节码指令对应的汇编片段中,如果_indices中的b2或b1不为字节码指令的操作码,说明方法还没有连接,需要调用InterpreterRuntime::resolve_invoke()方法生成ConstantPoolCacheEntry。
之前介绍了重写时调用Rewriter::Rewriter()构造函数,在构造函数中还会调用Rewriter::make_constant_pool_cache()方法,这个方法的实现如下:
// Creates a constant pool cache given a CPC map
void Rewriter::make_constant_pool_cache(TRAPS) {
InstanceKlass* ik = _pool->pool_holder();
ClassLoaderData* loader_data = ik->class_loader_data();
ConstantPoolCache* cache = ConstantPoolCache::allocate(loader_data,
_cp_cache_map,
_invokedynamic_cp_cache_map,
_invokedynamic_references_map, CHECK);
// initialize object cache in constant pool
_pool->initialize_resolved_references(loader_data,
_resolved_references_map,
_resolved_reference_limit,
CHECK);
_pool->set_cache(cache); // 设置ConstantPool类中的_cache属性
cache->set_constant_pool(_pool()); // 设置ConstantPoolCache中的_constant_pool属性
}
调用的ConstantPoolCache::allocate()函数的实现如下:
ConstantPoolCache* ConstantPoolCache::allocate(
ClassLoaderData* loader_data,
const intStack& index_map,
const intStack& invokedynamic_index_map,
const intStack& invokedynamic_map,
TRAPS
){
const int length = index_map.length() + invokedynamic_index_map.length();
int size = ConstantPoolCache::size(length);
return new (loader_data, size, false, MetaspaceObj::ConstantPoolCacheType, THREAD)
ConstantPoolCache( length,
index_map,
invokedynamic_index_map,
invokedynamic_map);
}
如上方法中调用的ConstantPoolCache::size()函数的实现如下:
static int size(int length) { // 返回的是字数量
// ConstantPoolCache加上length个ConstantPoolCacheEntry的大小
// in_words(ConstantPoolCacheEntry::size()) 的值为4
return align_object_size(header_size() + length * in_words(ConstantPoolCacheEntry::size()));
}
index_map和invokedynamic_index_map中存储的是常量池索引,这些索引需要建立对应的新的数据结构以表达更多的信息。
调用ConstantPoolCache类的构造函数,如下:
// Constructor
ConstantPoolCache(int length,
const intStack& inverse_index_map,
const intStack& invokedynamic_inverse_index_map,
const intStack& invokedynamic_references_map) :
_length(length),
_constant_pool(NULL) {
initialize( inverse_index_map,
invokedynamic_inverse_index_map,
invokedynamic_references_map);
}
void ConstantPoolCache::initialize(const intArray& inverse_index_map,
const intArray& invokedynamic_inverse_index_map,
const intArray& invokedynamic_references_map) {
for (int i = 0; i < inverse_index_map.length(); i++) {
ConstantPoolCacheEntry* e = entry_at(i);
int original_index = inverse_index_map[i];
e->initialize_entry(original_index); // 为ConstantPoolCacheEntry::_indices属性赋值
assert(entry_at(i) == e, "sanity");
}
// ...
}
void ConstantPoolCacheEntry::initialize_entry(int index) {
assert(0 < index && index < 0x10000, "sanity check");
_indices = index;
_f1 = NULL;
_f2 = _flags = 0;
assert(constant_pool_index() == index, "");
}
从inverse_index_map中取出原常量池索引后,存储到_indices中,之前介绍过,_indices的低16位存储原常量池索引,而传递的参数也一定不会超过16位所能表示的最大值。而对于_f1暂时初始化为NULL,_f2与_flags暂时初始化为0,后面还会看到对这些字段的初始化过程。
Rewriter::make_constant_pool_cache()函数中调用的ConstantPool::initialize_resolved_references()函数的实现如下:
// Create resolved_references array and mapping array for original cp indexes
// The ldc bytecode was rewritten to have the resolved reference array index so need a way
// to map it back for resolving and some unlikely miscellaneous uses.
// The objects created by invokedynamic are appended to this list.
void ConstantPool::initialize_resolved_references(ClassLoaderData* loader_data,
intStack reference_map,
int constant_pool_map_length,
TRAPS
){
// Initialized the resolved object cache.
int map_length = reference_map.length();
if (map_length > 0) {
// Only need mapping back to constant pool entries. The map isn't used for
// invokedynamic resolved_reference entries. For invokedynamic entries,
// the constant pool cache index has the mapping back to both the constant
// pool and to the resolved reference index.
if (constant_pool_map_length > 0) {
Array<u2>* om = MetadataFactory::new_array<u2>(loader_data, constant_pool_map_length, CHECK);
for (int i = 0; i < constant_pool_map_length; i++) {
int x = reference_map.at(i);
om->at_put(i, (jushort)x);
}
set_reference_map(om);
}
// Create Java array for holding resolved strings, methodHandles,
// methodTypes, invokedynamic and invokehandle appendix objects, etc.
objArrayOop stom = oopFactory::new_objArray(SystemDictionary::Object_klass(), map_length, CHECK);
Handle refs_handle(THREAD, (oop)stom); // must handleize.
jobject x = loader_data->add_handle(refs_handle);
set_resolved_references(x);
}
}
为ConstantPool类中的如下属性设置了值:
// Array of resolved objects from the constant pool and map from resolved // object index to original constant pool index jobject _resolved_references; // jobject是指针类型 Array<u2>* _reference_map;
对于引用来说,这2个属性可完成从以连接的引用索引到原常量池索引的映射,后面会接触到相关应用。这部分内容不太理解也没关系,我们在后面介绍在invokevirtual、invokespecial等字节码指令时,再重新梳理一下逻辑后就明白了。
相关文章的链接如下:
1、在Ubuntu 16.04上编译OpenJDK8的源代码
13、类加载器
14、类的双亲委派机制
15、核心类的预装载
16、Java主类的装载
17、触发类的装载
18、类文件介绍
19、文件流
20、解析Class文件
21、常量池解析(1)
22、常量池解析(2)
23、字段解析(1)
24、字段解析之伪共享(2)
25、字段解析(3)
28、方法解析
29、klassVtable与klassItable类的介绍
30、计算vtable的大小
31、计算itable的大小
32、解析Class文件之创建InstanceKlass对象
33、字段解析之字段注入
34、类的连接
35、类的连接之验证
36、类的连接之重写(1)
作者持续维护的个人博客 classloading.com。
关注公众号,有HotSpot源码剖析系列文章!
