在调用ClassFileParser::parseClassFile()方法对类文件进行解释时,会调用ClassFileParser::parse_constant_pool()方法对常量池进行解释,调用的语句如下:
constantPoolHandle cp = parse_constant_pool(CHECK_(nullHandle));
方法parse_constant_pool()的实现如下:
constantPoolHandle ClassFileParser::parse_constant_pool(TRAPS) {
ClassFileStream* cfs = stream();
constantPoolHandle nullHandle;
u2 length = cfs->get_u2_fast();
ConstantPool* constant_pool = ConstantPool::allocate(_loader_data, length,
CHECK_(nullHandle));
_cp = constant_pool; // save in case of errors
constantPoolHandle cp (THREAD, constant_pool);
// ...
// parsing constant pool entries
parse_constant_pool_entries(length, CHECK_(nullHandle));
return cp;
}
调用ConstantPool::allocate()创建ConstantPool对象,然后调用parse_constant_pool_entries()解析常量池中的项并将这些项保存到ConstantPool对象中。
首先介绍一下ConstantPool类,这个类的对象代码具体的常量池,保存着常量池元信息。
1、ConstantPool类
类的定义如下:
class ConstantPool : public Metadata {
private:
Array<u1>* _tags; // the tag array describing the constant pool's contents
ConstantPoolCache* _cache; // the cache holding interpreter runtime information 解释执行时的运行时信息
InstanceKlass* _pool_holder; // the corresponding class
Array<u2>* _operands; // for variable-sized (InvokeDynamic) nodes, usually empty
// Array of resolved objects from the constant pool and map from resolved
// object index to original constant pool index
jobject _resolved_references; // jobject是指针类型
Array<u2>* _reference_map;
int _flags; // old fashioned bit twiddling
int _length; // number of elements in the array
union {
// set for CDS to restore resolved references
int _resolved_reference_length;
// keeps version number for redefined classes (used in backtrace)
int _version;
} _saved;
Monitor* _lock;
...
}
类表示常量池元信息,所以继承了类Metadata。_tags表示常量池中的内容,常量池中的总项数通过_length来保存,所以_tags数组的长度也为_length,具体存储的内容就是每一项的tag值,这都是虚拟机规范定义好的;_cache辅助解释运行来保存一些信息,在介绍解释运行时会介绍。其它的属性暂时不做过多介绍。
常量池中包含的信息如下:

2、创建ConstantPool实例
在解析常量池的方法ClassFileParser::parse_constant_pool()中首先会调用ConstantPool::allocate()方法创建ConstantPool实例,方法的实现如下:
ConstantPool* ConstantPool::allocate(ClassLoaderData* loader_data, int length, TRAPS) {
// Tags are RW but comment below applies to tags also.
Array<u1>* tags = MetadataFactory::new_writeable_array<u1>(loader_data, length, 0, CHECK_NULL);
int size = ConstantPool::size(length);
// CDS considerations:
// Allocate read-write but may be able to move to read-only at dumping time
// if all the klasses are resolved. The only other field that is writable is
// the resolved_references array, which is recreated at startup time.
// But that could be moved to InstanceKlass (although a pain to access from
// assembly code). Maybe it could be moved to the cpCache which is RW.
return new (loader_data, size, false, MetaspaceObj::ConstantPoolType, THREAD) ConstantPool(tags);
}
参数length就表示常量池项的数量,调用ConstantPool::size()计算所需要分配内存的大小,然后创建ConstantPool对象返回。size()方法的实现如下:
static int size(int length){
int s = header_size();
return align_object_size(s + length);
}
// Sizing (in words)
static int header_size() {
int num = sizeof(ConstantPool);
return num/HeapWordSize;
}
由方法实现可知,就是ConstantPool实例本身占用的内存大小加上length个指针长度。ConstantPool对象最终的内存布局如下图所示。
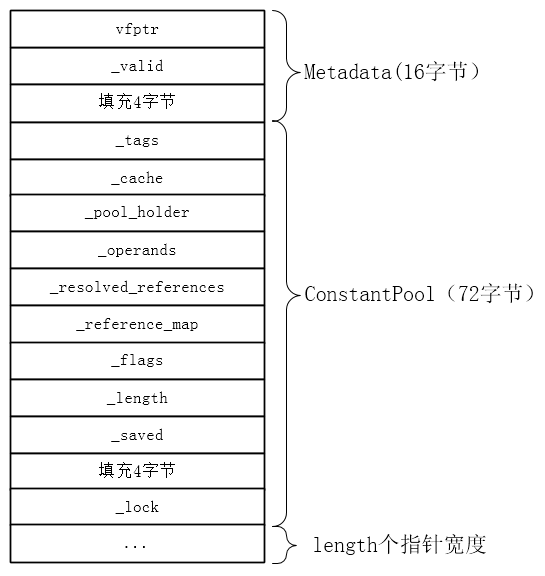
_valid是定义在Metadata中的int类型,只有debug版本才有,如果是product版本,则没有这个属性,那么Metadata就只占用8字节。关于对象的内存布局在之前已经介绍过,这里不再介绍。
调用header_size()在debug版本下得到的值为88(在不压缩指针的情况下,也就是使用命令XX禁止指针压缩),然后还需要加上length个指针宽度,这就是ConstantPool对象需要的内存空间大小。
通过重载new运算符进行堆内存分配,new运算符的重载定义在MetaspaceObj(ConstantPool间接继承此类)类中,如下:
void* MetaspaceObj::operator new(size_t size, ClassLoaderData* loader_data,
size_t word_size, bool read_only,
MetaspaceObj::Type type, TRAPS) throw() {
// Klass has it's own operator new
return Metaspace::allocate(loader_data, word_size, read_only,
type, CHECK_NULL);
}
调用的Metaspace::allocate()方法在堆中分配内存,这个方法在介绍垃圾收集时将详细介绍,这里只需要知道,这个方法会在堆中分配size大小的内存并且会将内存清零。
调用ConstantPool构造函数初始化一些属性,如下:
ConstantPool::ConstantPool(Array<u1>* tags) {
set_length(tags->length());
set_tags(NULL);
set_cache(NULL);
set_reference_map(NULL);
set_resolved_references(NULL);
set_operands(NULL);
set_pool_holder(NULL);
set_flags(0);
// only set to non-zero if constant pool is merged by RedefineClasses
set_version(0);
set_lock(new Monitor(Monitor::nonleaf + 2, "A constant pool lock"));
// initialize tag array
int length = tags->length();
for (int index = 0; index < length; index++) {
tags->at_put(index, JVM_CONSTANT_Invalid);
}
set_tags(tags);
}
可以看到对tags、_length及_lock等属性的初始化。其中tags数组中存储了JVM_CONSTANT_Invalid值,在分析具体的常量池项时会更新为如下枚举类中定义的值:
源代码位置:hotspot/src/share/vm/prims/jvm.h
enum {
JVM_CONSTANT_Utf8 = 1, // 1
JVM_CONSTANT_Unicode, // 2 /* unused */
JVM_CONSTANT_Integer, // 3
JVM_CONSTANT_Float, // 4
JVM_CONSTANT_Long, // 5
JVM_CONSTANT_Double, // 6
JVM_CONSTANT_Class, // 7
JVM_CONSTANT_String, // 8
JVM_CONSTANT_Fieldref, // 9
JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref, // 10
JVM_CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref, // 11
JVM_CONSTANT_NameAndType, // 12
JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle = 15, // JSR 292
JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType = 16, // JSR 292
//JVM_CONSTANT_(unused) = 17, // JSR 292 early drafts only
JVM_CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic = 18, // JSR 292
JVM_CONSTANT_ExternalMax = 18 // Last tag found in classfiles
};
这就是常量池项中的tag值,不过常量池第一项仍然为JVM_CONSTANT_Invalid。
下面介绍一下虚拟机规范规定的格式:
CONSTANT_Utf8_info {
u1 tag;
u2 length;
u1 bytes[length];
}
CONSTANT_Integer_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Float_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Long_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Double_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Class_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
}
CONSTANT_String_info {
u1 tag;
u2 string_index;
}
CONSTANT_Fieldref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
CONSTANT_Methodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info {
u1 tag;
u1 reference_kind;
u2 reference_index;
}
CONSTANT_MethodType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info {
u1 tag;
u2 bootstrap_method_attr_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
在常量池解析过程中,通过索引确定了常量池项后会将tag放到ConstantPool类中的_tags数组中,数组的下标与常量池索引相对应;剩下的信息只能存储到ConstantPool类后开辟的length个指针宽度的空间中,也可以成是length长度的指针数组,其中的下标也与常量池索引对应。指针在64位上的长度为8,所以能够存储除CONSTANT_Utf8_info外的所有常量池项信息(除tag外)。例如对于CONSTANT_Double_info来说,高4位存储high_bytes,低4位存储low_bytes。遇到CONSTANT_Utf8_info常量池项时,直接封装为Symbol对象,这样只要存储指向Symbol对象的指针即可。
相关文章的链接如下:
1、在Ubuntu 16.04上编译OpenJDK8的源代码
13、类加载器
14、类的双亲委派机制
15、核心类的预装载
16、Java主类的装载
17、触发类的装载
18、类文件介绍
19、文件流
20、解析Class文件
作者持续维护的个人博客classloading.com。
关注公众号,有HotSpot源码剖析系列文章!
