1.1:开启事物的注解及功能
1.1.1 注解
@EnableTransactionManagement
使用@Import注解:
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
最终会加在Bean:
case PROXY:
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(), ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
1.1.2 AutoProxyRegistrar
最终会为Spring注入Bean:
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class,和AOP的类似为Spring添加拦截器,并返回代理。
1.1.3 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
@Configuration
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
//添加Advisor:BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
//添加拦截器TransactionInterceptor
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
1.2:方法拦截
当调用方法的时候,首先会进入CglibAopProxy中:
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
会为当前类、方法和拦截器生成MethodInvocation。
其:
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
有一个拦截器TransactionInterceptor,调用其中invoke方法:
方法中invokeWithinTransaction会带有事物规则的逻辑
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new InvocationCallback() {
@Override
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
});
}
进入invokeWithinTransaction中,会首先获取PlatformTransactionManager,该接口的实现类Bean由用户自定义:
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() throws Exception{
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource());
}
然后再进行调用逻辑:
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
//为事物、提交、回滚的事物包装器
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
//进入invocation的proceedWithInvocation,会进入methodInvotion的return invokeJoinpoint();
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
//方法调用的时候出现异常,进行回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
//清楚回滚信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
//提交事物
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
-
1:completeTransactionAfterThrowing
就是获取事物处理器,并进行回滚
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
-
2:cleanupTransactionInfo
清除当前事物,并恢复之前事物,使用的是线程本地变量:
private static final ThreadLocal<TransactionInfo> transactionInfoHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal<TransactionInfo>("Current aspect-driven transaction");protected void cleanupTransactionInfo(TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null) {
txInfo.restoreThreadLocalStatus();
}
}
private void restoreThreadLocalStatus() {
// Use stack to restore old transaction TransactionInfo.
// Will be null if none was set.
transactionInfoHolder.set(this.oldTransactionInfo);
}
-
3:commitTransactionAfterReturning
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
2:@Transactional 失效的3种场景及解决办法
2.1 Transactional注解标注方法修饰符为非public
以上的访问方式,导致事务没开启,因此在方法抛出异常时,testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));操作不会进行回滚。如果TestServiceImpl#insertTestWrongModifier方法改为public的话将会正常开启事务,testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));将会进行回滚.
2.2 类内部调用调用类内部@Transactional标注的方法
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
调用一个方法在类内部调用内部被@Transactional标注的事务方法,运行结果是事务不会正常开启.
2.3 事务方法内部捕捉了异常
虽然抛出异常,但是异常被捕捉了,没有抛出到方法 外
2.4 原因分析
2.4.1 非Public
第一种@Transactional注解标注方法修饰符为非public时,@Transactional注解将会不起作用。这里分析 的原因是,@Transactional是基于动态代理实现的,@Transactional注解实现原理中分析了实现方法,在bean初始化过程中,对含有@Transactional标注的bean实例创建代理对象,这里就存在一个spring扫描@Transactional注解信息的过程,不幸的是源码中体现,标注@Transactional的方法如果修饰符不是public,那么就默认方法的@Transactional信息为空,那么将不会对bean进行代理对象创建或者不会对方法进行代理调用@Transactional注解实现原理中,介绍了如何判定一个bean是否创建代理对象,大概逻辑是。根据spring创建好一个aop切点BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例,遍历当前bean的class的方法对象,判断方法上面的注解信息是否包含@Transactional,如果bean任何一个方法包含@Transactional注解信息,那么就是适配这个BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor切点。则需要创建代理对象,然后代理逻辑为我们管理事务开闭逻辑。spring源码中,在拦截bean的创建过程,寻找bean适配的切点时,运用到下面的方法,目的就是寻找方法上面的@Transactional信息,如果有,就表示切点BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor能够应用(canApply)到bean中.
-
1:创建代理时,校验类方法是否存在Public的修饰方法
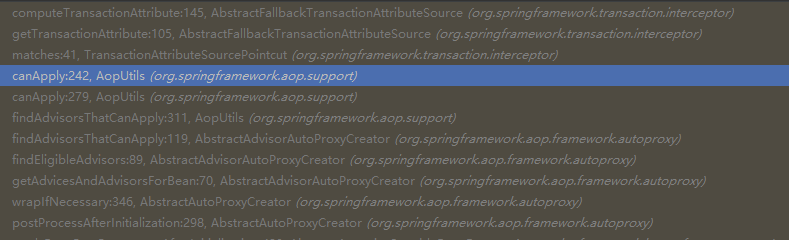
-
2:堆栈的最后方法存在对方法的校验
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
所以,如果所有方法上的修饰符都是非public的时候,那么将不会创建代理对象。
但是存在场景,两个事物注解的方法,一个有public修饰,一个没有,那么没有使用public修饰符修饰的方法,事物是否会生效。答案是否定的,因为在进行方法拦截的时候,同样会获取方法的事物属性信息。
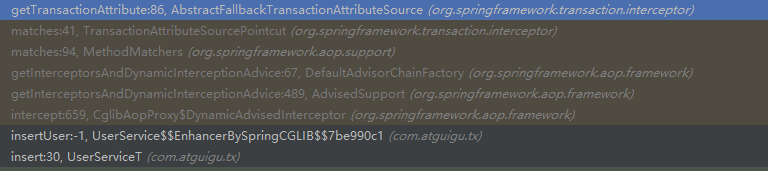
该方法中首先会从本地缓存获取,如果没有public修饰的时候,缓存中没有该方法的事物信息,会继续调用
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
该方法中继续校验是否public修饰。
总结:使用@Transaction注解进行事物,必须添加修饰符为public,否则可能没有办法创建拦截器或者进行方法调用的时候进行校验失败。说白了两个阶段都是涉及缓存:
private final Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache =
new ConcurrentHashMap<Object, TransactionAttribute>(1024);
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
......
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
只有修饰符为public,才会添加当前方法的key及其事物属性信息添加到缓存中,供方法调用的时候使用。
2.4.2 内部调用
事务管理是基于动态代理对象的代理逻辑实现的,那么如果在类内部调用类内部的事务方法,这个调用事务方法的过程并不是通过代理对象来调用的,而是直接通过this对象来调用方法,绕过的代理对象,肯定就是没有代理逻辑了。