一,
1 public class Grandparent { 2 public Grandparent() 3 { 4 System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); 5 } 6 public Grandparent(String string) 7 { 8 System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); 9 } 10 } 11 public class Parent extends Grandparent { 12 public Parent(){ 13 //super("Hello.Grandparent.");该语句可用于调用Grandparent中的有参数的构造函数 14 System.out.println("Parent Created"); 15 //super("Hello.Grandparent.");该语句必须写在子类构造方法的首句,否则编译会报错 16 } 17 } 18 public class Child extends Parent{ 19 public Child(){ 20 System.out.println("Child Created"); 21 } 22 } 23 public class TestInherits { 24 public static void main(String[] args){ 25 Child c = new Child(); 26 } 27 }
运行结果(调用Grandparent默认构造函数):

运行结果(调用Grandparent中的有参数的构造函数):

注意:通过super调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法的首句!
原因:构造方法的作用为初始化对象,必须先初始化父类,之后才能初始化子类对象。
二,
1 public class ExplorationJDKSource { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println(new A()); 4 } 5 6 } 7 class A{}
运行结果:
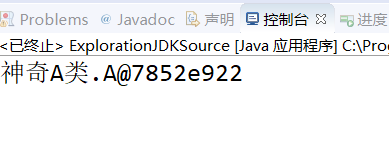
探究输出上述结果的原因:
(1)使用javap -c命令反汇编.class文件
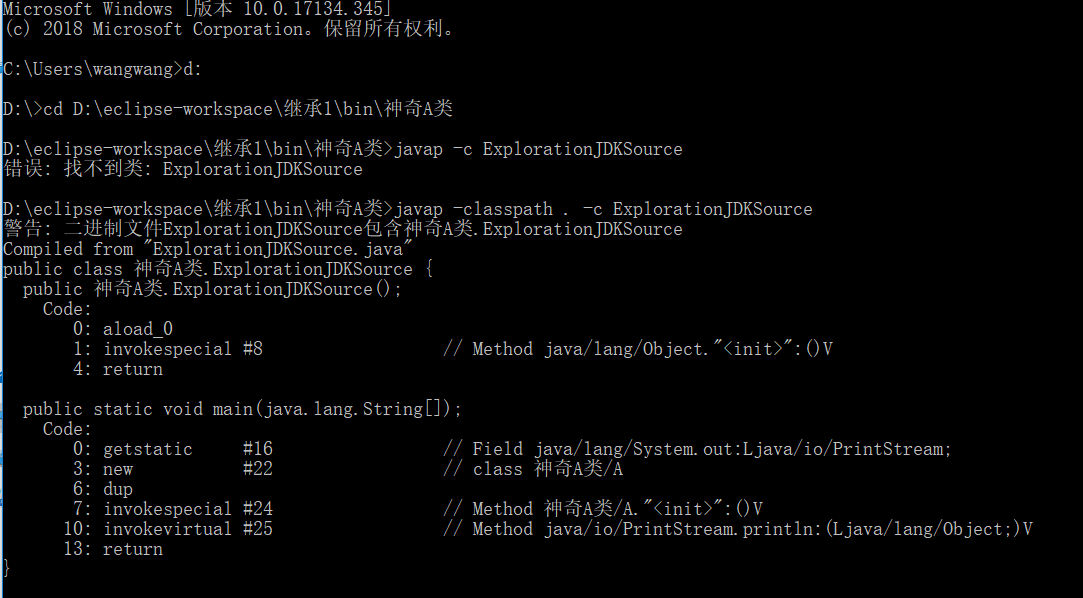
最后我们发现:
main方法实际上调用的是:
public void println(Object x),这一方法内部调用了String类的valueOf方法。
valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() +"@" +
Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现:
public native int hashCode();
也就是说输出的是java中顶层基类Object的toString()方法。
三,
1 public class Fruit 2 { 3 public String toString() 4 { 5 return "Fruit toString."; 6 } 7 public static void main(String args[]) 8 { 9 Fruit f=new Fruit(); 10 System.out.println("f="+f); 11 System.out.println("f="+f.toString()); 12 } 13 }
运行结果:
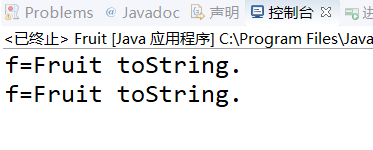
分析:
在“+”运算中,当任何一个对象与一个String对象,连接时,会隐式地调用其toString()方法,默认情况下,此方法返回“类名 @ + hashCode”。为了返回有意义的信息,子类可以重写toString()方法。
在这个例子中正是Fruit类覆盖了Object类的toString方法,所以才会输出“Fruit toString”。
四,
1 public class Parent { 2 public Parent() { 3 System.out.println("Parent Creat"); 4 } 5 public void show() { 6 System.out.println("Parent Wecome"); 7 } 8 } 9 public class Child extends Parent { 10 public Child() { 11 System.out.println("Child Creat"); 12 } 13 public void show() { 14 //super.show();该行是运用关键字super调用父类中被覆盖的函数 15 System.out.println("Child Wecome"); 16 } 17 } 18 public class text { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 Child a=new Child(); 21 a.show(); 22 } 23 24 }
运行截图(未使用super):

运行截图(使用super):

总结:若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字。
五,
1 public class TestInstanceof 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 //声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类 6 //但hello变量的实际类型是String 7 Object hello = "Hello"; 8 //String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。 9 System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object)); 10 //返回true。 11 System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String)); 12 //返回false。 13 System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math)); 14 //String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。 15 System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable)); 16 String a = "Hello"; 17 //String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过 18 //System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math)); 19 } 20 }
运行截图:

总结:
判断一个对象是否可以转换为指定的类型可以使用运算符instanceof
六,
1 class Mammal{} 2 class Dog extends Mammal {} 3 class Cat extends Mammal{} 4 5 public class TestCast { 6 public static void main(String args[]) 7 { 8 Mammal m; 9 Dog d=new Dog(); 10 Cat c=new Cat(); 11 m=d; 12 //d=m; 编译无法通过,类型不匹配,不能从Mammal转换为Dog 13 d=(Dog)m; //将m的类型强制转换为Dog,与d类型匹配,编译通过 14 //d=c; 编译无法通过,类型不匹配,不能从Cat转换为Dog 15 //c=(Cat)m; 该行会运行时出错,因为m已经被强制转换为Dog类型,但Dog类型不能强制转换为Cat. 16 17 } 18 }
七,
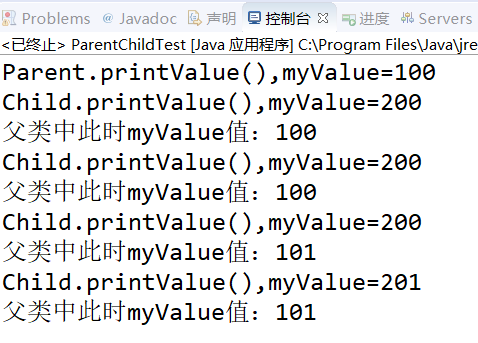
1 public class ParentChildTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Parent parent=new Parent(); 4 parent.printValue();//调用父类的printValue()方法,输出父类的myValue值 5 Child child=new Child(); 6 child.printValue();//调用子类的printValue()方法,输出子类的myValue值 7 8 parent=child;//用子类初始化父类对象 9 parent.printValue();//调用Child类的printValue()方法,输出Child类的myValue值 10 11 parent.myValue++;//使父类的myValue值+1 12 parent.printValue();//因为上面执行了“parent=child;”,所以仍调用的是子类的printValue()方法 13 14 ((Child)parent).myValue++;//因为前面使用了强制类型转换,所以使Child类的myValue值+1 15 parent.printValue();//同上 16 17 } 18 } 19 20 class Parent{ 21 public int myValue=100; 22 public void printValue() { 23 System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); 24 } 25 } 26 27 class Child extends Parent{ 28 public int myValue=200; 29 public void printValue() { 30 System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
//System.out.println("父类中此时myValue值:"+super.myValue); 此行代码可用于显示父类中呗被隐藏的同名字段 31 } 32 }
运行结果:

总结:
(1)当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
(2)如果子类与父类拥有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。
运行截图(添加super显示被隐藏的父类myValue值):