一、通过指定部门id,查询该部门下的所有后代部门。
二、通过cte编写sql语句。
1、第一次编写,查询整个过程花了近7秒时间。
#第一次编写,6.961s EXPLAIN with recursive r as ( #如果要包括自己,将这里的parent_id 改为id select * from dept where parent_id=0 and status='1' union all select dept.* from r , dept where r.id=dept.parent_id and r.status='1' and dept.status='1' ) select id,dept_name,parent_id,status from r
三、优化sql
1、第一次优化,先查询出所有相关信息,再通过结果id去关联整个dept表。查询时间到了只需4秒
#第一次优化 4.008s EXPLAIN with recursive r(id,parent_id,status) as ( select id,parent_id,status from dept where parent_id=0 and status='1' union all select dept.id,dept.parent_id,dept.status from r , dept where r.id=dept.parent_id and dept.status='1' ) select dept.* from r left join dept on r.id=dept.id
2、第二次优化,省略去不需要的字段,只留下结果集只留下 id,parent_id 这两个字段,后续再去关联。不过这优化不太明显。
#第二次优化,3.953s EXPLAIN with recursive r(id,parent_id) as ( select id,parent_id from dept where parent_id=0 and status='1' union all select dept.id,dept.parent_id from r , dept where r.id=dept.parent_id and dept.status='1' ) select dept.* from r left join dept on r.id=dept.id
3、后面是在想不出怎么去优化sql了,寻找别的办法,添加索引。
三、优化表结构,添加索引。
#第三次优化,添加普通索引,对parent_id字段加上索引 alter table dept add index(parent_id);
再次执行上面查询语句,0.049s
。。。。。。。。。。
真是哔了狗了,性能提升一大截。。
执行 describe dept;
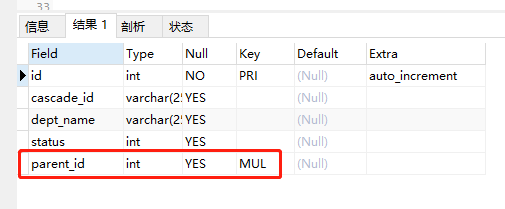
可以看到 parent_id 这一行上的key变成了MUL,如果Key是MUL,那么该列的值可以重复,该列是一个非唯一索引的前导列(第一列)或者是一个唯一性索引的组成部分但是可以含有空值NULL。