队列:先进先出
栈:先进后出
几个基础的问题:
- C++中stack 是容器么?
- 我们使用的stack是属于那个版本的STL?
- 我们使用的STL中stack是如何实现的?
- stack 提供迭代器来遍历stack空间么?
栈和队列和C++STL里面的两个数据结构。


栈:先进后出
栈提供push、pop等接口,所有元素必须符合先进后出规则,所以栈不提供走访功能,也不提供迭代器iterator,不像是set或者是map提供迭代器来遍历所有元素。
「栈是以底层容器完成其所有的工作,对外提供统一的接口,底层容器是可插拔的(也就是说我们可以控制使用哪种容器来实现栈的功能)。」
所以STL中栈往往不被归类为容器,而被归类为container adapter(容器适配器)
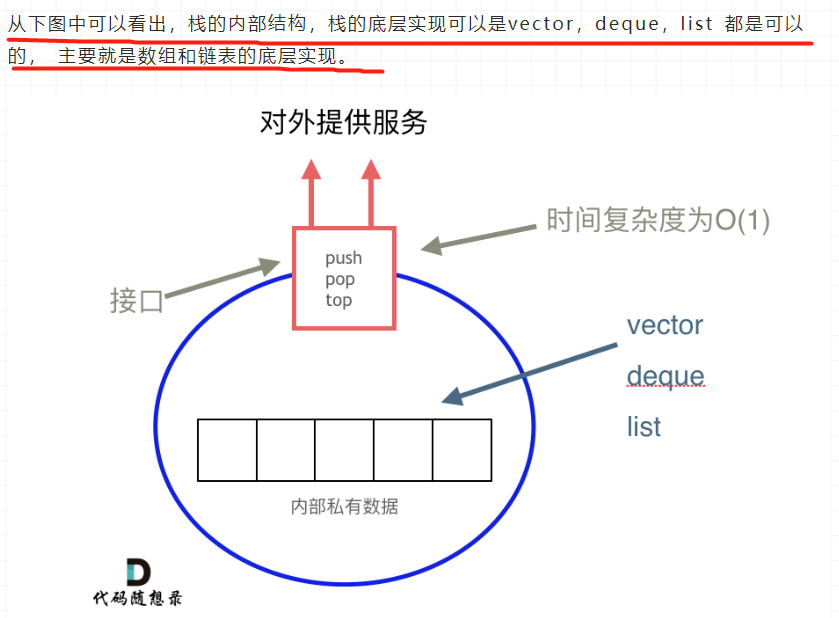
「我们常用的SGI STL,如果没有指定底层实现的话,默认是以deque为缺省情况下栈的低层结构。」
deque是一个双向队列,只要封住一段,只开通另一端就可以实现栈的逻辑了。
「SGI STL中 队列底层实现缺省情况下一样使用deque实现的。」
我们也可以指定vector为栈的底层实现
队列 先进先出的数据结构,同样不允许有遍历行为,不提供迭代器, SGI STL中队列一样是以deque为缺省情况下的底部结构。
也可以指定list 为起底层实现
所以STL中队列也不被归类为容器,而被归类为container adapter( 容器适配器)。
可以用栈来实现队列:两个栈可以实现队列!
class MyQueue { public: stack<int> stIn; stack<int> stOut; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ MyQueue() { } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ void push(int x) { stIn.push(x); } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ int pop() { if(stOut.empty()) { while(!stIn.empty()) { stOut.push(stIn.top()); stIn.pop(); } } int result = stOut.top(); stOut.pop(); return result; } /** Get the front element. */ int peek() { int res = this->pop();//这里弹出了res stOut.push(res); return res; } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ bool empty() { return (stOut.empty() && stIn.empty()); } }; /** * Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue(); * obj->push(x); * int param_2 = obj->pop(); * int param_3 = obj->peek(); * bool param_4 = obj->empty(); */
可以用队列还实现栈!
class MyStack { public: queue<int>que1; queue<int>que2;//用来备份的 /** Initialize your data structure here. */ MyStack() { } /** Push element x onto stack. */ void push(int x) { que1.push(x); } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ int pop() { //现在元素都在que1里,队尾的元素是需要pop的元素,需要把其他的都暂存到que2里 int size = que1.size(); size--; while(size--) { que2.push(que1.front()); que1.pop(); } int result = que1.front(); que1.pop(); que1 = que2;//恢复que1 while(!que2.empty()) que2.pop(); return result; } /** Get the top element. */ int top() { return que1.back(); } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ bool empty() { return que1.empty(); } }; /** * Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyStack* obj = new MyStack(); * obj->push(x); * int param_2 = obj->pop(); * int param_3 = obj->top(); * bool param_4 = obj->empty(); */
一个经典应用就是“有效的括号”问题。
逆波兰表达式问题是栈的经典应用,也是一道比较难的题目,题目一定要记住一个规则:遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中。
class Solution { public: int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) { stack<int> st; for(int i=0; i<tokens.size(); i++) { if(tokens[i]=="+" || tokens[i]=="-" || tokens[i]=="*" || tokens[i]=="/") {//这里一定要注意是双引号 int num1 = st.top(); st.pop(); int num2 = st.top(); st.pop(); if(tokens[i]=="+") st.push(num1+num2); else if(tokens[i]=="-") st.push(num2-num1);//这里一定要注意相减的顺序 else if(tokens[i]=="*") st.push(num1*num2); else//除法 st.push(num2/num1);//这里一定要注意相除的顺序 } else st.push(stoi(tokens[i])); } int result = st.top(); st.pop(); return result; } };