逻辑回归神经网络实现手写数字识别
如果更习惯看Jupyter的形式,请戳Gitthub_逻辑回归softmax神经网络实现手写数字识别.ipynb
1 - 导入模块
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
from ld_mnist import load_digits
%matplotlib inline
2 - 导入数据及数据预处理
mnist = load_digits()
Extracting C:/Users/marsggbo/Documents/Code/ML/TF Tutorial/data/MNIST_data rain-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting C:/Users/marsggbo/Documents/Code/ML/TF Tutorial/data/MNIST_data rain-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Extracting C:/Users/marsggbo/Documents/Code/ML/TF Tutorial/data/MNIST_data 10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting C:/Users/marsggbo/Documents/Code/ML/TF Tutorial/data/MNIST_data 10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
print("Train: "+ str(mnist.train.images.shape))
print("Train: "+ str(mnist.train.labels.shape))
print("Test: "+ str(mnist.test.images.shape))
print("Test: "+ str(mnist.test.labels.shape))
Train: (55000, 784)
Train: (55000, 10)
Test: (10000, 784)
Test: (10000, 10)
mnist数据采用的是TensorFlow的一个函数进行读取的,由上面的结果可以知道训练集数据X_train有55000个,每个X的数据长度是784(28*28)。
另外由于数据集的数量较多,所以TensorFlow提供了批量提取数据的方法,从而大大提高了运行速率,方法如下:
x_batch, y_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
print(x_batch.shape)
print(y_batch.shape)
>>>
(100, 784)
(100, 10)
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = mnist.train.images, mnist.train.labels, mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
因为训练集的数据太大,所以可以再划分成训练集,验证集,测试集,比例为6:2:2
x_train_batch, y_train_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(30000)
x_cv_batch, y_cv_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(15000)
x_test_batch, y_test_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(10000)
print(x_train_batch.shape)
print(y_cv_batch.shape)
print(y_test_batch.shape)
(30000, 784)
(15000, 10)
(10000, 10)
展示手写数字
nums = 6
for i in range(1,nums+1):
plt.subplot(1,nums,i)
plt.imshow(x_train[i].reshape(28,28), cmap="gray")

3 - 算法介绍
3.1 算法
对单个样本数据 (x^{(i)}):
[z^{(i)} = w^T x^{(i)} + b ag{1}
]
[hat{y}^{(i)} = a^{(i)} = softmax(z^{(i)}) ag{2}
]
损失函数

训练数据集总的损失函数表达式

需要注意的是公式(1)中的(w^Tx^{(i)}),这个需要视情况而定,因为需要根据数据维度的不同而进行改变。例如在本次项目中,(x∈R^{55000 × 784}, w∈R^{784 × 10},y∈R^{55000×10}),所以(z^{(i)} = x^{(i)}w + b)
关键步骤
- 初始化模型参数
- 使用参数最小化cost function
- 使用学习得到的参数进行预测
- 分析结果和总结
3.2 初始化模型参数
# 初始化模型参数
def init_params(dim1, dim2):
'''
dim: 表示权重w的个数,一般来说w维度要与样本x_train.shape[1]和y_train.shape[1]相匹配
'''
w = np.zeros((dim1,dim2))
return w
w = init_params(2,1)
print(w)
[[ 0.]
[ 0.]]
3.3 定义softmax函数
def softmax(x):
"""
Compute the softmax function for each row of the input x.
Arguments:
x -- A N dimensional vector or M x N dimensional numpy matrix.
Return:
x -- You are allowed to modify x in-place
"""
orig_shape = x.shape
if len(x.shape) > 1:
# Matrix
exp_minmax = lambda x: np.exp(x - np.max(x))
denom = lambda x: 1.0 / np.sum(x)
x = np.apply_along_axis(exp_minmax,1,x)
denominator = np.apply_along_axis(denom,1,x)
if len(denominator.shape) == 1:
denominator = denominator.reshape((denominator.shape[0],1))
x = x * denominator
else:
# Vector
x_max = np.max(x)
x = x - x_max
numerator = np.exp(x)
denominator = 1.0 / np.sum(numerator)
x = numerator.dot(denominator)
assert x.shape == orig_shape
return x
a = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]])
print(softmax(a))
np.sum(softmax(a))
[[ 0.0320586 0.08714432 0.23688282 0.64391426]
[ 0.0320586 0.08714432 0.23688282 0.64391426]]
2.0
3.4 - 前向&反向传播(Forward and Backward propagation)
参数初始化后,可以开始实现FP和BP算法来让参数自学习了。
Forward Propagation:
- 获取数据X
- 计算 (A = softmax(w^T X + b) = (a^{(0)}, a^{(1)}, ..., a^{(m-1)}, a^{(m)}))
- 计算 cost function:
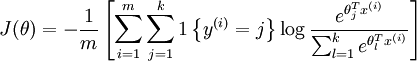
def propagation(w, c, X, Y):
'''
前向传播
'''
m = X.shape[0]
A = softmax(np.dot(X,w))
J = -1/m * np.sum(Y*np.log(A)) + 0.5*c*np.sum(w*w)
dw = -1/m * np.dot(X.T, (Y-A)) + c*w
update = {"dw":dw, "cost": J}
return update
def optimization(w, c, X, Y, learning_rate=0.1, iterations=1000, print_info=False):
'''
反向优化
'''
costs = []
for i in range(iterations):
update = propagation(w, c, X, Y)
w -= learning_rate * update['dw']
if i %100==0:
costs.append(update['cost'])
if i%100==0 and print_info==True:
print("Iteration " + str(i+1) + " Cost = " + str(update['cost']))
results = {'w':w, 'costs': costs}
return results
def predict(w, X):
'''
预测
'''
return softmax(np.dot(X, w))
def accuracy(y_hat, Y):
'''
统计准确率
'''
max_index = np.argmax(y_hat, axis=1)
y_hat[np.arange(y_hat.shape[0]), max_index] = 1
accuracy = np.sum(np.argmax(y_hat, axis=1)==np.argmax(Y, axis=1))
accuracy = accuracy *1.0/Y.shape[0]
return accuracy
def model(w, c, X, Y, learning_rate=0.1, iterations=1000, print_info=False):
results = optimization(w, c, X, Y, learning_rate, iterations, print_info)
w = results['w']
costs = results['costs']
y_hat = predict(w, X)
accuracy = accuracy(y_hat, Y)
print("After %d iterations,the total accuracy is %f"%(iterations, accuracy))
results = {
'w':w,
'costs':costs,
'accuracy':accuracy,
'iterations':iterations,
'learning_rate':learning_rate,
'y_hat':y_hat,
'c':c
}
return results
4 - 验证模型
w = init_params(x_train_batch.shape[1], y_train_batch.shape[1])
c = 0
results_train = model(w, c, x_train_batch, y_train_batch, learning_rate=0.3, iterations=1000, print_info=True)
print(results_train)
Iteration 1 Cost = 2.30258509299
Iteration 101 Cost = 0.444039646187
Iteration 201 Cost = 0.383446527394
Iteration 301 Cost = 0.357022940232
Iteration 401 Cost = 0.341184601147
Iteration 501 Cost = 0.330260258921
Iteration 601 Cost = 0.322097106964
Iteration 701 Cost = 0.315671301537
Iteration 801 Cost = 0.310423971361
Iteration 901 Cost = 0.306020145234
After 1000 iterations,the total accuracy is 0.915800
{'w': array([[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]]), 'costs': [2.302585092994045, 0.44403964618714781, 0.38344652739376933, 0.35702294023246306, 0.34118460114650634, 0.33026025892089478, 0.32209710696427363, 0.31567130153696982, 0.31042397136133199, 0.30602014523405535], 'accuracy': 0.91579999999999995, 'iterations': 1000, 'learning_rate': 0.3, 'y_hat': array([[ 1.15531353e-03, 1.72628369e-09, 2.24683134e-03, ...,
4.06392375e-08, 1.19337142e-04, 2.07493343e-06],
[ 1.41786837e-01, 1.11756123e-03, 2.79188805e-02, ...,
6.80002693e-03, 1.00000000e+00, 1.25721652e-01],
[ 9.52758112e-05, 1.41141596e-06, 2.04835561e-03, ...,
1.21014773e-04, 2.50044218e-02, 1.00000000e+00],
...,
[ 1.79945865e-07, 6.74560778e-05, 1.53151951e-05, ...,
2.44907396e-05, 1.71333912e-04, 1.08085629e-02],
[ 2.59724603e-05, 6.36785472e-10, 1.00000000e+00, ...,
2.70273729e-08, 2.10287536e-06, 2.48876734e-08],
[ 1.00000000e+00, 9.96462215e-15, 5.55562364e-08, ...,
2.01973615e-08, 1.57821049e-07, 3.37994451e-09]]), 'c': 0}
plt.plot(results_train['costs'])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x283b1d75ef0>]

params = [[0, 0.3],[0,0.5],[5,0.3],[5,0.5]]
results_cv = {}
for i in range(len(params)):
result = model(results_train['w'],0, x_cv_batch, y_cv_batch, learning_rate=0.5, iterations=1000, print_info=False)
print("{0} iteration done!".format(i))
results_cv[i] = result
After 1000 iterations,the total accuracy is 0.931333
0 iteration done!
After 1000 iterations,the total accuracy is 0.936867
1 iteration done!
After 1000 iterations,the total accuracy is 0.940200
2 iteration done!
After 1000 iterations,the total accuracy is 0.942200
3 iteration done!
for i in range(len(params)):
print("{0} iteration accuracy: {1} ".format(i+1, results_cv[i]['accuracy']))
for i in range(len(params)):
plt.subplot(len(params), 1,i+1)
plt.plot(results_cv[i]['costs'])
1 iteration accuracy: 0.9313333333333333
2 iteration accuracy: 0.9368666666666666
3 iteration accuracy: 0.9402
4 iteration accuracy: 0.9422

验证测试集准确率
y_hat_test = predict(w, x_test_batch)
accu = accuracy(y_hat_test, y_test_batch)
print(accu)
0.9111
5 - 测试真实手写数字
读取之前保存的权重数据
# w = results_cv[3]['w']
# np.save('weights.npy',w)
w = np.load('weights.npy')
w.shape
(784, 10)
图片转化成txt的代码可参考 python实现图片转化成可读文件
# 已经将图片转化成txt格式
files = ['3.txt','31.txt','5.txt','8.txt','9.txt','6.txt','91.txt']
# 将txt数据转化成np.array
def pic2np(file):
with open(file, 'r') as f:
x = f.readlines()
data = []
for i in range(len(x)):
x[i] = x[i].split('
')[0]
for j in range(len(x[0])):
data.append(int(x[i][j]))
data = np.array(data)
return data.reshape(-1,784)
# 验证准确性
i = 1
count = 0
for file in files:
x = pic2np(file)
y = np.argmax(predict(w, x))
print("实际值{0}-预测值{1}".format( int(file.split('.')[0][0]) , y) )
if y == int(file.split('.')[0][0]):
count += 1
plt.subplot(2, len(files), i)
plt.imshow(x.reshape(28,28))
i += 1
print("准确率为{0}".format(count/len(files)))
实际值3-预测值6
实际值3-预测值3
实际值5-预测值3
实际值8-预测值3
实际值9-预测值3
实际值6-预测值6
实际值9-预测值7
准确率为0.2857142857142857

由上面的结果可见我自己写的数字还是蛮有个性的。。。。居然7个只认对了2个。看来算法还是需要提高的
6 - Softmax 梯度下降算法推导
softmax损失函数求导推导过程
