https://unetbootin.github.io/linux_download.html
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gezakovacs/ppasudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install unetbootin
Other Packages (may be outdated): Ubuntu Debian Fedora Suse Arch Gentoo
1、UNetbootin
UNetbootin 让你创建 Ubuntu 或者其他 Linux 发行版的可引导 Live U 盘,而无需烧录 CD。
你既能让 UNetbootin 为你下载众多开箱即用的发行版,或者提供你自己的 Linux 的 .iso 文件。支持Linux和windows系统,官网有安装方法。
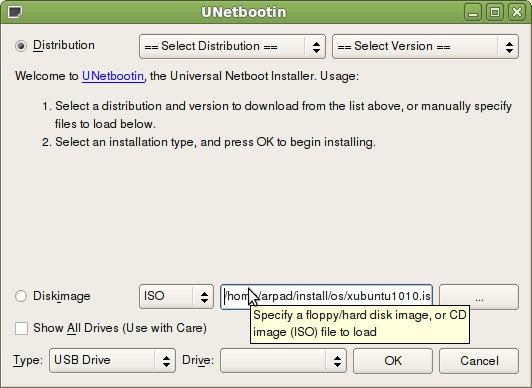
官方网址:https://unetbootin.github.io/
2、Rufus
Rufus是一个实用程序,可帮助格式化和创建可启动的U盘。它对以下情况特别有用:您需要从可启动的ISO(Windows,Linux,UEFI等)创建USB安装媒体,您需要在没有安装操作系统的系统上工作,你需要从DOS中刷新BIOS或其他固件,你想运行一个低级实用程序,尽管体积小,但Rufus提供您所需的一切!目前之支持Windows平台
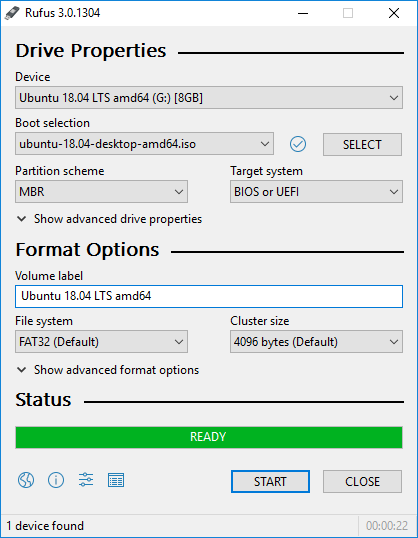
官方网站:https://rufus.ie/en_IE.html
3、universal-usb-installer
Universal USB Installer(通用USB安装程序)是一个自启动Linux U盘创建工具,您可从大量精选的Linux发行版中挑选一个安装到您的U盘上。通用USB安装程序使用方便,只需选择自启动Linux发行版,ISO文件,和您的U盘,单击“安装”即可。其他功能包括,持续保存(如果可用的话),以FAT32格式格式化U盘(推荐)确保一个干净的安装。安装完成后,您即拥有了一个安装了您所喜欢的Linux版本的自启动U盘。目前之支持Windows平台。
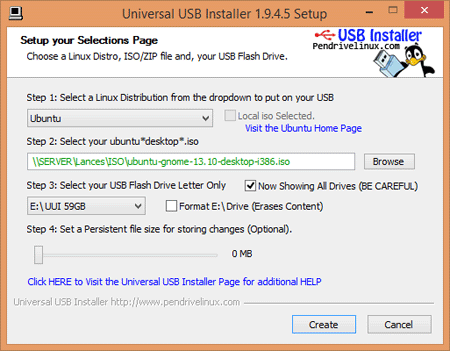
官方网址:https://www.pendrivelinux.com/universal-usb-installer-easy-as-1-2-3
4、Ubuntu系统的自带软件 Startup Disk Creator(启动盘创建器)
这个是Ubuntu系统的自带软件,安装完Ubuntu系统会默认安装。
usb-creator-common:使用CD或磁盘映像创建启动磁盘(通用文件)
usb-creator-gtk:使用CD或磁盘映像创建启动磁盘(适用于GNOME)
usb-creator-kde:使用CD或磁盘映像创建启动磁盘(适用于KDE)
没有安装可以通过下面的命令安装:
root@Ubuntu:~# apt install usb-creator-gtk
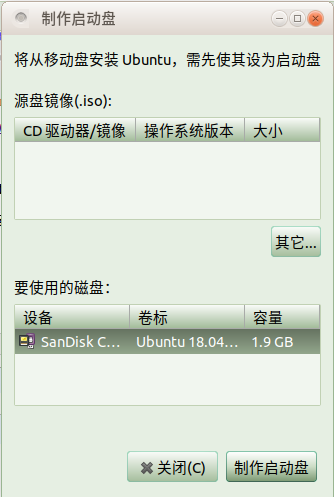
https://www.cnblogs.com/pipci/p/10103494.html
https://github.com/pbatard/rufus
Ubuntu has already an application called Startup Disk Creator, but this can only be used to make Linux bootable USB drives. To make a Windows bootable USB there was an application called WinUSB but it is no longer under active development. The following guide has been updated and works on any Linux distribution as long as it has GRUB and GParted installed and can make bootable USB for any Windows version newer than Vista: Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10. UEFI boot is only supported for Windows 7 x64 and newer.
Before starting, let's mention that there are two types of boot methods. There is the MBR code type where the bootable executable is stored in a reserved section at the beginning of the storage device. And there is the EFI type, where the boot loader executable file is stored at a standard path in an FAT32 filesystem. You must decide in advance what you will use. There are some variables for each boot type. If you have no idea what to use, the most common setup that works with unmodified Windows sources, is msdos partition table with fat32 filesystem and flag the partition with boot. In this way you will get both an MBR and UEFI bootable drive.
The latest Windows release can be downloaded from Microsoft as an ISO image. The ISO download page is available to non-Windows users. Otherwise, you are directed to download Media Creation Tool, which is Windows only software.
| Partition table | Filesystem | Partition flag | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBR bootable | msdos |
ntfs / fat32 |
boot |
| UEFI bootable | msdos / gpt |
fat32 |
boot / msftdata * |
msdos should be flagged with boot and gpt should be flagged with msftdata.UEFI can only boot FAT32 drives! If you need to make an NTFS UEFI bootable flashdrive to remove the 4 GB maximum file size restriction of FAT32 see this: UEFI NTFS: Bootable Windows USB from Linux. There is also a video version of what is about to follow.
Format USB drive
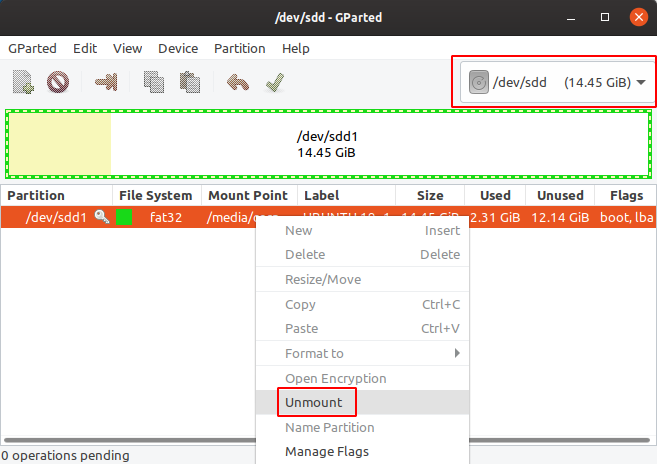
This is the first step. GParted has a nice GUI and it is easy to use for this. So, plug in your USB flashdrive and start GParted (root permissions required). Select the USB drive and unmount it, otherwise you won't be able to format it. Richt click on the mounted partition from the selected device and select Unmount in the context menu.
GParted main window. The first thing to do is select the USB drive and unmount it.
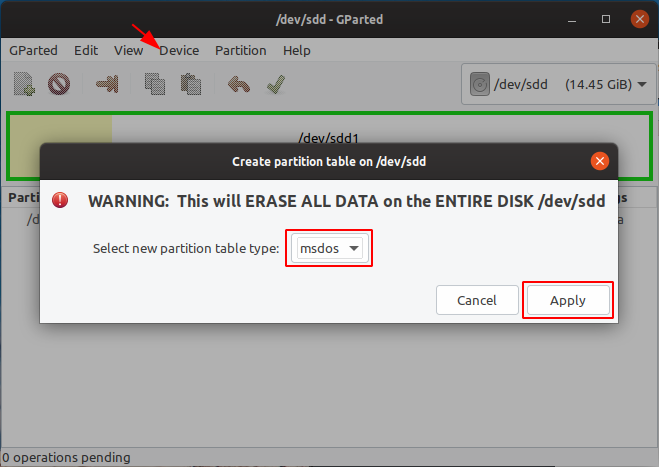
You must re-create the partition table by going to the Device menu then select Create Partition Table. Choose msdos (or gpt if you want an UEFI only bootable drive) and click Apply.
Write a new partition table on the device
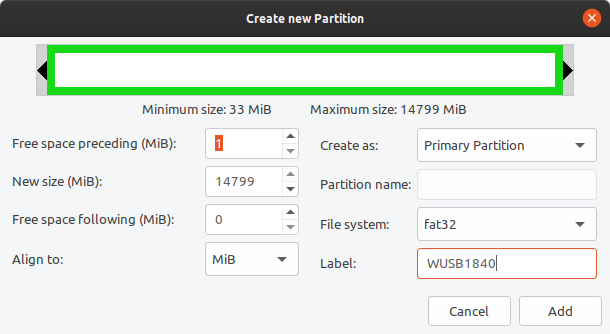
Right click the unallocated space and select New. Make a primary NTFS or FAT32 partition and give it a label too. The label must be as strange as possible because the bootloader will identify the bootable partition by this and you should not use windows (like I did in the video)! If the filesystem is FAT32 use only uppercase letters. For example: WUSB1840 would be a good label (W for Windows, USB for USB flash drive and 18:40 is the time I was writing this). Remember the label as you will need it later.
If you have a customized Windows with install.wim larger than 4 GB you should definitely go for NTFS. Otherwise, if you choose FAT32, you could get the flashdrive bootable from UEFI too.
New partition dialog
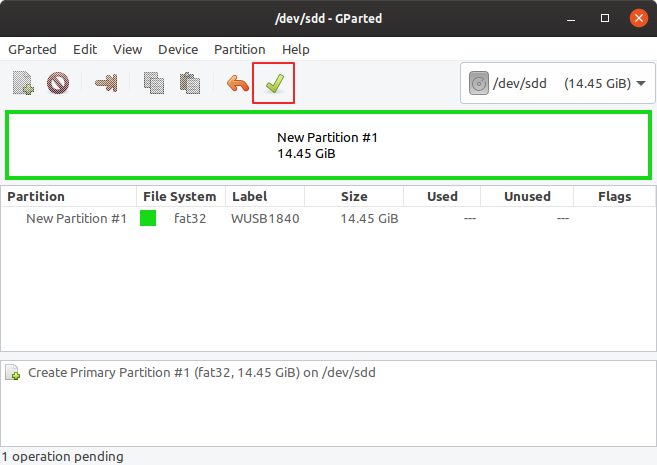
Apply all pending operation from Edit menu - Apply all operations or click the button on the main window. Right click the partition and choose Manage flags. If you chose the msdos partition table tick boot. If you chose the gpt partition table, msftdata should already be checked and you don't have to do anything.
The Apply button from the main window of GParted
Copy Windows files
Quit GParted and use the file manager to copy all files from Windows ISO to USB stick. Mount the ISO using Open with - Disk Image Mounter (if you use Nautilus as a file manager). If that fails you can use Furius ISO Mount and loop-mount the ISO. Select all files Ctrl+A and Copy to USB drive which will be automatically mounted when you click on it at /media/<username>/<drive_label>. After the copy process is finished, look in the USB root folder for the boot directory. If it is uppercase, rename it to lowercase.
Make it bootable
If you used NTFS filesystem and MSDOS table, only method A is available. If you used FAT32 and MSDOS table, you can apply method A, B or both. If you used GPT partition table, only method B should be followed.
Method A: MBR bootable
GRUB will be used for that. Open a Terminal and run:
sudo grub-install --target=i386-pc --boot-directory="/media/<username>/<drive_label>/boot" /dev/sdX
Replace:
/media/<username>/<drive_label>with the path where USB drive is mounted;/dev/sdXwith the USB drive, not the partition (e.g./dev/sdb)
/dev/sdX) may result in bootloader corruption of the running operating system!Wait for it to finish. If everything is OK, you should see:
Installing for i386-pc platform. Installation finished. No error reported.
Now, create a text file and write the following in it:
default=1
timeout=15
color_normal=light-cyan/dark-gray
menu_color_normal=black/light-cyan
menu_color_highlight=white/black
menuentry "Start Windows Installation" {
insmod ntfs
insmod search_label
search --no-floppy --set=root --label <USB_drive_label> --hint hd0,msdos1
ntldr /bootmgr
boot
}
menuentry "Boot from the first hard drive" {
insmod ntfs
insmod chain
insmod part_msdos
insmod part_gpt
set root=(hd1)
chainloader +1
boot
}
Replace <USB_drive_label> with the label you gave it when you formatted the drive (you can place it between quotes if it contains a space, although it is not recommended to use spaces in drive label). Save the file as grub.cfg and put it on the USB drive in the boot/grub folder. That's it. The USB drive is now bootable from BIOS and can be used to install Windows on your PC. The first time you boot from it in MBR BIOS or CSM mode select Start Windows Installation.
Method B: UEFI bootable
Not all Windows versions are supported. Windows 7 on 64 bits, Windows 8 and newer versions should work. After the copy process is finished, look in the USB root folder for the efi/boot directory. If there's a bootx64.efi or bootia32.efi file there, then you're done. You can boot from your USB in UEFI mode.
If the OS you are making a bootable USB for is Windows 7, browse the efi/microsoft folder and copy the entire boot folder from this path one level up in the efi folder. Merge folders if boot already exists. Here is what to do if you don't have the bootx64.efi file in efi/boot folder. Browse the mounted Windows ISO image into the sources folder. Open install.wim (or install.esd) with your archive manager (you will need 7z installed). Go to the path ./1/Windows/Boot/EFI and extract the file bootmgfw.efi anywhere you want. Rename it to bootx64.efi and put it on the USB drive, in the efi/boot folder. If you can't find bootmgfw.efi in install.wim then you probably have a 32 bit Windows ISO or other types of images (recovery disks, upgrade versions).
You can now boot from your USB in UEFI mode.
Errors
1. modinfo.sh doesn't exist
grub-install: error: /usr/lib/grub/i386-pc/modinfo.sh doesn't exist. Please specify --target or --directory.
Install the grub-pc-bin package with sudo apt install grub-pc-bin and run the grub-install command again.
2. Embedding errors
If you get embedding errors (something like filesystem 'x' does not support embedding or Embedding is not possible), be sure you are installing GRUB to USB device and not USB partition. Most likely you typed /dev/sdb1 instead of /dev/sdb (sdb is just an example here). If it still doesn't work, try zeroing the USB drive (at least some sectors at beggining) or use a different USB flash drive.
3. Blocklists
Sometimes, GRUB will not install on some flash drives. Try to force it by adding --force argument to the grub-install command.
4. Alternate root partition selection
The root partition selection may fail if your USB flash drive partition has the same label as one of the partitions on the target computer. The best way of setting the root partition is by UUID. Launch again GParted and select the USB flashdrive. Right click the partition and select Information. Note the UUID field.
Partition UUID
In grub.cfg, replace the line:
search --no-floppy --set=root --label <USB_drive_label> --hint hd0,msdos1
with:
insmod search_fs_uuid search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set root <drive_UUID>
where you will replace <drive_UUID> with the UUID you got from GParted.
Still getting errors? If you want an useful answer, please post a comment with the complete grub-install command and the error message.