上节分析了Mapper对象的创建。
在ORM的定义中可以理解为Object->SQLMapper抽象层(这一层并不负责具体的SQL执行。这一层可以理解为SQL代理层)
本节分析以下内容:
①SqlSession在具体执行SQL时,如果通过namespace+sqlid定位到具体的MappedStatement(sql的对象化表现形式)
②参数(Object) 如何填充到具体的SQL
③SQL是如何执行的
- 获取StateMentMapper.前面讲到初始化时,会缓存MappedStatement,MappedStatement被保存在StrictMap中.
StrictMap是Mybatis实现HashMap子类。Key重复放入的时候会报错。
- 参数(Object) 如何填充到具体的SQL(Param-SQL的Orm转换)
1、通过Executor执行SQL
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
2、Executor是如何获取的?
SqlSessionFactory工厂中代码如下:
从Configuration中获得Excecutor,默认的执行器类型为configuration.getDefaultExecutorType()在configuration类中定义为
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
ExecutorType.SIMPLE会创建何种执行器?
来看Configuraiton的获得执行器的方法
默认的执行器为:SimpleExecutor,而cacheEnabled默认值为true.所以实际是CachingExecutor,使用了装饰器模式。
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
- Excecutor是如何将参数成功映射到具体SQL的参数?
先看下MappedStatement中的类成员构成。sqlSource是具体获取待执行SQL的对象。
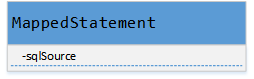
- sqlSource接口定义:
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject)的方法,改方调用实际的SqlSource的实现类,来获取真正执行的SQL
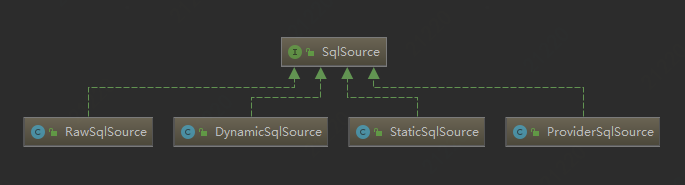
先说说几个处理类的区别:
DynamicSqlSource:sql中包含<where><if><choose>等条件是,会被定义为.通过具体的Node处理对象,拼接SQL。
看一段代码,我们关注rootSqlNode变量,以及getBoundSql()方法的执行。
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource { private final Configuration configuration; private final SqlNode rootSqlNode; public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) { this.configuration = configuration; this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode; } @Override public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject); rootSqlNode.apply(context); SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration); Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass(); SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings()); BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) { boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } return boundSql; }
解析过程描述:
①rootSqlNode为从XML解析的具体SQL节点,每一行作为一个node。对于<if><choose>等。每一个节点是一个node
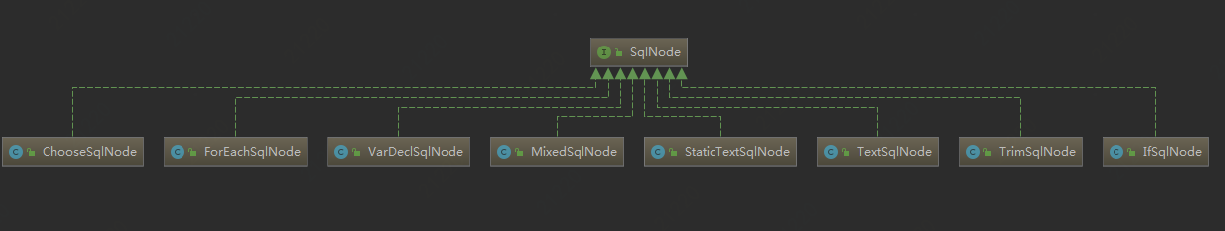
②<if></if>的判断是在具体的node中执行的。SQLNode有以下几种类型。
看一段IfSqlNode的代码:apply方法中的evaluateBoolean方法,将对<if>语句进行判断,返回结果。如果结果为真,则把条件添加到contents
/** * @author Clinton Begin */ public class IfSqlNode implements SqlNode { private final ExpressionEvaluator evaluator; private final String test; private final SqlNode contents; public IfSqlNode(SqlNode contents, String test) { this.test = test; this.contents = contents; this.evaluator = new ExpressionEvaluator(); } @Override public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) { if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) { contents.apply(context); return true; } return false; } }
mybatis中定义的SQL节点如下。
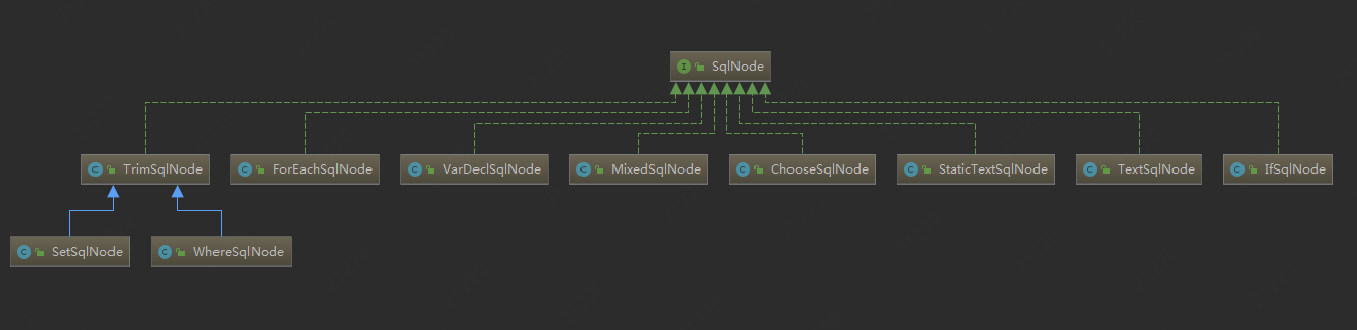
RawSqlSource:对于不包含<if>等条件判断,替换#{}变为? 在创建RawSqlSource对象时执行这项操作
DynamicSqlSource: 对sql中包含${}参数的会转换为该对象
- SqlSource的转换是在初始化加载时完成。那真正的参数是何时转换为SQL?
SimpleExecutor中,创建PrepareStateMent的过程。
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
//创建、初始化PreparedStatement stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//设置参数 handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }
离我们想知道的真相越来越近了,来看具体的参数化过程
StateMentHandler.parameterize
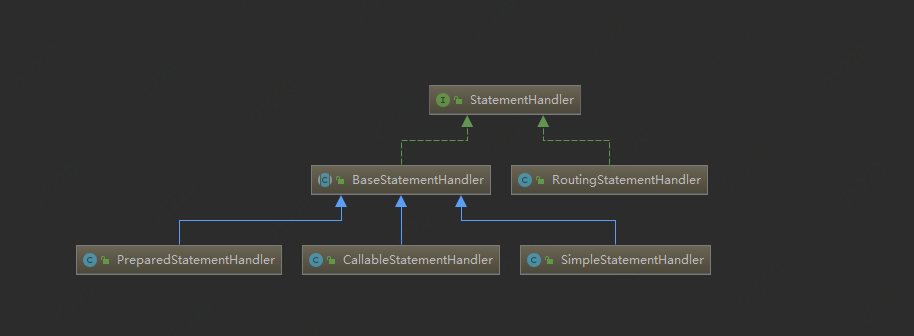
RoutingStatementHandler用来做路由器:根据实际的StatementType做路由
我们来看PreparedStatementHadler
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException { this.parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement)statement); }
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(this.mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
//获得所有的参数
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = this.boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for(int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); ++i) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = (ParameterMapping)parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); Object value; if (this.boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { value = this.boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (this.parameterObject == null) { value = null;
//如果有typeHandler则用TypeHandler处理参数
//一些基础类型是有typeHandler的
} else if (this.typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(this.parameterObject.getClass())) { value = this.parameterObject; } else {
//如果没有typeHandler,通过反射,获得Bean参数中的值 MetaObject metaObject = this.configuration.newMetaObject(this.parameterObject); value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } //根据参数的JDBCtype找到TypeHandler,设置到PrePareStatement中 TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType(); if (value == null && jdbcType == null) { jdbcType = this.configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull(); } try { typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType); } catch (TypeException var10) { throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + var10, var10); } catch (SQLException var11) { throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + var11, var11); } } } } }
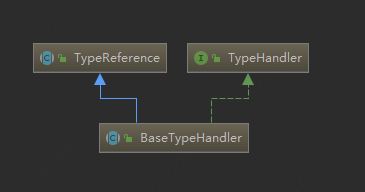
TypeHandler的继承关系如下:
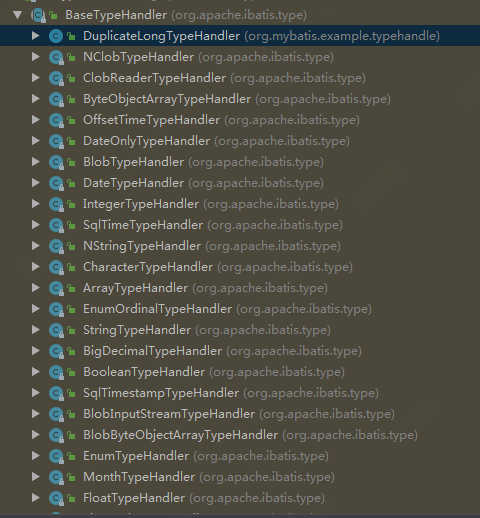
我们查看其中的BigDecimalTypeHandler的源码
public class BigDecimalTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<BigDecimal> { @Override public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, BigDecimal parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException { ps.setBigDecimal(i, parameter); } @Override public BigDecimal getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException { return rs.getBigDecimal(columnName); } @Override public BigDecimal getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { return rs.getBigDecimal(columnIndex); } @Override public BigDecimal getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { return cs.getBigDecimal(columnIndex); } }
会调用JDBCAPI中的相应方法获得正确的值