DirectShow SDK提供了一套开发Filter的基类源代码。基于这些基类开发Filter将大大简化开发过程。
1、CBaseObject
大部分SDK类都从CBaseObject类(参见combase.h)中继承而来的。
- class CBaseObject
- {
- private:
- // Disable the copy constructor and assignment by default so you will get
- // compiler errors instead of unexpected behaviour if you pass objects
- // by value or assign objects.
- CBaseObject(const CBaseObject& objectSrc); // no implementation
- void operator=(const CBaseObject& objectSrc); // no implementation
- private:
- static LONG m_cObjects; /* Total number of objects active */
- protected:
- #ifdef DEBUG
- DWORD m_dwCookie; /* Cookie identifying this object */
- #endif
- public:
- /* These increment and decrement the number of active objects */
- CBaseObject(const TCHAR *pName);
- #ifdef UNICODE
- CBaseObject(const char *pName);
- #endif
- ~CBaseObject();
- /* Call this to find if there are any CUnknown derived objects active */
- static LONG ObjectsActive() {
- return m_cObjects;
- };
- };
2、 CUnknown
作为COM组件(参见combase.cpp文件),最基本的当然是IUnknown接口的实现。SDK提供了CUnknown类,SDK实现了COM接口类都是直接或间接从这个类继承来的。
- class AM_NOVTABLE CUnknown : public INonDelegatingUnknown,
- public CBaseObject
- {
- private:
- const LPUNKNOWN m_pUnknown; /* Owner of this object */
- protected: /* So we can override NonDelegatingRelease() */
- volatile LONG m_cRef; /* Number of reference counts */
- public:
- CUnknown(const TCHAR *pName, LPUNKNOWN pUnk);
- virtual ~CUnknown() {};
- // This is redundant, just use the other constructor
- // as we never touch the HRESULT in this anyway
- CUnknown(TCHAR *pName, LPUNKNOWN pUnk,HRESULT *phr);
- #ifdef UNICODE
- CUnknown(const char *pName, LPUNKNOWN pUnk);
- CUnknown(char *pName, LPUNKNOWN pUnk,HRESULT *phr);
- #endif
- /* Return the owner of this object */
- LPUNKNOWN GetOwner() const {
- return m_pUnknown;
- };
- /* Called from the class factory to create a new instance, it is
- pure virtual so it must be overriden in your derived class */
- /* static CUnknown *CreateInstance(LPUNKNOWN, HRESULT *) */
- /* Non delegating unknown implementation */
- STDMETHODIMP NonDelegatingQueryInterface(REFIID, void **);
- STDMETHODIMP_(ULONG) NonDelegatingAddRef();
- STDMETHODIMP_(ULONG) NonDelegatingRelease();
- };
CUnknown类从CBaseObject中继承而来,另外CUnknown类还实现了INonDelegatingUnknown接口,用于支持引用计数、接口查询、COM组件“聚合”等。
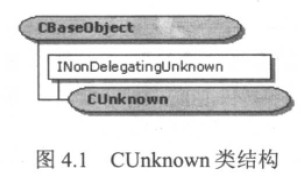
CUnknown类的使用方法如下:
(1) 从CUnknown派生一个子类,并在子类的public区加入DECLARE_IUNKNOWN宏;
(2) 重写NonDelegatingQueryInterface函数,用以支持IUnknown外的其他接口;
(3) 在子类的构造函数中调用CUnknown的构造函数。
eg:
- class CSeekingPassThru : public ISeekingPassThru, public CUnknown
- {
- public:
- static CUnknown *CreateInstance(LPUNKNOWN pUnk, HRESULT *phr);
- CSeekingPassThru(TCHAR *pName, LPUNKNOWN pUnk, HRESULT *phr);
- ~CSeekingPassThru();
- DECLARE_IUNKNOWN;
- STDMETHODIMP NonDelegatingQueryInterface(REFIID riid, void ** ppv);
- STDMETHODIMP Init(BOOL bSupportRendering, IPin *pPin);
- private:
- CPosPassThru *m_pPosPassThru;
- };
- CSeekingPassThru::CSeekingPassThru( TCHAR *pName, LPUNKNOWN pUnk, HRESULT *phr )
- : CUnknown(pName, pUnk, phr),
- m_pPosPassThru(NULL)
- {
- }
3、 CBaseFilter
最基本的Filter由CBaseFilter 类(参见amfilter.cpp)实现。
作为Filter的基本特征,CBaseFilter实现了IBaseFilter接口(IbaseFilter从IMediaFilter继承而来)。
同时CBaseFilter还实现了Filter框架(描述了各个Pin组件的情况)。

- class AM_NOVTABLE CBaseFilter : public CUnknown, // Handles an IUnknown
- public IBaseFilter, // The Filter Interface
- public IAMovieSetup // For un/registration
- {
- friend class CBasePin;
- protected:
- FILTER_STATE m_State; // current state: running, paused
- IReferenceClock *m_pClock; // this graph's ref clock
- CRefTime m_tStart; // offset from stream time to reference time
- CLSID m_clsid; // This filters clsid
- // used for serialization
- CCritSec *m_pLock; // Object we use for locking
- WCHAR *m_pName; // Full filter name
- IFilterGraph *m_pGraph; // Graph we belong to
- IMediaEventSink *m_pSink; // Called with notify events
- LONG m_PinVersion; // Current pin version
- public:
- CBaseFilter(
- const TCHAR *pName, // Object description
- LPUNKNOWN pUnk, // IUnknown of delegating object
- CCritSec *pLock, // Object who maintains lock
- REFCLSID clsid); // The clsid to be used to serialize this filter
- CBaseFilter(
- TCHAR *pName, // Object description
- LPUNKNOWN pUnk, // IUnknown of delegating object
- CCritSec *pLock, // Object who maintains lock
- REFCLSID clsid, // The clsid to be used to serialize this filter
- HRESULT *phr); // General OLE return code
- #ifdef UNICODE
- CBaseFilter(
- const CHAR *pName, // Object description
- LPUNKNOWN pUnk, // IUnknown of delegating object
- CCritSec *pLock, // Object who maintains lock
- REFCLSID clsid); // The clsid to be used to serialize this filter
- CBaseFilter(
- CHAR *pName, // Object description
- LPUNKNOWN pUnk, // IUnknown of delegating object
- CCritSec *pLock, // Object who maintains lock
- REFCLSID clsid, // The clsid to be used to serialize this filter
- HRESULT *phr); // General OLE return code
- #endif
- ~CBaseFilter();
- DECLARE_IUNKNOWN
- // override this to say what interfaces we support where
- STDMETHODIMP NonDelegatingQueryInterface(REFIID riid, void ** ppv);
- #ifdef DEBUG
- STDMETHODIMP_(ULONG) NonDelegatingRelease();
- #endif
- //
- // --- IPersist method ---
- //
- STDMETHODIMP GetClassID(CLSID *pClsID);
- // --- IMediaFilter methods ---
- STDMETHODIMP GetState(DWORD dwMSecs, FILTER_STATE *State);
- STDMETHODIMP SetSyncSource(IReferenceClock *pClock);
- STDMETHODIMP GetSyncSource(IReferenceClock **pClock);
- // override Stop and Pause so we can activate the pins.
- // Note that Run will call Pause first if activation needed.
- // Override these if you want to activate your filter rather than
- // your pins.
- STDMETHODIMP Stop();
- STDMETHODIMP Pause();
- // the start parameter is the difference to be added to the
- // sample's stream time to get the reference time for
- // its presentation
- STDMETHODIMP Run(REFERENCE_TIME tStart);
- // --- helper methods ---
- // return the current stream time - ie find out what
- // stream time should be appearing now
- virtual HRESULT StreamTime(CRefTime& rtStream);
- // Is the filter currently active?
- BOOL IsActive() {
- CAutoLock cObjectLock(m_pLock);
- return ((m_State == State_Paused) || (m_State == State_Running));
- };
- // Is this filter stopped (without locking)
- BOOL IsStopped() {
- return (m_State == State_Stopped);
- };
- //
- // --- IBaseFilter methods ---
- //
- // pin enumerator
- STDMETHODIMP EnumPins(
- IEnumPins ** ppEnum);
- // default behaviour of FindPin assumes pin ids are their names
- STDMETHODIMP FindPin(
- LPCWSTR Id,
- IPin ** ppPin
- );
- STDMETHODIMP QueryFilterInfo(
- FILTER_INFO * pInfo);
- STDMETHODIMP JoinFilterGraph(
- IFilterGraph * pGraph,
- LPCWSTR pName);
- // return a Vendor information string. Optional - may return E_NOTIMPL.
- // memory returned should be freed using CoTaskMemFree
- // default implementation returns E_NOTIMPL
- STDMETHODIMP QueryVendorInfo(
- LPWSTR* pVendorInfo
- );
- // --- helper methods ---
- // send an event notification to the filter graph if we know about it.
- // returns S_OK if delivered, S_FALSE if the filter graph does not sink
- // events, or an error otherwise.
- HRESULT NotifyEvent(
- long EventCode,
- LONG_PTR EventParam1,
- LONG_PTR EventParam2);
- // return the filter graph we belong to
- IFilterGraph *GetFilterGraph() {
- return m_pGraph;
- }
- // Request reconnect
- // pPin is the pin to reconnect
- // pmt is the type to reconnect with - can be NULL
- // Calls ReconnectEx on the filter graph
- HRESULT ReconnectPin(IPin *pPin, AM_MEDIA_TYPE const *pmt);
- // find out the current pin version (used by enumerators)
- virtual LONG GetPinVersion();
- void IncrementPinVersion();
- // you need to supply these to access the pins from the enumerator
- // and for default Stop and Pause/Run activation.
- virtual int GetPinCount() PURE;
- virtual CBasePin *GetPin(int n) PURE;
- // --- IAMovieSetup methods ---
- STDMETHODIMP Register(); // ask filter to register itself
- STDMETHODIMP Unregister(); // and unregister itself
- // --- setup helper methods ---
- // (override to return filters setup data)
- virtual LPAMOVIESETUP_FILTER GetSetupData(){ return NULL; }
- };
CBaseFilter类的使用方法如下:
(1) 声明一个新类是从CBaseFilter中继承而来;
(2) 在新类中定义Filter上的Pin的实例(Pin从CBasePin类继承而来);
(3) 实现纯虚函数CBaseFilter::GetPin,用于返回Filter上各个Pin的对象指针;
(4) 实现纯虚函数CBaseFilter::GetPinCount,用于返回Filter上Pin 的数量;
(5) 考虑如何处理从输入Pin进来的Sample数据。
eg:
- //
- // The filter object itself. Supports IBaseFilter through
- // CBaseFilter and also IFileSourceFilter directly in this object
- // CAsyncReader类实现了一个Filter,它从CBaseFilter派生,实现了仅含一个输出
- // Pin(CAsyncOutputPin类的实例)的Source filter框架。
- class CAsyncReader : public CBaseFilter
- {
- protected:
- // filter-wide lock
- CCritSec m_csFilter;
- // all i/o done here
- CAsyncIo m_Io;
- // (2)在新类中定义Filter上的Pin的实例(Pin从CBasePin类继承而来);
- // our output pin
- CAsyncOutputPin m_OutputPin;
- // Type we think our data is
- CMediaType m_mt;
- public:
- // construction / destruction
- CAsyncReader(
- TCHAR *pName,
- LPUNKNOWN pUnk,
- CAsyncStream *pStream, // 它是Filter获取数据的源
- HRESULT *phr);
- ~CAsyncReader();
- //(3) 实现纯虚函数CBaseFilter::GetPin,用于返回Filter上各个Pin的对象指针;
- //(4) 实现纯虚函数CBaseFilter::GetPinCount,用于返回Filter上Pin 的数量;
- int GetPinCount();
- CBasePin *GetPin(int n);
- // --- Access our media type
- const CMediaType *LoadType() const
- {
- return &m_mt;
- }
- virtual HRESULT Connect(
- IPin * pReceivePin,
- const AM_MEDIA_TYPE *pmt // optional media type
- )
- {
- return m_OutputPin.CBasePin::Connect(pReceivePin, pmt);
- }
- };
还有SDK类的CSource、CBaseRenderer、 CTracsformFilter都是从CBaseFilter继承来的,实现开发Filter时,
使用这些子类作为Filter类。
4、CBasePin
Filter 上最基本的Pin由CBasePin类(参见 amfilter.h)实现。
作为Pin的基本特征,CBasePin实现了IPin接口。CBasePin设计了Pin 的整个连接过程。
另外,这个类还实现了IQualityControl接口,该接口用于质量控制。
- class AM_NOVTABLE CBasePin : public CUnknown, public IPin, public IQualityControl
- {
- protected:
- WCHAR * m_pName; // This pin's name
- IPin *m_Connected; // Pin we have connected to
- PIN_DIRECTION m_dir; // Direction of this pin
- CCritSec *m_pLock; // Object we use for locking
- bool m_bRunTimeError; // Run time error generated
- bool m_bCanReconnectWhenActive; // OK to reconnect when active
- bool m_bTryMyTypesFirst; // When connecting enumerate
- // this pin's types first
- CBaseFilter *m_pFilter; // Filter we were created by
- IQualityControl *m_pQSink; // Target for Quality messages
- LONG m_TypeVersion; // Holds current type version
- CMediaType m_mt; // Media type of connection
- CRefTime m_tStart; // time from NewSegment call
- CRefTime m_tStop; // time from NewSegment
- double m_dRate; // rate from NewSegment
- #ifdef DEBUG
- LONG m_cRef; // Ref count tracing
- #endif
- // displays pin connection information
- #ifdef DEBUG
- void DisplayPinInfo(IPin *pReceivePin);
- void DisplayTypeInfo(IPin *pPin, const CMediaType *pmt);
- #else
- void DisplayPinInfo(IPin *pReceivePin) {};
- void DisplayTypeInfo(IPin *pPin, const CMediaType *pmt) {};
- #endif
- // used to agree a media type for a pin connection
- // given a specific media type, attempt a connection (includes
- // checking that the type is acceptable to this pin)
- HRESULT
- AttemptConnection(
- IPin* pReceivePin, // connect to this pin
- const CMediaType* pmt // using this type
- );
- // try all the media types in this enumerator - for each that
- // we accept, try to connect using ReceiveConnection.
- HRESULT TryMediaTypes(
- IPin *pReceivePin, // connect to this pin
- const CMediaType *pmt, // proposed type from Connect
- IEnumMediaTypes *pEnum); // try this enumerator
- // establish a connection with a suitable mediatype. Needs to
- // propose a media type if the pmt pointer is null or partially
- // specified - use TryMediaTypes on both our and then the other pin's
- // enumerator until we find one that works.
- HRESULT AgreeMediaType(
- IPin *pReceivePin, // connect to this pin
- const CMediaType *pmt); // proposed type from Connect
- public:
- CBasePin(
- TCHAR *pObjectName, // Object description
- CBaseFilter *pFilter, // Owning filter who knows about pins
- CCritSec *pLock, // Object who implements the lock
- HRESULT *phr, // General OLE return code
- LPCWSTR pName, // Pin name for us
- PIN_DIRECTION dir); // Either PINDIR_INPUT or PINDIR_OUTPUT
- #ifdef UNICODE
- CBasePin(
- CHAR *pObjectName, // Object description
- CBaseFilter *pFilter, // Owning filter who knows about pins
- CCritSec *pLock, // Object who implements the lock
- HRESULT *phr, // General OLE return code
- LPCWSTR pName, // Pin name for us
- PIN_DIRECTION dir); // Either PINDIR_INPUT or PINDIR_OUTPUT
- #endif
- virtual ~CBasePin();
- DECLARE_IUNKNOWN
- STDMETHODIMP NonDelegatingQueryInterface(REFIID riid, void ** ppv);
- STDMETHODIMP_(ULONG) NonDelegatingRelease();
- STDMETHODIMP_(ULONG) NonDelegatingAddRef();
- // --- IPin methods ---
- // take lead role in establishing a connection. Media type pointer
- // may be null, or may point to partially-specified mediatype
- // (subtype or format type may be GUID_NULL).
- STDMETHODIMP Connect(
- IPin * pReceivePin,
- const AM_MEDIA_TYPE *pmt // optional media type
- );
- // (passive) accept a connection from another pin
- STDMETHODIMP ReceiveConnection(
- IPin * pConnector, // this is the initiating connecting pin
- const AM_MEDIA_TYPE *pmt // this is the media type we will exchange
- );
- STDMETHODIMP Disconnect();
- STDMETHODIMP ConnectedTo(IPin **pPin);
- STDMETHODIMP ConnectionMediaType(AM_MEDIA_TYPE *pmt);
- STDMETHODIMP QueryPinInfo(
- PIN_INFO * pInfo
- );
- STDMETHODIMP QueryDirection(
- PIN_DIRECTION * pPinDir
- );
- STDMETHODIMP QueryId(
- LPWSTR * Id
- );
- // does the pin support this media type
- STDMETHODIMP QueryAccept(
- const AM_MEDIA_TYPE *pmt
- );
- // return an enumerator for this pins preferred media types
- STDMETHODIMP EnumMediaTypes(
- IEnumMediaTypes **ppEnum
- );
- // return an array of IPin* - the pins that this pin internally connects to
- // All pins put in the array must be AddReffed (but no others)
- // Errors: "Can't say" - FAIL, not enough slots - return S_FALSE
- // Default: return E_NOTIMPL
- // The filter graph will interpret NOT_IMPL as any input pin connects to
- // all visible output pins and vice versa.
- // apPin can be NULL if nPin==0 (not otherwise).
- STDMETHODIMP QueryInternalConnections(
- IPin* *apPin, // array of IPin*
- ULONG *nPin // on input, the number of slots
- // on output the number of pins
- ) { return E_NOTIMPL; }
- // Called when no more data will be sent
- STDMETHODIMP EndOfStream(void);
- // Begin/EndFlush still PURE
- // NewSegment notifies of the start/stop/rate applying to the data
- // about to be received. Default implementation records data and
- // returns S_OK.
- // Override this to pass downstream.
- STDMETHODIMP NewSegment(
- REFERENCE_TIME tStart,
- REFERENCE_TIME tStop,
- double dRate);
- //================================================================================
- // IQualityControl methods
- //================================================================================
- STDMETHODIMP Notify(IBaseFilter * pSender, Quality q);
- STDMETHODIMP SetSink(IQualityControl * piqc);
- // --- helper methods ---
- // Returns true if the pin is connected. false otherwise.
- BOOL IsConnected(void) {return (m_Connected != NULL); };
- // Return the pin this is connected to (if any)
- IPin * GetConnected() { return m_Connected; };
- // Check if our filter is currently stopped
- BOOL IsStopped() {
- return (m_pFilter->m_State == State_Stopped);
- };
- // find out the current type version (used by enumerators)
- virtual LONG GetMediaTypeVersion();
- void IncrementTypeVersion();
- // switch the pin to active (paused or running) mode
- // not an error to call this if already active
- virtual HRESULT Active(void);
- // switch the pin to inactive state - may already be inactive
- virtual HRESULT Inactive(void);
- // Notify of Run() from filter
- virtual HRESULT Run(REFERENCE_TIME tStart);
- // check if the pin can support this specific proposed type and format
- virtual HRESULT CheckMediaType(const CMediaType *) PURE;
- // set the connection to use this format (previously agreed)
- virtual HRESULT SetMediaType(const CMediaType *);
- // check that the connection is ok before verifying it
- // can be overridden eg to check what interfaces will be supported.
- virtual HRESULT CheckConnect(IPin *);
- // Set and release resources required for a connection
- virtual HRESULT BreakConnect();
- virtual HRESULT CompleteConnect(IPin *pReceivePin);
- // returns the preferred formats for a pin
- virtual HRESULT GetMediaType(int iPosition,CMediaType *pMediaType);
- // access to NewSegment values
- REFERENCE_TIME CurrentStopTime() {
- return m_tStop;
- }
- REFERENCE_TIME CurrentStartTime() {
- return m_tStart;
- }
- double CurrentRate() {
- return m_dRate;
- }
- // Access name
- LPWSTR Name() { return m_pName; };
- // Can reconnectwhen active?
- void SetReconnectWhenActive(bool bCanReconnect)
- {
- m_bCanReconnectWhenActive = bCanReconnect;
- }
- bool CanReconnectWhenActive()
- {
- return m_bCanReconnectWhenActive;
- }
- protected:
- STDMETHODIMP DisconnectInternal();
- };
在CBasePin实现的成员函数中,有3个与Filter的状态转换相对应。
- // 转换pin到活动状态(暂停或运行)
- // not an error to call this if already active
- virtual HRESULT Active(void);
- // 转换pin到不活动状态 - 可能已经处于非活动状态
- virtual HRESULT Inactive(void);
- // 通知运行filter 的 Run()
- virtual HRESULT Run(REFERENCE_TIME tStart);
我们来看一下Filter的Stop的实现,实际上就是调用Filter的所有pin的Inactive函数
- STDMETHODIMP
- CBaseFilter::Stop()
- {
- CAutoLock cObjectLock(m_pLock);
- HRESULT hr = NOERROR;
- // 通知所有pin改变状态
- if (m_State != State_Stopped) {
- int cPins = GetPinCount();
- for (int c = 0; c < cPins; c++) {
- CBasePin *pPin = GetPin(c);
- // Disconnected pins are not activated - this saves pins worrying
- // about this state themselves. We ignore the return code to make
- // sure everyone is inactivated regardless. The base input pin
- // class can return an error if it has no allocator but Stop can
- // be used to resync the graph state after something has gone bad
- // 仅在完成连接的pin上调用Inactive函数
- // 如果Inactive函数返回一个错误值,则暂时忽略,
- // 以便所有Pin都有机会被调用Inactive
- if (pPin->IsConnected()) {
- HRESULT hrTmp = pPin->Inactive();
- if (FAILED(hrTmp) && SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- hr = hrTmp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- m_State = State_Stopped;
- return hr;
- }
在实际开发Filter的过程中,很有可能重写CBasePin::Inactive、 CBasePin::Active和CBasePin::Run这3个函数,以进行必要的初始化、释放资源等。
CBasePin类的使用方法如下:
(1) 从CBasePin派生一个子类;
(2) 实现纯虚函数CBasePIn::CheckMediaType,进行Pin连接时的媒体类型检查;
(3) 实现纯虚函数CBasePin::GetMediaType,提供Pin上的首选媒体类型。
(4) 实现IPin::BeginFlush和IPin::EndFlush两个函数。
(5) 可能需要重写的函数包括
CBasePin::Active() 实现资源分配
CBasePin::Inactive 实现资源释放
CBasePin::Run 在Filter运行前进行一些初始化
CBasePin::CheckConnect 连接时检查,如查询对方Pin上是否支持某个特殊接口
CBasePin::BreakConnect 断开连接,并进行必要的资源释放
CBasePin::CompleteConnect 完成连接时被调用,可以在这个函数中获得当前连接的媒体类型参数
CBasePin::EndOfStream 当上流数据全部传送完毕后被调用。
如果这个是Transform Filter,则将EndOfStream继续入下传送;
如果是Renderer Filter,需要向Filter Graph Manager发送一个EC_COMPLETE事件
CBasePin::Noftify 直接响应质量控制。
eg:
- // CAsyncOutputPin实现了一个输出Pin
- // 继承自IAsyncReader、CBasePin,这是对拉模式的Source Filter的基本要求
- /* IAsyncReader接口方法及描述如下:
- BeginFlush 放弃所有正在进行的数据读取
- EndFlush 与BeginFlush配对,标示Flush过程结束
- Length 得到数据总长度和当前可以读取的长度
- RequestAlloctor 要求一个输入Pin上的Sample管理器
- Request 发出一个数据请求
- SyncReadAligned 同步读取数据(边界对齐)
- SyncRead 同步读取数据
- WaitForNext 等待一个请求的完成
- ======================================================================
- 可以看出CAsyOutputPin类上实现的IAsyncReader的各个接口方法,都“委托”
- 给了CAsyncIo类对象的同名成员函数
- */
- class CAsyncOutputPin
- : public IAsyncReader,
- public CBasePin
- {
- protected:
- CAsyncReader* m_pReader;
- CAsyncIo * m_pIo;
- // This is set every time we're asked to return an IAsyncReader
- // interface
- // This allows us to know if the downstream pin can use
- // this transport, otherwise we can hook up to thinks like the
- // dump filter and nothing happens
- BOOL m_bQueriedForAsyncReader;
- HRESULT InitAllocator(IMemAllocator **ppAlloc);
- public:
- // constructor and destructor
- CAsyncOutputPin(
- HRESULT * phr,
- CAsyncReader *pReader,
- CAsyncIo *pIo,
- CCritSec * pLock);
- ~CAsyncOutputPin();
- // --- CUnknown ---
- // need to expose IAsyncReader
- DECLARE_IUNKNOWN
- STDMETHODIMP NonDelegatingQueryInterface(REFIID, void**);
- // --- IPin methods ---
- STDMETHODIMP Connect(
- IPin * pReceivePin,
- const AM_MEDIA_TYPE *pmt // optional media type
- );
- // --- CBasePin methods ---
- // return the types we prefer - this will return the known
- // file type
- HRESULT GetMediaType(int iPosition, CMediaType *pMediaType);
- // can we support this type?
- HRESULT CheckMediaType(const CMediaType* pType);
- // Clear the flag so we see if IAsyncReader is queried for
- HRESULT CheckConnect(IPin *pPin)
- {
- m_bQueriedForAsyncReader = FALSE;
- return CBasePin::CheckConnect(pPin);
- }
- // See if it was asked for
- HRESULT CompleteConnect(IPin *pReceivePin)
- {
- if (m_bQueriedForAsyncReader) {
- return CBasePin::CompleteConnect(pReceivePin);
- } else {
- #ifdef VFW_E_NO_TRANSPORT
- return VFW_E_NO_TRANSPORT;
- #else
- return E_FAIL;
- #endif
- }
- }
- // Remove our connection status
- HRESULT BreakConnect()
- {
- m_bQueriedForAsyncReader = FALSE;
- return CBasePin::BreakConnect();
- }
- // --- IAsyncReader methods ---
- // pass in your preferred allocator and your preferred properties.
- // method returns the actual allocator to be used. Call GetProperties
- // on returned allocator to learn alignment and prefix etc chosen.
- // this allocator will be not be committed and decommitted by
- // the async reader, only by the consumer.
- STDMETHODIMP RequestAllocator(
- IMemAllocator* pPreferred,
- ALLOCATOR_PROPERTIES* pProps,
- IMemAllocator ** ppActual);
- // queue a request for data.
- // media sample start and stop times contain the requested absolute
- // byte position (start inclusive, stop exclusive).
- // may fail if sample not obtained from agreed allocator.
- // may fail if start/stop position does not match agreed alignment.
- // samples allocated from source pin's allocator may fail
- // GetPointer until after returning from WaitForNext.
- STDMETHODIMP Request(
- IMediaSample* pSample,
- DWORD_PTR dwUser); // user context
- // block until the next sample is completed or the timeout occurs.
- // timeout (millisecs) may be 0 or INFINITE. Samples may not
- // be delivered in order. If there is a read error of any sort, a
- // notification will already have been sent by the source filter,
- // and STDMETHODIMP will be an error.
- STDMETHODIMP WaitForNext(
- DWORD dwTimeout,
- IMediaSample** ppSample, // completed sample
- DWORD_PTR * pdwUser); // user context
- // sync read of data. Sample passed in must have been acquired from
- // the agreed allocator. Start and stop position must be aligned.
- // equivalent to a Request/WaitForNext pair, but may avoid the
- // need for a thread on the source filter.
- STDMETHODIMP SyncReadAligned(
- IMediaSample* pSample);
- // sync read. works in stopped state as well as run state.
- // need not be aligned. Will fail if read is beyond actual total
- // length.
- STDMETHODIMP SyncRead(
- LONGLONG llPosition, // absolute file position
- LONG lLength, // nr bytes required
- BYTE* pBuffer); // write data here
- // return total length of stream, and currently available length.
- // reads for beyond the available length but within the total length will
- // normally succeed but may block for a long period.
- STDMETHODIMP Length(
- LONGLONG* pTotal,
- LONGLONG* pAvailable);
- // cause all outstanding reads to return, possibly with a failure code
- // (VFW_E_TIMEOUT) indicating they were cancelled.
- // these are defined on IAsyncReader and IPin
- STDMETHODIMP BeginFlush(void);
- STDMETHODIMP EndFlush(void);
- };
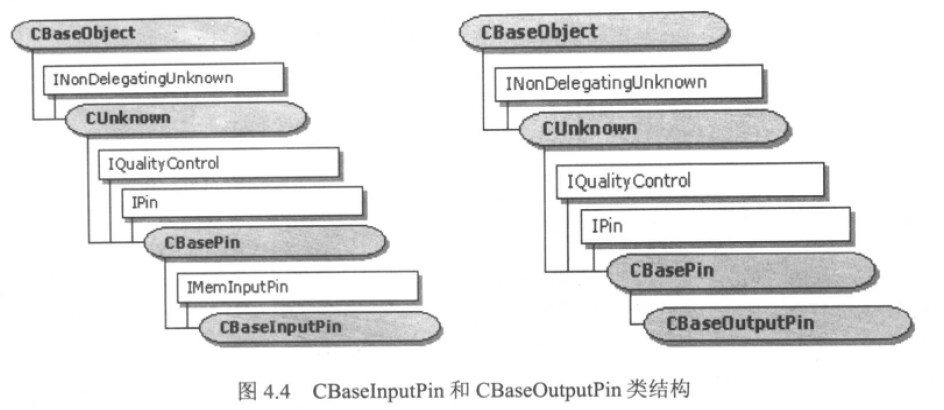
5、 CBaseInputPin和CBaseOutputPin
从CBasePin类派生的,也是很基本的输入或输出pin。
它们的实现可参见 amfilter.cpp
CBaseInputPin实现了IMemInputPin(用于推模式的数据传送),
而CBaseOutputPin主要完成了传送数据所使用的Sample管理器(Allocator)的协商,并重写了CBasePin::Active(用于实际的Sample内存分配)
以及CBasePin::Inactive(用于Sample内存的释放)
- class AM_NOVTABLE CBaseInputPin : public CBasePin,
- public IMemInputPin
- {
- protected:
- IMemAllocator *m_pAllocator; // Default memory allocator
- // allocator is read-only, so received samples
- // cannot be modified (probably only relevant to in-place
- // transforms
- BYTE m_bReadOnly;
- // in flushing state (between BeginFlush and EndFlush)
- // if TRUE, all Receives are returned with S_FALSE
- BYTE m_bFlushing;
- // Sample properties - initalized in Receive
- AM_SAMPLE2_PROPERTIES m_SampleProps;
- public:
- CBaseInputPin(
- TCHAR *pObjectName,
- CBaseFilter *pFilter,
- CCritSec *pLock,
- HRESULT *phr,
- LPCWSTR pName);
- #ifdef UNICODE
- CBaseInputPin(
- CHAR *pObjectName,
- CBaseFilter *pFilter,
- CCritSec *pLock,
- HRESULT *phr,
- LPCWSTR pName);
- #endif
- virtual ~CBaseInputPin();
- DECLARE_IUNKNOWN
- // override this to publicise our interfaces
- STDMETHODIMP NonDelegatingQueryInterface(REFIID riid, void **ppv);
- // return the allocator interface that this input pin
- // would like the output pin to use
- STDMETHODIMP GetAllocator(IMemAllocator ** ppAllocator);
- // tell the input pin which allocator the output pin is actually
- // going to use.
- STDMETHODIMP NotifyAllocator(
- IMemAllocator * pAllocator,
- BOOL bReadOnly);
- // do something with this media sample
- STDMETHODIMP Receive(IMediaSample *pSample);
- // do something with these media samples
- STDMETHODIMP ReceiveMultiple (
- IMediaSample **pSamples,
- long nSamples,
- long *nSamplesProcessed);
- // See if Receive() blocks
- STDMETHODIMP ReceiveCanBlock();
- // Default handling for BeginFlush - call at the beginning
- // of your implementation (makes sure that all Receive calls
- // fail). After calling this, you need to free any queued data
- // and then call downstream.
- STDMETHODIMP BeginFlush(void);
- // default handling for EndFlush - call at end of your implementation
- // - before calling this, ensure that there is no queued data and no thread
- // pushing any more without a further receive, then call downstream,
- // then call this method to clear the m_bFlushing flag and re-enable
- // receives
- STDMETHODIMP EndFlush(void);
- // this method is optional (can return E_NOTIMPL).
- // default implementation returns E_NOTIMPL. Override if you have
- // specific alignment or prefix needs, but could use an upstream
- // allocator
- STDMETHODIMP GetAllocatorRequirements(ALLOCATOR_PROPERTIES*pProps);
- // Release the pin's allocator.
- HRESULT BreakConnect();
- // helper method to check the read-only flag
- BOOL IsReadOnly() {
- return m_bReadOnly;
- };
- // helper method to see if we are flushing
- BOOL IsFlushing() {
- return m_bFlushing;
- };
- // Override this for checking whether it's OK to process samples
- // Also call this from EndOfStream.
- virtual HRESULT CheckStreaming();
- // Pass a Quality notification on to the appropriate sink
- HRESULT PassNotify(Quality& q);
- //================================================================================
- // IQualityControl methods (from CBasePin)
- //================================================================================
- STDMETHODIMP Notify(IBaseFilter * pSender, Quality q);
- // no need to override:
- // STDMETHODIMP SetSink(IQualityControl * piqc);
- // switch the pin to inactive state - may already be inactive
- virtual HRESULT Inactive(void);
- // Return sample properties pointer
- AM_SAMPLE2_PROPERTIES * SampleProps() {
- ASSERT(m_SampleProps.cbData != 0);
- return &m_SampleProps;
- }
- };
- class AM_NOVTABLE CBaseOutputPin : public CBasePin
- {
- protected:
- IMemAllocator *m_pAllocator;
- IMemInputPin *m_pInputPin; // interface on the downstreaminput pin
- // set up in CheckConnect when we connect.
- public:
- CBaseOutputPin(
- TCHAR *pObjectName,
- CBaseFilter *pFilter,
- CCritSec *pLock,
- HRESULT *phr,
- LPCWSTR pName);
- #ifdef UNICODE
- CBaseOutputPin(
- CHAR *pObjectName,
- CBaseFilter *pFilter,
- CCritSec *pLock,
- HRESULT *phr,
- LPCWSTR pName);
- #endif
- // override CompleteConnect() so we can negotiate an allocator
- virtual HRESULT CompleteConnect(IPin *pReceivePin);
- // negotiate the allocator and its buffer size/count and other properties
- // Calls DecideBufferSize to set properties
- virtual HRESULT DecideAllocator(IMemInputPin * pPin, IMemAllocator ** pAlloc);
- // override this to set the buffer size and count. Return an error
- // if the size/count is not to your liking.
- // The allocator properties passed in are those requested by the
- // input pin - use eg the alignment and prefix members if you have
- // no preference on these.
- virtual HRESULT DecideBufferSize(
- IMemAllocator * pAlloc,
- ALLOCATOR_PROPERTIES * ppropInputRequest
- ) PURE;
- // returns an empty sample buffer from the allocator
- virtual HRESULT GetDeliveryBuffer(IMediaSample ** ppSample,
- REFERENCE_TIME * pStartTime,
- REFERENCE_TIME * pEndTime,
- DWORD dwFlags);
- // deliver a filled-in sample to the connected input pin
- // note - you need to release it after calling this. The receiving
- // pin will addref the sample if it needs to hold it beyond the
- // call.
- virtual HRESULT Deliver(IMediaSample *);
- // override this to control the connection
- virtual HRESULT InitAllocator(IMemAllocator **ppAlloc);
- HRESULT CheckConnect(IPin *pPin);
- HRESULT BreakConnect();
- // override to call Commit and Decommit
- HRESULT Active(void);
- HRESULT Inactive(void);
- // we have a default handling of EndOfStream which is to return
- // an error, since this should be called on input pins only
- STDMETHODIMP EndOfStream(void);
- // called from elsewhere in our filter to pass EOS downstream to
- // our connected input pin
- virtual HRESULT DeliverEndOfStream(void);
- // same for Begin/EndFlush - we handle Begin/EndFlush since it
- // is an error on an output pin, and we have Deliver methods to
- // call the methods on the connected pin
- STDMETHODIMP BeginFlush(void);
- STDMETHODIMP EndFlush(void);
- virtual HRESULT DeliverBeginFlush(void);
- virtual HRESULT DeliverEndFlush(void);
- // deliver NewSegment to connected pin - you will need to
- // override this if you queue any data in your output pin.
- virtual HRESULT DeliverNewSegment(
- REFERENCE_TIME tStart,
- REFERENCE_TIME tStop,
- double dRate);
- //================================================================================
- // IQualityControl methods
- //================================================================================
- // All inherited from CBasePin and not overridden here.
- // STDMETHODIMP Notify(IBaseFilter * pSender, Quality q);
- // STDMETHODIMP SetSink(IQualityControl * piqc);
- };
CBaseInputPin类的使用方法(派生一个子类,并且至少需要重写以下函数)如下:
(1) CBaseInputPin::BeginFlush
(2) CBaseInputPin::EndFlush
(3) CBaseInputPin::Receive
(4) CBaseInputPin::CheckMediaType
(5) CBaseInputPin::GetMediaType
eg:
- class CRendererInputPin : public CBaseInputPin
- {
- protected:
- CBaseRenderer *m_pRenderer;
- public:
- CRendererInputPin(CBaseRenderer *pRenderer,
- HRESULT *phr,
- LPCWSTR Name);
- // Overriden from the base pin classes
- HRESULT BreakConnect();
- HRESULT CompleteConnect(IPin *pReceivePin);
- HRESULT SetMediaType(const CMediaType *pmt);
- HRESULT CheckMediaType(const CMediaType *pmt);
- HRESULT Active();
- HRESULT Inactive();
- // Add rendering behaviour to interface functions
- STDMETHODIMP QueryId(LPWSTR *Id);
- STDMETHODIMP EndOfStream();
- STDMETHODIMP BeginFlush();
- STDMETHODIMP EndFlush();
- STDMETHODIMP Receive(IMediaSample *pMediaSample);
- // Helper
- IMemAllocator inline *Allocator() const
- {
- return m_pAllocator;
- }
- };
CBaseOutputPin类的使用方法(派生一个子类,并且最少需要重写以下函数)如下:
(1) 重写CBasePin::CheckMediaType进行连接时媒体类型的检查;
(2) 实现纯虚函数CBaseOutputPin::DecideBufferSize,决定Sample内存的大小;
(3) 重写CBasePin::GetMediaType, 提供Pin 上的首选媒体类型。
- class CTransformOutputPin : public CBaseOutputPin
- {
- friend class CTransformFilter;
- protected:
- CTransformFilter *m_pTransformFilter;
- public:
- // implement IMediaPosition by passing upstream
- IUnknown * m_pPosition;
- CTransformOutputPin(
- TCHAR *pObjectName,
- CTransformFilter *pTransformFilter,
- HRESULT * phr,
- LPCWSTR pName);
- #ifdef UNICODE
- CTransformOutputPin(
- CHAR *pObjectName,
- CTransformFilter *pTransformFilter,
- HRESULT * phr,
- LPCWSTR pName);
- #endif
- ~CTransformOutputPin();
- // override to expose IMediaPosition
- STDMETHODIMP NonDelegatingQueryInterface(REFIID riid, void **ppv);
- // --- CBaseOutputPin ------------
- STDMETHODIMP QueryId(LPWSTR * Id)
- {
- return AMGetWideString(L"Out", Id);
- }
- // Grab and release extra interfaces if required
- HRESULT CheckConnect(IPin *pPin);
- HRESULT BreakConnect();
- HRESULT CompleteConnect(IPin *pReceivePin);
- // check that we can support this output type
- HRESULT CheckMediaType(const CMediaType* mtOut);
- // set the connection media type
- HRESULT SetMediaType(const CMediaType *pmt);
- // called from CBaseOutputPin during connection to ask for
- // the count and size of buffers we need.
- HRESULT DecideBufferSize(
- IMemAllocator * pAlloc,
- ALLOCATOR_PROPERTIES *pProp);
- // returns the preferred formats for a pin
- HRESULT GetMediaType(int iPosition,CMediaType *pMediaType);
- // inherited from IQualityControl via CBasePin
- STDMETHODIMP Notify(IBaseFilter * pSender, Quality q);
- // Media type
- public:
- CMediaType& CurrentMediaType() { return m_mt; };
- };
===================================================================
如果开发的是一个Transform Filter,Filter的父类很多时候都是选择CTransformFilter或CTransInPlaceFilter,这种Filter的开发相对简单。
但有时,Filter框架不得不选择CBaseFilter、 CBaseInputPin、CBaseOutputFilter等类来实现,这就有点麻烦了。
这时候可以参考CTransformFilter、CTransformInputPin、CTransformOutputPin对上述3上基类的使用,以此来指导Filter的开发。
===================================================================
6、 CSource
DirectShow SDK还提供了其他更加实用的Filter类,如:
CSource、CTransformFilter、CTransInPlaceFilter、CVideoTransformFilter、 CBaseRender、CBase Video Render等。
它们的继承关系如图:
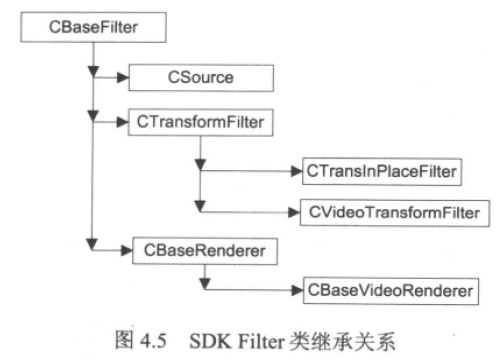
如上图所示,CSource类(参见source.cpp的实现)直接从CaseFilter中继承而来,一般作为推模式Source Filter的父类。
CSource类的使用方法如下:
(1)从CSource类中派生一个新的Filter类;
(2)在新的Filter类的构造函数中创建各个CSourceStream类实例(CSourceStream类的构造函数会自动将该Pin加入Filter中,并在析构函数中自动删除);
(3)使用CSource::pStateLock函数返回的同步对象进行Filter对象上的多线程同步。
注意: 使用CSource作为Filter父类的Filter未必就是Source Filter。在有些开发Transform Filter的应用中,输出Pin需要使用独立的线程。(即与输入Pin上传送数据
不同的线程)传关,也可以考虑使用CSource。
eg: 参照我的另一篇文章:
- class CPushSourceBitmap : public CSource
- {
- private:
- // Constructor is private because you have to use CreateInstance
- CPushSourceBitmap(IUnknown *pUnk, HRESULT *phr);
- ~CPushSourceBitmap();
- CPushPinBitmap *m_pPin;
- public:
- static CUnknown * WINAPI CreateInstance(IUnknown *pUnk, HRESULT *phr);
- };
- CPushSourceBitmap::CPushSourceBitmap(IUnknown *pUnk, HRESULT *phr)
- : CSource(NAME("PushSourceBitmap"), pUnk, CLSID_PushSourceBitmap)
- {
- // The pin magically adds itself to our pin array.
- m_pPin = new CPushPinBitmap(phr, this);
- if (phr)
- {
- if (m_pPin == NULL)
- *phr = E_OUTOFMEMORY;
- else
- *phr = S_OK;
- }
- }
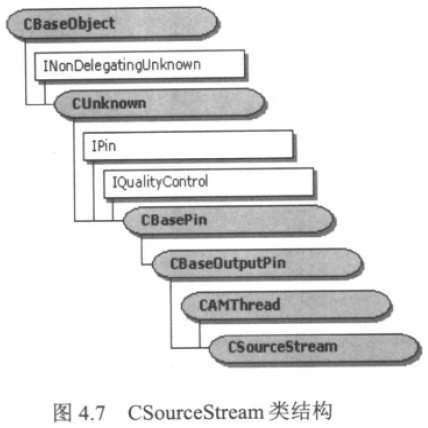
7 、 CSourceStream
CSource实际上继承自CBaseFilter,提供了一个“推”数据的能力,这种Filter至少有一个输出
Pin采用了CSourecStream类(或CSourceStream的子类)。如下图所示:
CSourceStream上实现了一个线程(CSourceStream从CAMThread类继承而来),Sample数据就是靠这个线程向一线Filter发送的。
CSourceStream类的使用方法如下:
(1)从CSourceStream派生一个输出Pin类;
(2)重写CSourceStream::GetMediaType,提供输出Pin上的首选媒体类型;
(3)重写CSourceStream::CheckMediaType,进行连续时媒体类型的检查;(可选)
(4)实现CBaseOutPin::DecideBufferSize,决定Sample内存的大小;
(5)实现CSourceStream::FillBuffer,为即将传送出去的Sample 填充数据;
(6)可选地实现CSourceStream::OnThreadCreate、CSourceSream::OnThreadDestroy、CSourceStream::OnThreadStartPlay等函数,
进行适当时节的初始化、资源管理等操作。
eg: 参照我的另一篇文章:
- class CPushPinBitmap : public CSourceStream
- {
- protected:
- int m_FramesWritten; // To track where we are in the file
- BOOL m_bZeroMemory; // Do we need to clear the buffer?
- CRefTime m_rtSampleTime; // The time stamp for each sample
- BITMAPINFO *m_pBmi; // Pointer to the bitmap header
- DWORD m_cbBitmapInfo; // Size of the bitmap header
- // File opening variables
- HANDLE m_hFile; // Handle returned from CreateFile
- BYTE * m_pFile; // Points to beginning of file buffer
- BYTE * m_pImage; // Points to pixel bits
- int m_iFrameNumber;
- const REFERENCE_TIME m_rtFrameLength;
- CCritSec m_cSharedState; // Protects our internal state
- CImageDisplay m_Display; // Figures out our media type for us
- public:
- CPushPinBitmap(HRESULT *phr, CSource *pFilter);
- ~CPushPinBitmap();
- // Override the version that offers exactly one media type
- HRESULT GetMediaType(CMediaType *pMediaType);
- HRESULT DecideBufferSize(IMemAllocator *pAlloc, ALLOCATOR_PROPERTIES *pRequest);
- HRESULT FillBuffer(IMediaSample *pSample);
- // Quality control
- // Not implemented because we aren't going in real time.
- // If the file-writing filter slows the graph down, we just do nothing, which means
- // wait until we're unblocked. No frames are ever dropped.
- STDMETHODIMP Notify(IBaseFilter *pSelf, Quality q)
- {
- return E_FAIL;
- }
- };
8、 CTransformFilter
CTransformFilter类是开发Transform Filter最基本的类,也是最常用到的类。结构如下:
它有一个输入Pin和一个输出Pin,分别使用CTransformInputPin类和CTransformOutputPin类。

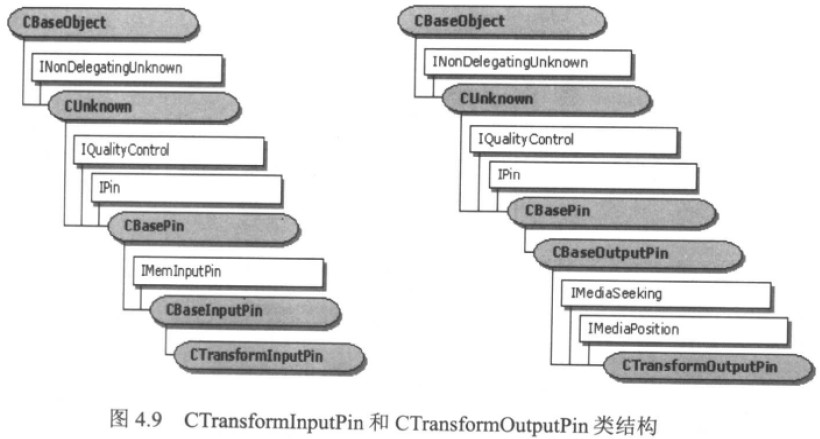
从图4.8和图4.9可以看出,
CTransformFilter从CBaseFilter继承而来,
CTransformInputPin从CBaseInputPin继承而来,
CTransformOutputPin从CBaseOutputPin继承而来。另个,在CTransformOutputPin上还实现了IMdiaSeeking 和 IMediaPosition接口。
(其实,CTransformOutputPin并没有真正实现各个Seek操作。在实际的Seek操作请发生时,CTransformOutpPin会将这些操作请求转发给上一级Filter的输出Pin)。
CTransformFilter实现的最大特征是,它将Pin上必须实现的函数都“委托”到了Filter上(Pin上必须实现的函数在Filter上有类似的函数定义)。
一般无须重写输入和输出Pin类,而只须在Filter上实现相应的函数就行了)。
提示:CTransformFilter默认在GetPin函数实现中创建输入和输出Pin。因此,如果重写了自己的输入或输出Pin类,需要重写GetPin函数。
CTransformFilter类的使用方法(派生一个Filter子类,且最少需要重写以下函数):
(1)CTransformFilter::CheckInputType
(2)CTransformFilter::CheckTransform
(3)CTransformFilter::DecideBufferSize
(4)CTransformFilter::GetMeiaType
(5)CTransformFilter::Transform
eg:CVideoTransformFilter虽然没有实现上面五个函数,但CVideoTransformFilter 的继承类去实现它们。
- class CVideoTransformFilter : public CTransformFilter
- {
- public:
- CVideoTransformFilter(TCHAR *, LPUNKNOWN, REFCLSID clsid);
- ~CVideoTransformFilter();
- HRESULT EndFlush();
- // =================================================================
- // ----- override these bits ---------------------------------------
- // =================================================================
- // The following methods are in CTransformFilter which is inherited.
- // They are mentioned here for completeness
- //
- // These MUST be supplied in a derived class
- //
- // NOTE:
- // virtual HRESULT Transform(IMediaSample * pIn, IMediaSample *pOut);
- // virtual HRESULT CheckInputType(const CMediaType* mtIn) PURE;
- // virtual HRESULT CheckTransform
- // (const CMediaType* mtIn, const CMediaType* mtOut) PURE;
- // static CCOMObject * CreateInstance(LPUNKNOWN, HRESULT *);
- // virtual HRESULT DecideBufferSize
- // (IMemAllocator * pAllocator, ALLOCATOR_PROPERTIES *pprop) PURE;
- // virtual HRESULT GetMediaType(int iPosition, CMediaType *pMediaType) PURE;
- //
- // These MAY also be overridden
- //
- // virtual HRESULT StopStreaming();
- // virtual HRESULT SetMediaType(PIN_DIRECTION direction,const CMediaType *pmt);
- // virtual HRESULT CheckConnect(PIN_DIRECTION dir,IPin *pPin);
- // virtual HRESULT BreakConnect(PIN_DIRECTION dir);
- // virtual HRESULT CompleteConnect(PIN_DIRECTION direction,IPin *pReceivePin);
- // virtual HRESULT EndOfStream(void);
- // virtual HRESULT BeginFlush(void);
- // virtual HRESULT EndFlush(void);
- // virtual HRESULT NewSegment
- // (REFERENCE_TIME tStart,REFERENCE_TIME tStop,double dRate);
- #ifdef PERF
- // If you override this - ensure that you register all these ids
- // as well as any of your own,
- virtual void RegisterPerfId() {
- m_idSkip = MSR_REGISTER(TEXT("Video Transform Skip frame"));
- m_idFrameType = MSR_REGISTER(TEXT("Video transform frame type"));
- m_idLate = MSR_REGISTER(TEXT("Video Transform Lateness"));
- m_idTimeTillKey = MSR_REGISTER(TEXT("Video Transform Estd. time to next key"));
- CTransformFilter::RegisterPerfId();
- }
- #endif
- protected:
- // =========== QUALITY MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION ========================
- // Frames are assumed to come in three types:
- // Type 1: an AVI key frame or an MPEG I frame.
- // This frame can be decoded with no history.
- // Dropping this frame means that no further frame can be decoded
- // until the next type 1 frame.
- // Type 1 frames are sync points.
- // Type 2: an AVI non-key frame or an MPEG P frame.
- // This frame cannot be decoded unless the previous type 1 frame was
- // decoded and all type 2 frames since have been decoded.
- // Dropping this frame means that no further frame can be decoded
- // until the next type 1 frame.
- // Type 3: An MPEG B frame.
- // This frame cannot be decoded unless the previous type 1 or 2 frame
- // has been decoded AND the subsequent type 1 or 2 frame has also
- // been decoded. (This requires decoding the frames out of sequence).
- // Dropping this frame affects no other frames. This implementation
- // does not allow for these. All non-sync-point frames are treated
- // as being type 2.
- //
- // The spacing of frames of type 1 in a file is not guaranteed. There MUST
- // be a type 1 frame at (well, near) the start of the file in order to start
- // decoding at all. After that there could be one every half second or so,
- // there could be one at the start of each scene (aka "cut", "shot") or
- // there could be no more at all.
- // If there is only a single type 1 frame then NO FRAMES CAN BE DROPPED
- // without losing all the rest of the movie. There is no way to tell whether
- // this is the case, so we find that we are in the gambling business.
- // To try to improve the odds, we record the greatest interval between type 1s
- // that we have seen and we bet on things being no worse than this in the
- // future.
- // You can tell if it's a type 1 frame by calling IsSyncPoint().
- // there is no architected way to test for a type 3, so you should override
- // the quality management here if you have B-frames.
- int m_nKeyFramePeriod; // the largest observed interval between type 1 frames
- // 1 means every frame is type 1, 2 means every other.
- int m_nFramesSinceKeyFrame; // Used to count frames since the last type 1.
- // becomes the new m_nKeyFramePeriod if greater.
- BOOL m_bSkipping; // we are skipping to the next type 1 frame
- #ifdef PERF
- int m_idFrameType; // MSR id Frame type. 1=Key, 2="non-key"
- int m_idSkip; // MSR id skipping
- int m_idLate; // MSR id lateness
- int m_idTimeTillKey; // MSR id for guessed time till next key frame.
- #endif
- virtual HRESULT StartStreaming();
- HRESULT AbortPlayback(HRESULT hr); // if something bad happens
- HRESULT Receive(IMediaSample *pSample);
- HRESULT AlterQuality(Quality q);
- BOOL ShouldSkipFrame(IMediaSample * pIn);
- int m_itrLate; // lateness from last Quality message
- // (this overflows at 214 secs late).
- int m_tDecodeStart; // timeGetTime when decode started.
- int m_itrAvgDecode; // Average decode time in reference units.
- BOOL m_bNoSkip; // debug - no skipping.
- // We send an EC_QUALITY_CHANGE notification to the app if we have to degrade.
- // We send one when we start degrading, not one for every frame, this means
- // we track whether we've sent one yet.
- BOOL m_bQualityChanged;
- // When non-zero, don't pass anything to renderer until next keyframe
- // If there are few keys, give up and eventually draw something
- int m_nWaitForKey;
- };
9、 CTransInPlaceFilter
CTransInPlaceFilter是一个“就地”处理的Transform Filter类。结构如下:
与CTransformFilter,CTransInPlaceFilter也有一个输入Pin和一个输出Pin,但使用CTransInPlaceOutputPin类。


CTransInPlaceFilter的输入和输出Pin上一般使用相同的媒体类型进行连接,并且使用同一个Sample管理器(如果Filter实现时要修改Sample数据,
而协商达成一致的Sample管理器只读的,那么CTransInPlaceFilter的输入和输出Pin将不得不使用各自的Sample管理器)。
CTransInPlaceFilter类要实现上述的目标,主要依赖于CTransInPlaceFilter::CompleteConnect、CTransInPlaceInputPin::GetAllocator和
CTransInPlaceInputPin::NotifyAlocator的函数实现。代码如下:
- // 当输入或输出Pin完成连接时被调用,
- // 经过一个反复重连的过程,来达到输入和输出Pin使用相同的媒体类型的目的
- HRESULT CTransInPlaceFilter::CompleteConnect(PIN_DIRECTION dir,IPin *pReceivePin)
- {
- UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(pReceivePin);
- ASSERT(m_pInput);
- ASSERT(m_pOutput);
- // if we are not part of a graph, then don't indirect the pointer
- // this probably prevents use of the filter without a filtergraph
- if (!m_pGraph) {
- return VFW_E_NOT_IN_GRAPH;
- }
- // Always reconnect the input to account for buffering changes
- //
- // Because we don't get to suggest a type on ReceiveConnection
- // we need another way of making sure the right type gets used.
- //
- // One way would be to have our EnumMediaTypes return our output
- // connection type first but more deterministic and simple is to
- // call ReconnectEx passing the type we want to reconnect with
- // via the base class ReconeectPin method.
- // 当输出Pin调用该函数(并且此时输入Pin已连上)时,使用输出Pin上的媒体类型对
- // 输入Pin进行重连接
- if (dir == PINDIR_OUTPUT) {
- if( m_pInput->IsConnected() ) {
- return ReconnectPin( m_pInput, &m_pOutput->CurrentMediaType() );
- }
- return NOERROR;
- }
- ASSERT(dir == PINDIR_INPUT);
- // Reconnect output if necessary
- // 当输入Pin调用该函数(并且此时输出Pin已连上)时,如果输入和输出Pin上使用的
- // 媒体类型不一致,则使用输入Pin上的媒体类型对输出Pin进行重新连接
- if( m_pOutput->IsConnected() ) {
- if ( m_pInput->CurrentMediaType()
- != m_pOutput->CurrentMediaType()
- ) {
- return ReconnectPin( m_pOutput, &m_pInput->CurrentMediaType() );
- }
- }
- return NOERROR;
- } // ComnpleteConnect
- // 当上一级Filter的输出Pin要求我们的输入Pin提供Sample管理器时,
- // 如果我们的输出Pin已连接上,则可以取出输出Pin上的Sample管理器提供给上一级
- // Filter,以此达到我们的输入和输出Pin使用同一个Sample管理器的目的
- STDMETHODIMP CTransInPlaceInputPin::GetAllocator(IMemAllocator ** ppAllocator)
- {
- CheckPointer(ppAllocator,E_POINTER);
- ValidateReadWritePtr(ppAllocator,sizeof(IMemAllocator *));
- CAutoLock cObjectLock(m_pLock);
- HRESULT hr;
- if ( m_pTIPFilter->m_pOutput->IsConnected() ) {
- // Store the allocator we got
- hr = m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->ConnectedIMemInputPin()
- ->GetAllocator( ppAllocator );
- if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->SetAllocator( *ppAllocator );
- }
- }
- else {
- // Help upstream filter (eg TIP filter which is having to do a copy)
- // by providing a temp allocator here - we'll never use
- // this allocator because when our output is connected we'll
- // reconnect this pin
- hr = CTransformInputPin::GetAllocator( ppAllocator );
- }
- return hr;
- } // GetAllocator
- // 上一级Filter调用该函数,告知输入Pin上到底使用哪一个Sample管理器
- // 如果设置进来的Sample管理器是只读的,而我们在Filter中又想修改数据,
- // 则我们的Filter不得不最终使用不同的Sample管理器
- STDMETHODIMP
- CTransInPlaceInputPin::NotifyAllocator(
- IMemAllocator * pAllocator,
- BOOL bReadOnly)
- {
- HRESULT hr = S_OK;
- CheckPointer(pAllocator,E_POINTER);
- ValidateReadPtr(pAllocator,sizeof(IMemAllocator));
- CAutoLock cObjectLock(m_pLock);
- m_bReadOnly = bReadOnly;
- // If we modify data then don't accept the allocator if it's
- // the same as the output pin's allocator
- // If our output is not connected just accept the allocator
- // We're never going to use this allocator because when our
- // output pin is connected we'll reconnect this pin
- if (!m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->IsConnected()) {
- return CTransformInputPin::NotifyAllocator(pAllocator, bReadOnly);
- }
- // If the allocator is read-only and we're modifying data
- // and the allocator is the same as the output pin's
- // then reject
- if (bReadOnly && m_pTIPFilter->m_bModifiesData) {
- IMemAllocator *pOutputAllocator =
- m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->PeekAllocator();
- // Make sure we have an output allocator
- if (pOutputAllocator == NULL) {
- hr = m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->ConnectedIMemInputPin()->
- GetAllocator(&pOutputAllocator);
- if(FAILED(hr)) {
- hr = CreateMemoryAllocator(&pOutputAllocator);
- }
- if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->SetAllocator(pOutputAllocator);
- pOutputAllocator->Release();
- }
- }
- if (pAllocator == pOutputAllocator) {
- hr = E_FAIL;
- } else if(SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- // Must copy so set the allocator properties on the output
- ALLOCATOR_PROPERTIES Props, Actual;
- hr = pAllocator->GetProperties(&Props);
- if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- hr = pOutputAllocator->SetProperties(&Props, &Actual);
- }
- if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- if ( (Props.cBuffers > Actual.cBuffers)
- || (Props.cbBuffer > Actual.cbBuffer)
- || (Props.cbAlign > Actual.cbAlign)
- ) {
- hr = E_FAIL;
- }
- }
- // Set the allocator on the output pin
- if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- hr = m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->ConnectedIMemInputPin()
- ->NotifyAllocator( pOutputAllocator, FALSE );
- }
- }
- } else {
- hr = m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->ConnectedIMemInputPin()
- ->NotifyAllocator( pAllocator, bReadOnly );
- if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- m_pTIPFilter->OutputPin()->SetAllocator( pAllocator );
- }
- }
- if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {
- // It's possible that the old and the new are the same thing.
- // AddRef before release ensures that we don't unload it.
- pAllocator->AddRef();
- if( m_pAllocator != NULL )
- m_pAllocator->Release();
- m_pAllocator = pAllocator; // We have an allocator for the input pin
- }
- return hr;
- } // NotifyAllocator
CTransInPlaceFilter类定义了一个成员变量m_bModifiesData ,用于指示我们在Filter中是否会修改Saple 数据。
这个变量在CTransInPlaceFilter构造函数调用时被默认初始化为true。如果我们确定不会在Filter中修改Sample数据,
那么,将m_bModifiesData设置为false, 可以保证输入和输出Pin连接完成后使用同一个Sample管理器。
10、 CVideoTransformFilter
CVieoTransformFilter是一个实现了视频的质量控制的Transform Filter类。其结构如下:

CVieoTransformFilter通过输入Pin上的Receive 函数接收Sample时,能够根据质量消息决定是否丢帧。这个类主要是为开发AVI解码Filter而设计的。
CVieoTransformFilter类的使用基本上与CTransformFilter相同。
11、 CBaseRenderer
CBaseRender是最基本的实现Renderer Filter的类。它默认实现了一个使用CRendererInputPin类的输入Pin(Renderer Filter没有输出Pin)。
这两个类的结构如下:
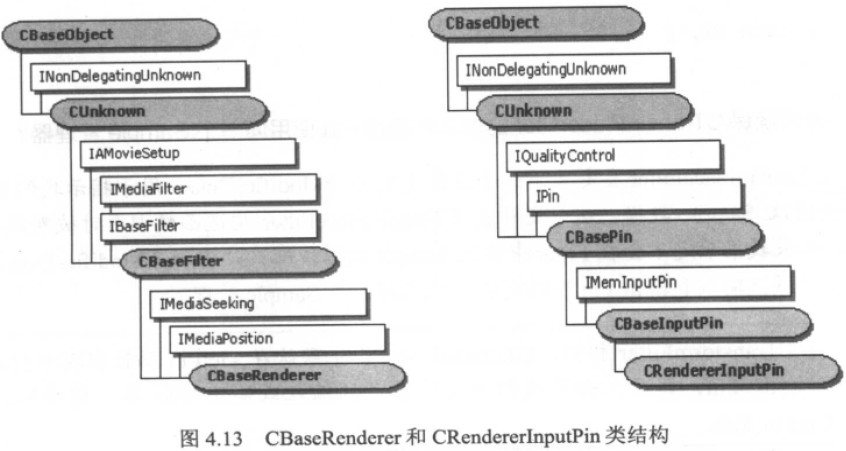
从图中可以看出,CBaseRenderer从CBaseFilter继承而来。另外,CBaseRenderer上还实现了IMediaSeekin和IMediaPosition接口。
CRendererInputPin从CBaseInputPin 继承而来,它把各个主要函数调用都“委托”到Filter上。值得注意的是,当输入Pin接收到EndOfStream调用时,
Renderer Filter 有责任向Filter Graph Manager发送一个EC_COMPLETE事件。
CBaseRenderer类的使用方法(派生一个子类,并至少实现如下函数)如下:
(1)CBaseRenderer::CheckMediaType,用于检查输入Pin连接用的媒体类型;
(2)CBaseRenderer::DoRenderSample,处理当前的Sample。
提示:CBaseRenderer实际上是为了用于播放的Render Filter设计的,对于Sample的安排比较复杂。
如果我们要开发Renderer Filter不播放Sample(比如写文件的Filter、或者负责网络的Filter),Fitler的基类可以选择CBaseFilter,而此时输入Pin最
好选择CRenderedInputPin类派生。
12、CBaseVideoRenderer
CBaseVideoRenderer是一个实现Video Renderer类的基类,结构如下:
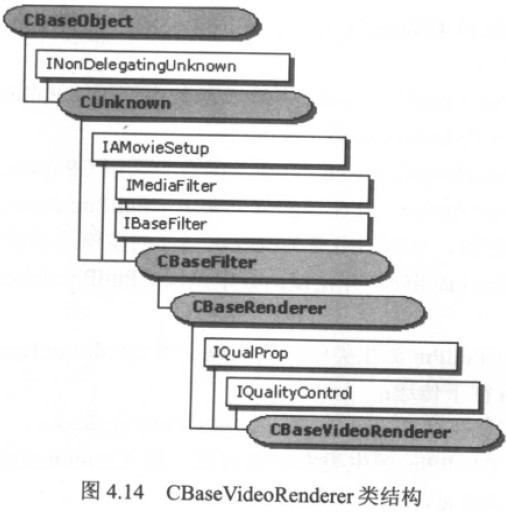
CBaseVideoRenderer在CBaseRenderer的基础上增加了IQualityControl和IQualProp接口的实现。
其中IQualityControl用于视频质量控制,IQualProp用于在Filter属性页显示一些实时性能参数。CBaseVideoRenderer类的使用方法基本上与CBaseRenderer相同。
在DirectShow SDK基类库中,除了上述Filter和Pin类外,还有很多工具类,有了这些类的支持,我们开发Fitler或DirectShow应用程序会更加轻松。
这些类包括: CPullPin、 COutputQueue、 CSourceSeeking 、CEnumPins、 CEnumMediaTypes 、CMemAllocator 、 CMediaSample 、
CBaseReferenceClock 、CMediaType、 CBasePropertyPage 等。
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。