使用Angularjs和Vue.js对比
首先需要说明的是:现在默认angularjs指angular1.0+版本,angular默认指2.0以上版本。本文的名词也默认指定angular的1.0+版本。
先让我们看一下 这两个框架的设计上的一些不同。
Angularjs
- 1,MVC框架
- 2,模块化(Module)控制器(Contoller)依赖注入:这种模块话的注入,其实在代码层面上显得并不够整洁,比如我任何一个控制器controller 里面其实要注入很多的服务。
- 3,双向数据绑定:界面的操作能实时反映到数据,数据的变更能实时展现到界面。
- 4,指令(ng-click ng-bind ng-model ng-href ng-src ng-if/ng-show...),可以自定义指令Directive,比jQuery插件要灵活,但是需要深入了解Directive的一些特性,简单的封装容易,复杂一点官方没有提供详细的介绍文档,我们可以通过阅读源代码来找到某些我们需要的东西,如:在directive使用 $parse;
- 5,服务Service($compile $filter $interval $timeout $http...)
- 6,路由(ng-Route原生路由),ui-router(路由组件)
- 7,Ajax封装($http)
- 8,使用于一些增删改查的管理系统开发。
缺点:
1:其中双向数据绑定的实现使用了$scope变量的脏值检测,使用$scope.$watch(视图到模型),$scope.$apply(模型到视图)检测,内部调用的都是digest,当然也可以直接调用$scope.$digest进行脏检查。值得注意的是当数据变化十分频繁时,脏检测对浏览器性能的消耗将会很大,官方注明的最大检测脏值为2000个数据。
2:ngView只能有一个,不能嵌套多个视图,虽然有 angular-router解决,但是貌似ui-router 对于URL的控制不是很灵活,必须是嵌套式的。
3:ng提倡在控制器里面不要有操作DOM的代码,对于一些jQuery 插件的使用,如果想不破坏代码的整洁性,需要写一些directive去封装插件。但其实我们在tms里,控制器对dom的操作还是有不少的,其实按理说 这些操作应该被封装为指令去进行。
4:Angular 太笨重了,没有让用户选择一个轻量级的版本,当然1.2.X后,Angular也在做一些更改,比如把route,animate等模块独立出去,让用户自己去选择。像animate 这个是一个动画的插件,我们在tms里用的还是比较少的。
Vue
vue.js官网:是一套构建用户界面的 渐进式框架。与其他重量级框架不同的是,Vue 采用自底向上增量开发的设计。Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,并且非常容易学习,非常容易与其它库或已有项目整合。另一方面,Vue 完全有能力驱动采用单文件组件和 Vue 生态系统支持的库开发的复杂单页应用。
Vue.js 的目标是通过尽可能简单的 API 实现响应的数据绑定和组合的视图组件。
- (1)模块化,目前最热的方式是在项目中直接使用ES6的模块化,结合Webpack进行项目打包
- (2)组件化,创造单个component后缀为.vue的文件,包含template(html代码),script(es6代码),style(css样式)
- (3)双向数据绑定:界面的操作能实时反映到数据,数据的变更能实时展现到界面。
- (4)指令(v-html v-bind v-model v-if/v-show...)
- (5)路由(vue-router)
- (6)vuex 数据共享
- (7)Ajax插件(vue-resource,axios)
vue非常小巧,压缩后min源码为72.9kb,gzip压缩后只有25.11kb,想比Angular为144kb,可以自驾搭配使用需要的库插件,类似路由插件(Vue-router),Ajax插件(vue-resource,axios)等
模块引入的对比:
//比如:angularjs 举一个service服务的栗子 (function() { ydCreditApp.factory('myCarService', function($resource, configuration, $http) { // 其实能够在这里看到,$resource 等的依赖注入了。 var myCarList=$resource(configuration.apiBaseUrl+'/api/tms/car/listCars',{ },{ get:{ method:'GET' } }); var carDetail=$resource(configuration.apiBaseUrl+'/api/tms/car/getCar',{ },{ get:{ method:'GET' } }); return { myCarList:myCarList, carDetail:carDetail }) })() // 在这个栗子中,我们启用了一个名为myCarService的服务。然后在需要的地方,比如myCarCtr.js文件里,即控制器里,调用这个myCarService模块时: (function() { ydCreditApp.controller('myCarController', function($scope,myCarService) { myCarService.myCarList.get({ params },function(data) { console.log(data) // 后台返回的数据 } } }); // vue 比如我想把vue里的一个组件 或者说某个单独的js文件里的一些信息给输出,想在别的地方调用 。举一个api文件栗子 文件位置是:api/index.js export default { //报销主体 getCompany(params) { return fetchGet('/api/oa/reimburse/getAllCompanyName', params) }, //用户登录 Login(params) { return fetchPost('/api/oa/login', params) }, ... } // 在想引入的文件里这样写 import API from 'api文件的路径' // 这样在欲使用这个api文件里 就可以使用 API.getCompany() API.Login() 等方法
当然 至于 export与import的写法并不止这一个,可以在需要的时候,看看其他文件 比如 mian.js文件 ,或者是router下的indexjs文件,项目里很多文件也都会有这种写法 能够看懂 并且将想要的模块引入即可。
另外:对于前端模块化的解释 是这样的:
前端模块化其实就是将一个完整的单一的功能整合起来形成单独的一个功能组件,当需要用的的时候只需要加载这个组件,然后便可以通过该组件唯一的名称去使用其中的内容。 像我们的angularjs里的myCarService myCarCtr 其实都是一个模块。vue里的那个Api/index.js 也是一个模块。其实关于前端模块化 还有几个模块化框架的 比如:commomJs AMD CMD ES6规范。像刚才介绍的angularjs的那种 包含 依赖 回调 特征的 采用的是异步模块定义 (AMD) 像我们的vue 采用的就是现在最新的ES6模块化。
Vue与 Angular 双向数据绑定原理
angular.js :脏值检查
angular.js 是通过脏值检测的方式比对数据是否有变更,来决定是否更新视图,我们知道,更新页面最简单的方法莫过于设置一个定时器,规定多久时间之后去进行更新页面,angularjs作为一个google开发的框架,肯定也不会这样做,angular实现双向绑定,是在一些特定的事件触发下进行的,比如
- DOM事件,譬如用户输入文本,点击按钮等。( ng-click )
- XHR响应事件 ( $http )
- 浏览器Location变更事件 ( $location )
- Timer事件( $timeout , $interval )
- 执行 $digest() 或 $apply()
vue :数据劫持
vue.js 则是采用数据劫持结合发布者-订阅者模式的方式,通过Object.defineProperty()来劫持各个属性的setter,getter,在数据变动时发布消息给订阅者,触发相应的监听回调。
写法上的一些比较
首先当然是Hello World了
1:数据的绑定
在数据的绑定层面 都可以使用 {{ }} 这个特殊的字符来代表某个要被绑定的数据 这个像jsp里的 ${ messgae }
vue
<div id="app"> {{ message }} </div> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: 'Hello Vue.js!' } })
Angularjs
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl"> {{message}} </div> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); // 在我们的tms里 这个app 就是 我们的 ydapp app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) { $scope.message = "Hello world"; });
相比较来看,vue采用了json的数据格式进行dom和data的编写,编写风格更加靠进js的数据编码格式,通俗易懂。
2:数据的双向绑定
二者在实现的原理上是有差距的,刚才也已经介绍
vue的双向数据绑定
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<input v-model="message">
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue.js!'
}
})
Angularjs的双向数据绑定
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
<p>{{message}}</p>
<input ng-model="message">
</div>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.message = "Hello world!";
});
在双向绑定这一个层面上,其实也是差不多的,只是,angularjs需要引入一个$scope 作用域,所有的数据都绑定在$scope这一个特殊的符号上。
3:事件绑定方面
我们知道 在angular里,官方提供的指令的形式都是形如 ng-事件的形式,但vue里,支持一些简写的方式
angularjs
<a ng-click = 'greet(param) '></a>
vue:
<a v-on: click="fn"></a> 简写方式: <a @click="fn"></a>
不过在vue里,我们需要知道一个vue的周期函数 ,比如这个方法greet要被写在一个名为methods的实例属性。就像上面的data属性写法一样。
<div id="example-2">
<!-- `greet` 是在下面定义的方法名 -->
<button v-on:click="greet">Greet</button>
</div>
//example2 就是一个实例
var example2 = new Vue({ el: '#example-2', data: { name: 'Vue.js' }, // 在 `methods` 对象中定义方法 methods: { greet: function (event) { // `this` 在方法里指向当前 Vue 实例 alert('Hello ' + this.name + '!') // `event` 是原生 DOM 事件 if (event) { alert(event.target.tagName) } } } }) // 也可以用 JavaScript 直接调用方法 example2.greet() // => 'Hello Vue.js!
当然 vue里面还有其他很多的简写方式,但是基本上也能像angularjs里面的一样 , 将 ng- 改为 v- 也就行了。
自定义指令:
angularjs
angular.module('app', []).directive('myDirective', function() {
return {
restrict:String,
priority:Number,
terminal:Boolean,
template:String or Template Function,
templateUrl:String or Template Function,
replace:Boolean or String,
transclude:Boolean,
scope:Boolean or Object,
controller:String or function(scope, element, attrs, transclude, otherInjectables) { ... },
controllerAs:String,
require:String,
link: function(scope, iElement, iAttrs) {
//进行一些时间的绑定渲染等
},
compile:function(tElement, tAttrs, transclude) {
return {
pre: function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller) { ... },
post: function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller) { ... }
}
return function postLink(...) { ... }
}
};
vuejs
// 注册一个全局自定义指令 `v-focus` Vue.directive('focus', { // 当被绑定的元素插入到 DOM 中时…… inserted: function (el) { // 事件 } })
4:渲染列表的写法
vue.渲染列表
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="name in names">
{{ name.first }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
names: [
{ first: 'summer', last: '7310' },
{ first: 'David', last:'666' },
{ first: 'Json', last:'888' }
]
}
})
Angularjs渲染列表
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
<li ng-repeat="name in names">{{name.first}}</li>
</div>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.names = [
{ first: 'summer', last: '7310' },
{ first: 'David', last:'666' },
{ first: 'Json', last:'888' }
]
});
看的出来 其实也是没有多大的区别的
5:循环写法
vue的循环
<ul>
<li v-for="item in list">
<a :href="item.url">{{item.title}}</a>
</li>
</ul>
angularjs循环
<div class="item" ng-repeat="item in list">
<a ng-href="{{item.url}}">{{news.title}}</a>
</div>
vue和Angular处理用户输入
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="reverseMessage">Reverse Message</button>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue.js!'
},
methods: {
reverseMessage: function () {
this.message = this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
})
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button ng-click="reverseMessage()">Reverse Message</button>
</div>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.message = "Hello world!";
$scope.reverseMessage = function() {
this.message = this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
});
以上也基本上是一些写法上的比较。
6:路由
angularjs
angularjs自带的路由是ngRouter 但是这个路由不能完成多视图 与 嵌套视图 。原因是在于,ngRouter的每个视图 不能有唯一的标志,当视图发生变化时,所有的视图都会变为一样的视图。
后来有了ui.router 帮助来完成这些功能。
多视图:页面可以显示多个动态变化的不同区块。
<div ui-view></div> <div ui-view="main"></div> $stateProvider .state('home', { url: '/', views: { '': { templateUrl: 'views/home' }, 'main': { template: 'views/main' } }
嵌套视图:在main视图里,继续添加其他的视图,该视图是一个独立的区域。
<div ui-view></div> <div ui-view="main"> 我是父视图 <div ui-view='home'></home> </div> $stateProvider .state('main', { abstract: true, url: '/main', templateUrl: 'views/main.html' }) .state('main.home', { url: '/home', templateUrl: 'views/home.html' });
传参:
.state('main.myWork', {
url: '/myWork/:page/:mobile/:name/:sendCity/:arriveCity',
params: { page: null, mobile: null,name:null,arriveCity:null,sendCity:null},
templateUrl: 'views/myWork/myWorkList.html',
controller: 'myWorkController',
ncyBreadcrumb: {
label: '审批待办',
parent: 'main'
},
data: {
requiredLogin: true
}
})
在ui.router里面,通过 parent.child 确定父子视图的关系。
vue
vue所提倡的官方路由是:vue-route,也可以自己选择自己的路由。
首先来看这个图片,这个图片 包括了 三个同级的视图。在内容部分 也有三个视图组件被引入。可以说 是体现出了vue的视图的嵌套与多视图的特性。
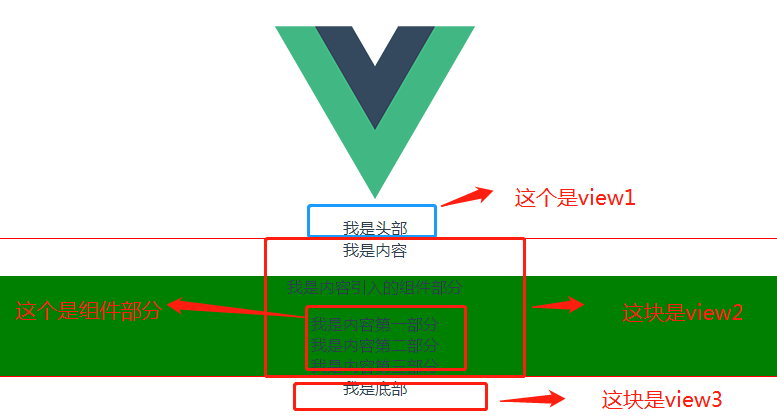
多视图:

<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<router-view class="view two" name="a"></router-view>
<router-view class="view one"></router-view>
<router-view class="view three" name="b"></router-view>
</div>
</template>

import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' const Data = () => import('../components/Data.vue') const Bar = { template: '<div>子路由<router-view /></div>' }; const car = { template: '<div>孙子路由</div>' }; const d = { template: '<div>我是头部</div>' }; const f = { template: '<div>我是底部</div>' }; Vue.use(Router) export default new Router({ routes: [ { path: '/', name:'首页', components: { default: HelloWorld, a:d, b:f } } ,{ path:'/content', name:'数据', component:Data, children:[{ path:'h', component:Bar }] } ] })

<template> <div class="hello" style="border:1px solid red"> 我是内容 <div style="background-color: green"> <p>我是内容引入的组件部分</p> <head-top></head-top> <content-view></content-view> <footer-view></footer-view> </div> </div> </template> <script> import headTop from './headTop' import footerView from './footer' import contentView from './content.vue' export default { name: 'HelloWorld', data () { return { msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App' } }, components:{ headTop, contentView, footerView } } </script> <!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only --> <style scoped> h1, h2 { font-weight: normal; } ul { list-style-type: none; padding: 0; } li { display: inline-block; margin: 0 10px; } a { color: #42b983; } </style>
路由的嵌套
一般来说
就拿上面的代码来说 ,其中的name属性是路由的名称,path:‘h’ 指定的是路由地址 /content/h component 就是你注册引入的组件模块

7:与服务器的通信
angularjs
angularjs提供了对ajax请求的封装 $http 服务 当然 这个params可以传递的参数有很多,可以根据需要去定义一些传值。
比如:
<script> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.controller('siteCtrl', function($scope, $http) { $http.get("http://www.runoob.com/try/angularjs/data/sites.php",{params}) .then(function (response) {$scope.names = response.data.sites;}); }); </script>
我们在tms里,大多数使用的是$resource服务,这个是引入的一个模块
<script type="text/javascript" src="/javascripts/angular-resource.js">
我们在现在的tms实际的打包时,也经常会由于这个包拉不下来 导致打包失败,这个我们也已经有了优化的方案。这里也不再细说。
下面时$resource在tms系统里使用的一个栗子
var myCarList=$resource(configuration.apiBaseUrl+'/api/tms/car/listCars',{
params },{ get:{ method:'GET' } });
vue
vue跟服务端的通信 有 vue-resource插件,但是在vue2.0之后 就不再维护这个插件,官方也推荐使用axios。一款基于promise(‘承诺于未来发生’的一个对象)的http请求客户端,可同时在浏览器和nodejs中使用。
同样 我们也需要引入这个插件模块。
// 安装 axios $ npm install axios // 在要使用的文件中引入axios import axios from 'axios'
看一下axios的写法把 一个基于promise的新写法:
axios.get('/user', {
// params也可以不要的
params: {
ID: 12345
}
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
当然 对应的还有post请求 都是类似的写法。
vuex 是vue的一个状态管理工具
为什么vue 需要一个这样的工具
这个工具怎么使用
待续...
