1.数据库简单介绍
1.1.数据库
概念:存储数据,以文件的形式存储
好处:
- 永久保存数据(理论上)
- 数据共享
- 可以通过命令进行数据的精准查找
1.2.数据库分类
1.关系型数据
mysql、 oracle、 sql server db2 ....
特点:以表格形式进行数据库存储
2.非关系型数据(NOSQL数据库)
MongoDB 、redis
2.mysql数据库操作
1.连接数据
mysql -uroot -p 回车
输入密码 ******
2.数据库的操作
1.创建
create database 库名;
2.进库
use 库名;
3.删库
drop database ku;
4.显示当前用户下所有的数据库
show databases;
3.mysql数据库中数据的类型:
1)整数类型的储存和范围

2)日期和时间类型:

3)字符串型:
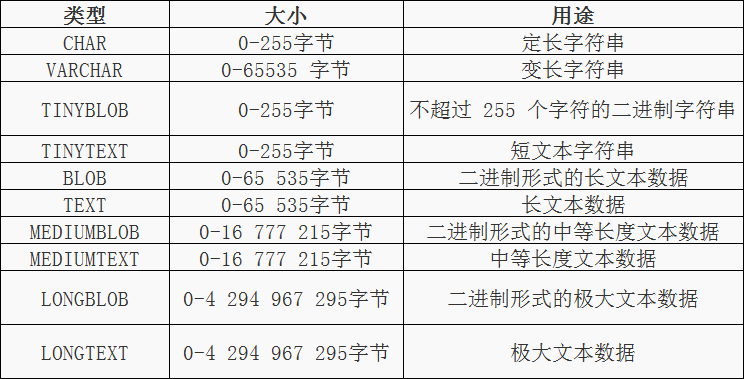
2.1. 表操作
1.创建
create table 表名(
字段名 类型(长度) 是否为空 是否为主键
);
create table city( #设置主键并自增 id int(11) primary key auto_increment, #设置变长字符串,并设置不能为空 title varchar(32) not null, #时间设置 date1 timestamp not null default '0000-00-00 00:00:00'on update current_timestamp, date2 date default null, date3 datetime default null, time1 time default null, #text设置 #text:与char和varchar不同的是,text不可以有默认值,其最大长度是2的16次方-1 #TINYTEXT: 256 bytes #TEXT: 65,535 bytes => ~64kb #MEDIUMTEXT: 16,777,215 bytes => ~16MB #LONGTEXT: 4,294,967,295 bytes => ~4GB content text not null );
2. 删除表
drop table 表名;
3.修改表的字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名称 类型(长度) 约束条件;
alter table 表名 drop 字段名称;
alter table 表名 change 旧字段 新字段 类型(长度) 约束条件;
4.查看表
desc 表名;
2.2.表中数据的操作
1 新增
insert into 表名 values(要求:字段的位置与个数必须一一对应)
insert into 表名(表字段名称,多个以“,”间隔)values(字段值多个以“,”间隔)
insert into 表名2 (select * from 表名)
2 修改
update 表名 set 字段名=‘值’ where 字段名=‘条件值’
update 表名 set 字段1 =‘值1’,字段2=‘值2’ where 字段1="条件1" and 字段2=‘条件2’
3 删除
delete from 表名 where 条件1 =‘值1’
delete from 表名;
4 清空表
truncate 表名;
5查询(核心)
1).查询所有
select * from 表名;
select :表示查询
* :表示所有(通配符)
from :表示从哪个表进行查询
注意:最好把“*”换成具体字段
2).查询某两个字段
select 字段1,字段2 from 表名
3). 根据条件查询
select * from 表 where 字段1 =‘值1’
where :表示条件,跟在where后面的统统称之为条件
4). 多条件查询
select * from 表名 where 字段1=‘值1’ and/or 字段2=‘值2’ and/or 字段3=‘值3’
注意: and 表示并且
or 表示 或者
5). 逻辑运算符查询
select * from 表 where 字段1 != 值1 and z2 >=v2
逻辑运算符: = ,<,>,!=,<>,<=,>=
6).模糊查询
select * from 表名 where 字段 like '%羊蝎子'
like :表示模糊查询
以什么开头: "s%"
以什么结尾:'%s'
包含: '%s%'
7 ).集合查询
select * from 表名 where 字段 in('值1','值2','值3')
in :表示 集合
not in:表示反向集合
8).区间查询
select * from 表 where 字段 between z1 and z2;
注意: between ... and ... 表示区间查询
9).排序
select * from 表 order by 字段 asc
注意:order by 表示排序
正序: ASC 默认
倒序: DESC
10).嵌套查询
select * from 表 where 字段 in(select 字段 from 表 where id=“值1”)
注意:()优先执行
总结: 遇到"="值唯一, 遇到in值为集合
3.sql语法进阶
在数据库操作中,单张表的增删改查,也有多表联查,以及聚合及分组等多种情况,以下是常用到的语法及函数:
聚合函数:
最大 max()
最小 min()
平均 avg()
求和 sum()
总个数 count()
分组函数 : group by having
排序 order BY ASC desc
去重复 :distinct
分页: limit 参数1:从第几条开始,起始位置为0,参数2:显示的条数
多表联合查询 (笛卡尔乘积)
左连接查询 :A left join B on 条件 left join C on 条件
右连接查询 : right join
内连接查询 : inner join
1.总结(执行顺序)
第1步.where ...
第2步.group by ...
第3步.select ...聚合函数 from ...
第4步.having ...
第5步.order by ...
第6步.limit ...
2.order by
1.作用:给查询的结果进行排序
2.排序方式
1.ASC(默认) : 升序
2.DESC : 降序