实现JDBC简单封装
JDBCUtil类可以较方便地执行常用的DQL、DML、DLL语句。
package base.jdbc.util;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @author QX
* JDBC简易封装类
*/
public class JDBCUtil {
private String[] queryFields = null; // 所有的字段
private Connection connection = null; // 数据库连接对象
private static String url = null;
private static String user = null;
private static String password = null;
/**
*
* @param queryFields 设置待查询的字段
*/
public void setQueryFields(String[] queryFields) {
this.queryFields = queryFields;
}
static {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\db.properties"));
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
JDBCUtil(String[] queryFields) throws SQLException {
this.queryFields = queryFields;
this.connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
}
private PreparedStatement getPreStatement(String sql, Object... params) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sql.length(); i++) {
if (sql.charAt(i) == '?') {
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt != params.length || params.length > this.queryFields.length) {
return null;
}
PreparedStatement preStatement = null; // 预编译sql执行对象
try {
preStatement = this.connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
preStatement.setObject(i, params[i - 1]);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return preStatement;
}
/**
*
* @param sql 待执行的sql语句
* @param params ?对应的参数
* @return 更新数据的总数
* @throws SQLException SQL执行异常
*/
public int update(String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement preStatement = getPreStatement(sql, params);
assert preStatement != null;
int ret = preStatement.executeUpdate();
release(preStatement, null);
return ret;
}
/**
*
* @param sql 待执行的sql语句
* @param params ?对应的参数
* @return 查询的结果
* @throws SQLException SQL执行异常
*/
public LinkedList<HashMap<String, Object>> query(String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement preStatement = getPreStatement(sql, params);
assert preStatement != null;
ResultSet resultSet = preStatement.executeQuery();
LinkedList<HashMap<String, Object>> allRecords = new LinkedList<>();
// LinkedHashMap为有序集合,可以保证记录的顺序,与数据库的显示一致
while (resultSet.next()) {
HashMap<String, Object> oneRecordMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // 一条记录
for (String field : this.queryFields) {
Object value = resultSet.getObject(field);
oneRecordMap.put(field, value);
}
allRecords.add(oneRecordMap);
}
release(preStatement, resultSet);
return allRecords;
}
/**
* 开启事务
*/
public void setAutoCommit(boolean isAuto){
try{
if(connection != null && !connection.isClosed()){
connection.setAutoCommit(isAuto);
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 提交
*/
public void commit(){
try{
if(connection != null && !connection.isClosed()){
connection.commit();
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 回滚
*/
public void rollback(){
try{
if(connection != null && !connection.isClosed()){
connection.rollback();
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
private void release(PreparedStatement pre, ResultSet res){
try{
if(pre != null){
pre.close();
}
if(res != null){
res.close();
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*/
public void close() {
try {
if (connection != null && !connection.isClosed()) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这里为什么要用PreparedStatement,而不是Statement,有两个原因:
-
提高性能
- 它可以使用占位符?,是预编译的,批处理比Statement效率高
-
可防止SQL注入攻击
- 所谓SQL注入即是指web应用程序对用户输入数据的合法性没有判断或过滤不严,攻击者可以在web应用程序中事先定义好的查询语句的结尾上添加额外的SQL语句,在管理员不知情的情况下实现非法操作,以此来实现欺骗数据库服务器执行非授权的任意查询,从而进一步得到相应的数据信息。例如登录时执行这样一条sql语句:
select * from t_login where username='xx' and password='xx' or 1=1,无论用户名和密码是什么,后面的1=1始终成立,从而获取所有用户的账号密码
- 所谓SQL注入即是指web应用程序对用户输入数据的合法性没有判断或过滤不严,攻击者可以在web应用程序中事先定义好的查询语句的结尾上添加额外的SQL语句,在管理员不知情的情况下实现非法操作,以此来实现欺骗数据库服务器执行非授权的任意查询,从而进一步得到相应的数据信息。例如登录时执行这样一条sql语句:
测试类
package base.jdbc.util;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class UtilTest {
@Test
public void queryTest() {
JDBCUtil demo = null;
try {
demo = new JDBCUtil(new String[]{"id", "name", "age", "sex", "money", "dpt_id", "phone", "update_time"});
demo.setAutoCommit(false);
demo.setQueryFields(new String[]{"id", "name", "age", "sex", "money", "dpt_id"}); // 设置要查询的字段
String sql = "select * from user where id < ? and sex = ?";
LinkedList<HashMap<String, Object>> result = demo.query(sql, 7, "男");
for (var oneRecordMap : result) {
System.out.println(oneRecordMap);
}
demo.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
demo.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
demo.close();
}
}
@Test
public void updateTest() {
JDBCUtil demo = null;
try {
demo = new JDBCUtil(new String[]{"id", "name", "age", "sex", "money", "dpt_id", "phone", "update_time"});
demo.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "update user set dpt_id = ?, money = ?";
System.out.println(demo.update(sql, 2, 50.8));
demo.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
demo.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
demo.close();
}
}
}
原数据库表为
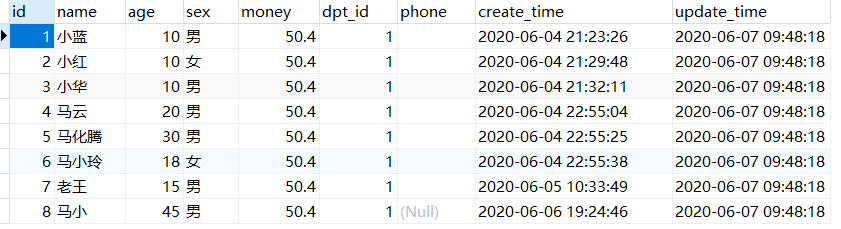 查询结果为:
查询结果为:
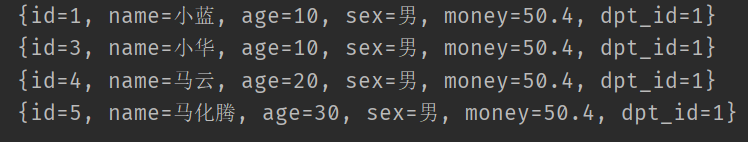
更新结果为:
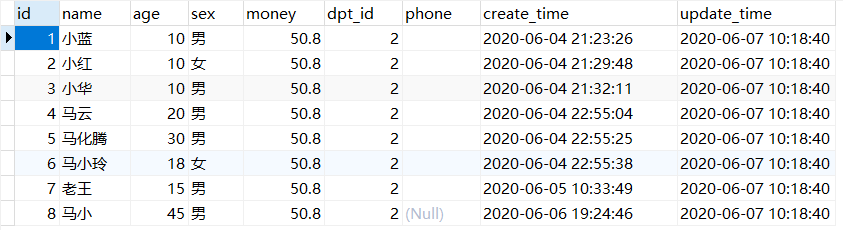
money、dpt_id字段已更新。
该类的缺点是,调用close()后,系统将回收数据库连接对象的资源,频繁地申请连接对象,将消耗资源,执行效率不高,于是便有了数据库连接池,所谓连接池,就是提前申请了多个连接池对象资源,将它们放入某个容器中,当需要时,从容器中拿出供使用,使用完后,调用封装好的close(),并不会将资源归还系统,而是再将它放回容器中(非常类似于多线程池)。使用较广泛数据库连接池的有c3p0、druid(阿里开发),druid相对于c3p0使用更简单,效率更高。