linux内核版本:4.14.2
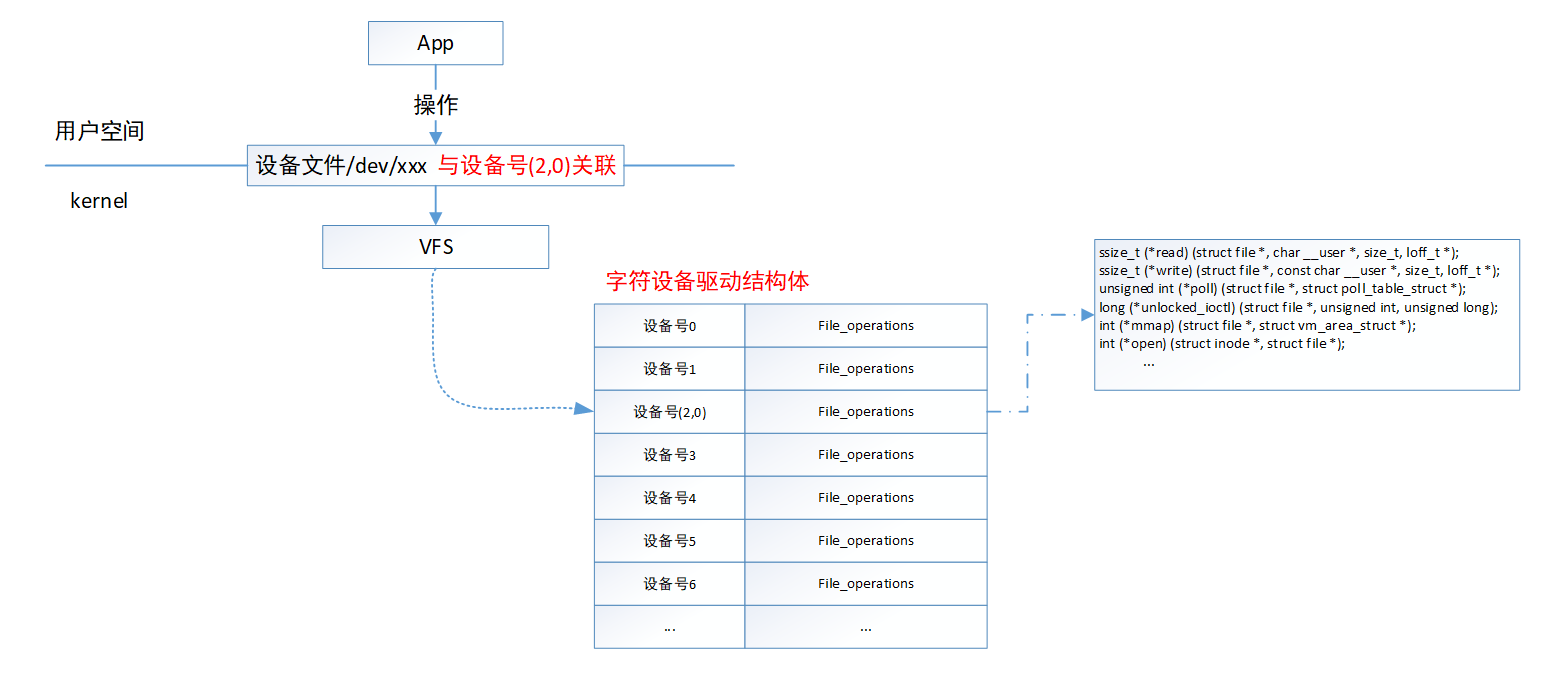
内核把所有的字符设备驱动放在一个长度为255的数组中统一管理。每一个数组元素标识一个字符设备驱动,数组元素主要包含两个内容:设备号(包括主设备号和次设备号)和file_operations结构体。数组下标直接对应主设备号,因此,主设备号相同的字符设备驱动只能有255个;file_operations结构体是文件标准操作集,包括open、read、write、ioctl等基本文件操作。
字符设备在注册时,会将设备号和file_operations结构体绑定;在创建设备文件时会将设备文件和设备号绑定;应用程序操作设备文件时,VFS会通过设备号将对设备文件的操作映射到file_operations对应的操作;因此,设备驱动程序中只要在file_operations相关操作函数中对硬件操作,那么用户空间的app通过设备文件就能调用file_operations结构体提供的操作间接地对设备进行操作。
如上所述,编写一个字符设备驱动需要完成如下工作:
1)申请设备号;
2)定义一个file_operations结构体,并填充结构体,包括对硬件的相关操作;
3)将设备号和file_operations结构体绑定并注册到kernel;
4)用设备号创建设备文件。
编写字符设备驱动有两种接口:
一种接口是使用register_chrdev函数,这个函数直接完成设备号申请、file_operations结构体的绑定以及注册到kernel中;
另一种接口将设备号申请、file_operrations结构体绑定以及注册步骤分开,其中,设备号申请用register_chrdev_region(静态申请)/ alloc_chrdev_region(动态申请)函数,file_operrations结构体绑定以及注册用cdev_alloc、cdev_init、cdev_add函数完成;
其实,两种接口内部调用的函数都是一样的,第二种接口只是将第一种接口函数内部的函数拆分开来实现,如下是两种接口内部的函数调用
|
老接口分析 register_chrdev -->只能指定主设备号,不能指定次设备号 __register_chrdev __register_chrdev_region -->注册主次设备号 cdev_alloc -->kobject_init cdev->owner = fops->owner; cdev->ops = fops; cdev_add -->kobj_map kobject_get |
|
新接口分析 register_chrdev_region __register_chrdev_region
alloc_chrdev_region __register_chrdev_region *dev = MKDEV(cd->major, cd->baseminor) |
两种接口创建设备文件的方法都是一样的,有两种方法创建设备文件:
1)在shell中直接用命令行创建
mknod /dev/xxx c 主设备号 次设备号
2)在驱动程序用class_create、device_create函数创建,这种方法中,先用class_create创建一个设备类,然后调用device_create使用设备号基于这个设备类创建设备文件。设备文件最后是由应用程序udev(嵌入式中用的是mdev)来创建的,驱动程序调用class_create、device_create函数会通过netlink向udev传递消息(设备号和设备文件名),udev收到消息后会创建设备文件。
class_create、device_create函数内部调用如下:
|
class_create __class_create struct class *cls; __class_register kset_register kobject_uevent -->向udev发送一个事件 |
|
device_create device_create_vargs device_create_groups_vargs struct device *dev = NULL; /* device_initialize和device_add完成设备注册 */ device_initialize lockdep_set_novalidate_class device_pm_init device_add kobject_add -->将设备添加 /* 操作sysfs的函数 */ /* */ device_create_file sysfs_create_file device_add_class_symlinks /* 创建符号链接 subsystem -> ../../../../class/lzt_class */ sysfs_create_link(&dev->kobj, &dev->class->p->subsys.kobj, "subsystem"); device_add_attrs bus_add_device dpm_sysfs_add device_create_sys_dev_entry devtmpfs_create_node kobject_uevent bus_probe_device |
程序示例:
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/uaccess.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #define USE_OLD 0 #define USE_NEW 1 #define MYCNT 1 #define MYNAME "testchar" //设备文件名/dev/char_test #define DEVNAME "char_test" static int major = -1; static struct class *char_test_class; static dev_t mydev; static struct cdev *pcdev; static char kbuf[100]; static int char_test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_INFO "char_test_open "); return 0; } static int char_test_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_INFO "char_test_close "); return 0; } static const struct file_operations char_test = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = char_test_open, .release = char_test_close, }; static int __init chrdev_init(void) { int ret; printk(KERN_INFO "chrdev_init "); #if USE_OLD /* 注册字符设备 */ if ((major = register_chrdev(0, MYNAME, &char_test)) < 0) { printk(KERN_ERR "%s: register_chrdev failed. ", MYNAME); goto lable0; } else { printk(KERN_INFO "register_chrdev successful, major is %d. ", major); } mydev = MKDEV(major, 0); #endif #if USE_NEW //动态获取主次设备号,即mydev ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&mydev, 0, MYCNT, MYNAME); if (ret < 0) { printk(KERN_INFO "alloc_chrdev_region failed. "); goto lable0; } printk(KERN_INFO "alloc_chrdev_region success. "); printk(KERN_INFO "major = %d minor = %d. ", MAJOR(mydev), MINOR(mydev)); // 第二步:注册字符设备驱动 pcdev = cdev_alloc(); //分配内存,实例化指针 cdev_init(pcdev, &char_test); ret = cdev_add(pcdev, mydev, MYCNT); if (ret) { printk(KERN_INFO "cdev_add failed. "); goto lable1; } printk(KERN_INFO "cdev_add success. "); #endif /* 创建设备文件 */ char_test_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "lll_class"); if (IS_ERR(char_test_class)) { goto lable2; } // 最后一个参数就是在/dev目录下创建的设备文件的名字 device_create(char_test_class, NULL, mydev, NULL, DEVNAME); return 0; lable2: cdev_del(pcdev); lable1: #if USE_OLD unregister_chrdev(major, DEVNAME); #endif #if USE_NEW unregister_chrdev_region(mydev, MYCNT); #endif lable0: return -EINVAL; } static void __exit chrdev_exit(void) { // 注销设备文件 device_destroy(char_test_class, mydev); class_destroy(char_test_class); //注销字符设备 #if USE_OLD unregister_chrdev(major, DEVNAME); #endif #if USE_NEW // 注销设备文件 device_destroy(char_test_class, mydev); class_destroy(char_test_class); // 注销cdev cdev_del(pcdev); // 第二步去注销申请的主次设备号 unregister_chrdev_region(mydev, MYCNT); #endif printk(KERN_INFO "chrdev_exit "); } module_init(chrdev_init); module_exit(chrdev_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("lll"); MODULE_DESCRIPTION("module test"); MODULE_ALIAS("alias xxx");
insmod加载驱动后,生成设备文件/dev/char_test,在/sys/class目录下还会生成一个类/sys/class/lll_class