一、display(元素显示模式)
display属性用来设置元素的显示方式。如果display设置为none,float及position属性定义将生效。
语法:display: block | none | inline | inline-block
1)block:块对象值的是元素显示为一个方块,默认显示状态下将占据整行,其它元素只能另起一行显示。(块元素)
2)inline:行间对象与block刚好相反,它允许其它元素在同一行显示。(内联元素)
3)inline-block:指定对象为内联块元素。可以在同一行的块元素吧。
4)none:隐藏对象。与visibility属性的hidden值不同,其不为被隐藏的对象保留其物理空间。
如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .display{width:100px;height:100px;display:inline-block;} .displayInline1{background-color:red;} .displayInline2{background-color:green;} </style> </head> <body> <div class="display displayInline1"></div><div class="display displayInline2"></div><!--注意:两个div代码之间写在同一行,要不然会出现中间会多出空白或者不能在同一行--> </body> </html>
二、float(元素的浮动)
用来控制元素是否浮动显示。浮动的时候元素的显示属性也变化了,变为“行内元素”
语法:float: none | left | right
1)left:向左浮动
2)right:向右浮动
3)none:不浮动
如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .box{width:100px;height:100px;} .floatLeft1{background-color:blue;float:left;} .floatLeft2{background-color:red;float:left;} </style> </head> <body> <div class="box floatLeft1"></div> <div class="box floatLeft2"></div> </body> </html>
浮动的目的:
就是要打破文档流的默认显示规则。如果要让元素按照我们的布局要求进行显示,这时就要利用float属性。
说明:
1.任何声明为float的元素自动被设置为一个“块级元素”。
2.在标准浏览器中,浮动元素脱离了文档流,所以浮动元素后的元素会占据浮动元素本来应该所处的位置。
3.如果水平方向上没有足够的空间容纳浮动元素,则转向下一行。
4.文字内容会围绕在浮动元素周围。
5.浮动元素只能浮动至左侧或者右侧。
清除浮动:
语法:clear: none | left | right | both
1)none:默认值。允许两边都可以有浮动对象。
2)left:不允许左边有浮动对象。
3)right:不允许右边有浮动对象。
4)both:不允许有浮动对象。
三、position(元素的定位)
设置元素定位方式
语法:position: static | absolute | fixed | relative
1)static:无定位,默认值。
2)absolute:绝对定位
3)relative:相对定位
4)fixed:固定定位
absolute说明:
- 脱离文档流
- 通过top,bottom,left,right定位
- 如果父元素position为static时,将以body坐标原点进行定位
- 如果父元素position为relative时,将以父元素进行定位
div{ position:absolute; left:100px; top:100px; }
relative说明:
- 相对定位(相对自己原来的位置而言)
- 不脱离文档流
- 参考自身静态位置通过top,bottom,left,right定位
div{ position:relative; left:100px; top:100px; }
fixed说明:
固定定位实际上只是绝对定位的特殊形式;固定定位的元素是相对浏览器窗口而固定,而不是相对于其包含元素;即使页面在滚动了,他们仍然会处在浏览器窗口中跟原来完全一样的地方。
fixed属性可以用来做网页返回顶端按钮
请看右边那个蓝色的东东
div{ position:fixed; right:0; top:50% }
z-index(元素的层叠关系)
当元素发生重叠时,可以通过z-index属性,设置其层叠的先后顺序。较大number值的对象会覆盖在较小number值的对象之上。
语法:z-index:auto | number
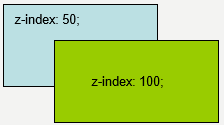
以下通过调整div的z-index值换颜色:(点击)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .box0{ position: relative; } .box{ width: 300px; height: 150px; position: absolute; left: 0; top: 0; } .box1{ background: red; } .box2{ background: blue; } .box3{ background: green; } .input{ z-index: 99; position: relative; top: 150px; } .radio{ display: none; } .radio:nth-of-type(1):checked~.box1{ z-index: 10; } .radio:nth-of-type(2):checked~.box2{ z-index: 10; } .radio:nth-of-type(3):checked~.box3{ z-index: 10; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box0"> <input type="radio" name="bg" id="bg1" class="radio"/><label for="bg1"class="input">红色</label> <input type="radio" name="bg" id="bg2" class="radio"/><label for="bg2"class="input">蓝色</label> <input type="radio" name="bg" id="bg3" class="radio"/><label for="bg3"class="input">绿色</label> <div class="box box1"></div> <div class="box box2"></div> <div class="box box3"></div> </div> </body> </html>