N pots, each with some number of gold coins, are arranged in a line. You are playing a game against another player. You take turns picking a pot of gold. You may pick a pot from either end of the line, remove the pot, and keep the gold pieces. The player with the most gold at the end wins. Develop a strategy for playing this game.
After drawing the following flow diagram, it is clear that we have overlapping subproblems such as p1 for A[1-6]. As a result, we'll use dynamic programming here.
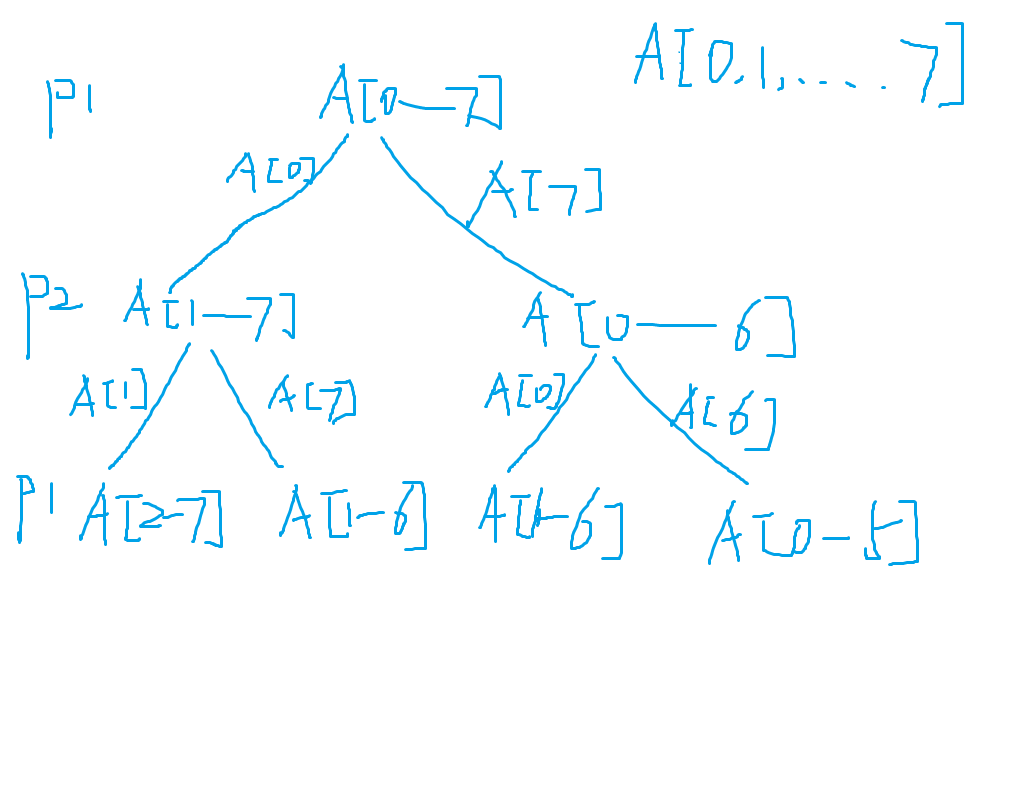
Solution 1. Dynamic Programming, only from player 1's perspective.
State: T[i][j]: the max value player 1 can get when pots[i......j] are available.
Function: T[i][j] = Max {pots[i] + Min {T[i + 2][j]}, T[i + 1][j - 1], pots[j] + Min {T[i + 1][j - 1], T[i][j - 2]} }. Min is used here is because player 2 is trying to play for the best strategy too.
Init: If there is only 1 pot, pick it; If there are 2 pots, pick the one that has a bigger value.
Answer: T[0][pots.length - 1]
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 3 public class OptimalGamePick { 4 private ArrayList<Integer> picks; 5 public int getOptimalStrategy(int[] pots) { 6 picks = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 7 if(pots == null || pots.length == 0){ 8 return 0; 9 } 10 int[][] T = new int[pots.length][pots.length]; 11 for(int i = 0; i < pots.length; i++) { 12 T[i][i] = pots[i]; 13 } 14 for(int i = 0; i < pots.length - 1; i++) { 15 T[i][i + 1] = Math.max(pots[i], pots[i + 1]); 16 } 17 for(int len = 3; len <= pots.length; len++) { 18 for(int i = 0; i <= pots.length - len; i++) { 19 T[i][i + len - 1] = Math.max(pots[i] + Math.min(T[i + 2][i + len - 1], T[i + 1][i + len - 2]), 20 pots[i + len - 1] + Math.min(T[i + 1][i + len -2], T[i][i + len - 3])); 21 } 22 } 23 //reconstruct player 1's picks 24 int start = 0, end = pots.length - 1; 25 while(end - start >= 2) { 26 int pickFront = pots[start] + Math.min(T[start + 2][end], T[start + 1][end - 1]); 27 int pickEnd = pots[end] + Math.min(T[start + 1][end - 1], T[start][end - 2]); 28 if(pickFront > pickEnd) { 29 picks.add(start); 30 if(T[start + 2][end] < T[start + 1][end - 1]) { 31 start++; 32 } 33 else { 34 end--; 35 } 36 start++; 37 } 38 else { 39 picks.add(end); 40 if(T[start + 1][end - 1] < T[start][end - 2]) { 41 start++; 42 } 43 else { 44 end--; 45 } 46 end--; 47 } 48 } 49 if(end - start == 1) { 50 if(pots[start] > pots[end]) { 51 picks.add(start); 52 } 53 else { 54 picks.add(end); 55 } 56 } 57 else { 58 picks.add(start); 59 } 60 return T[0][pots.length - 1]; 61 } 62 public static void main(String[] args) { 63 int[] pots = {3, 9, 1, 2}; 64 OptimalGamePick test = new OptimalGamePick(); 65 System.out.println(test.getOptimalStrategy(pots)); 66 } 67 }
Solution 2. Dynamic Programming, from both player 1 and 2's perspective.
State: T[i][j] stores the max value both players can get given pots i to j. Whoever picks first becomes player 1, so as the range of pots changes, player 1 and player 2 take turns to pick first.
Function: If player 1 picks pots[i], then for pots i + 1 to j he becomes player 2 as he is the second player to pick from i + 1 to j.
T[i][j]. first = max {T[i + 1][j].second + pots[i], T[i][j - 1].second + pots[j]};
T[i][j].second = T[i + 1][j].first or T[i][j - 1].first, depending on which pot was picked previously by the other player.
1 public ResultEntry getOptimalStrategy(int[] pots) { 2 ResultEntry[][] T = new ResultEntry[pots.length][pots.length]; 3 for(int i = 0; i < T.length; i++) { 4 for(int j = 0; j < T[0].length; j++) { 5 T[i][j] = new ResultEntry(0, 0); 6 } 7 } 8 for(int i = 0; i < T.length; i++) { 9 T[i][i].p1 = pots[i]; 10 } 11 for(int i = 0; i < T.length - 1; i++) { 12 T[i][i + 1].p1 = Math.max(pots[i], pots[i + 1]); 13 T[i][i + 1].p2 = Math.min(pots[i], pots[i + 1]); 14 } 15 for(int len = 3; len <= pots.length; len++) { 16 for(int i = 0; i <= pots.length - len; i++) { 17 int pickFront = pots[i] + T[i + 1][i + len - 1].p2; 18 int pickEnd = pots[i + len - 1] + T[i][i + len -2].p2; 19 if(pickFront >= pickEnd) { 20 T[i][i + len - 1].p1 = pickFront; 21 T[i][i + len - 1].p2 = T[i + 1][i + len - 1].p1; 22 } 23 else { 24 T[i][i + len - 1].p1 = pickEnd; 25 T[i][i + len - 1].p2 = T[i][i + len - 2].p1; 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 return T[0][pots.length - 1]; 30 }