Given the root of a binary tree, each node has a value from 0 to 25 representing the letters 'a' to 'z': a value of 0 represents 'a', a value of 1 represents 'b', and so on.
Find the lexicographically smallest string that starts at a leaf of this tree and ends at the root.
(As a reminder, any shorter prefix of a string is lexicographically smaller: for example, "ab" is lexicographically smaller than "aba". A leaf of a node is a node that has no children.)
Example 1:
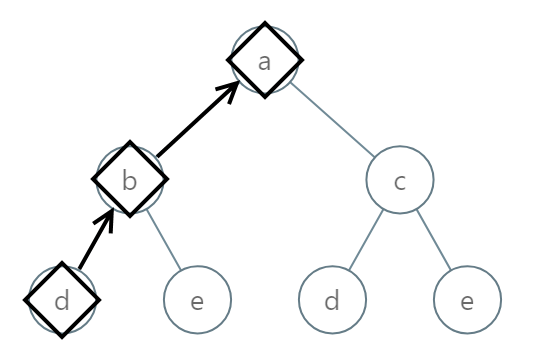
Input: [0,1,2,3,4,3,4]
Output: "dba"
Example 2:
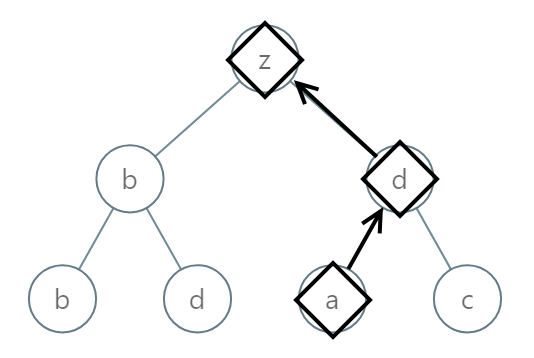
Input: [25,1,3,1,3,0,2]
Output: "adz"
Example 3:
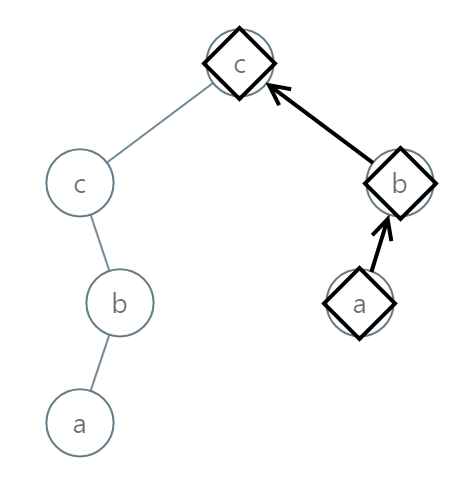
Input: [2,2,1,null,1,0,null,0]
Output: "abc"
Note:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be between
1and1000. - Each node in the tree will have a value between
0and25.
We can use dfs to get all strings, sort them then get the smallest one. Even better, we can just keep a global variable of the current smallest string, each time we get a new string, compare it with the current smallest string and update it if necessary. This way it avoids keeping all the strings in a list and sorting them.
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 private String ans = null; 12 13 public String smallestFromLeaf(TreeNode root) { 14 dfs(root, new StringBuilder()); 15 return ans; 16 } 17 18 private void dfs(TreeNode node, StringBuilder sb) { 19 if(node == null) { 20 return; 21 } 22 sb.append((char)('a' + node.val)); 23 if(node.left == null && node.right == null) { 24 sb.reverse(); 25 String s = sb.toString(); 26 sb.reverse(); 27 28 if(ans == null || s.compareTo(ans) < 0) { 29 ans = s; 30 } 31 } 32 dfs(node.left, sb); 33 dfs(node.right, sb); 34 sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1); 35 } 36 }
StringBuilder vs StringBuffer
The StringBuilder class should generally be used in preference to the StringBuffer class, as it supports all of the same operations but it is faster, as it performs no synchronization. Instances of StringBuilder are not safe for use by multiple threads. If such synchronization is required then it is recommended that StringBuffer be used.