
上图首先描述了在TaskTracker端Task(MapTask、ReduceTask)的执行过程,MapTask(org.apache.hadoop.mapred)首先被TaskRunner调用,然后在MapTask内部首先进行一些初始化工作,然后调用run()方法,判断如果使用了新版API就调用RunNewMapper()开始执行Map操作。
1)runNewMapper()分析
1.首先创建一个Mapper对象
// make a mapper org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
2.创建一个InputFormat对象
1 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat = 2 (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>) 3 ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
3.创建InputSplit对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null; split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()), splitIndex.getStartOffset());//获得分片的详细信息
其中,splitIndex是TaskSplitIndex类型(用于指示此mapTask处理的分片),TaskSplitIndex有两个字段:
String splitLocation //job.split在HDFS上的路径
long startOffset //此次处理的分片在job.split中的位置。
利用上述两个字段首先找到job.split,然后就可以在startOffset的位置处找到这次处理的分片的详细信息。
4.利用InputFormat和InputSplit创建RecordReader对象input,这里应该是已经确定了input具体是那种记录读取器,例如LineRecordReader
1 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input = 2 new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> 3 (split, inputFormat, reporter, job, taskContext);
5.创建输出收集器OutputCollector对象output(如果reduce=0创建NewDirectOutputCollector类对象,否则创建NewOutputCollector类对象)
// get an output object if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {//reduce数量如果是0 output = new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter); } else { output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter); }
6.利用上述对象创建MapContext类的对象mapperContext
mapperContext = contextConstructor.newInstance(mapper, job, getTaskID(),
input, output, committer,
reporter, split);
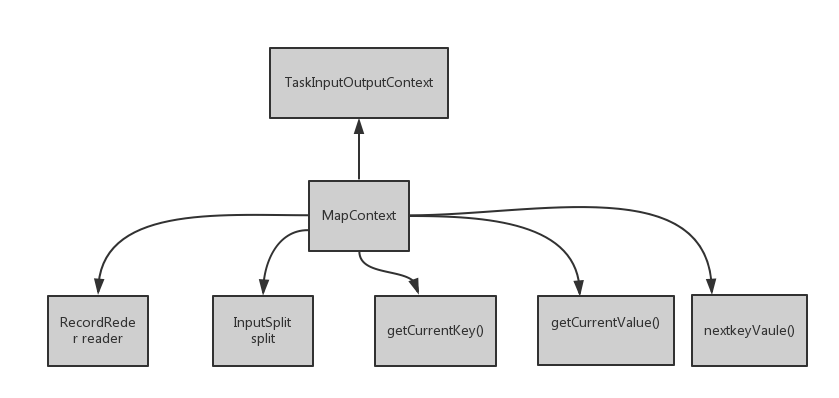
其中reader和split是数据成员,getCurrentKey()是获得当前的key,同样getCurrentValue().如果还有下条记录,nextKeyValue()返回true,否则返回false,这三个方法均由reader调用。由于RecordReader是抽象类,并未实现相关方法,其子类实现了这些方法。
1 @Override 2 public KEYIN getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 3 return reader.getCurrentKey(); 4 } 5 6 @Override 7 public VALUEIN getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 8 return reader.getCurrentValue(); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 13 return reader.nextKeyValue(); 14 }
在MapContext的构造函数中,字段reader就是由input初始化的,所以reader的具体类型也是已经确定了的,所以会调用具体实现了的这些方法,例如LineRecorReader的方法
(在org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input中找到,因为新版API重写了LineRecordReader),以下是LineRecordReader部分源码():
1 private CompressionCodecFactory compressionCodecs = null; 2 private long start; 3 private long pos; 4 private long end; 5 private LineReader in; 6 private int maxLineLength; 7 private LongWritable key = null; 8 private Text value = null; 9 private Seekable filePosition; 10 private CompressionCodec codec; 11 public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit, 12 TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException { 13 FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit; 14 Configuration job = context.getConfiguration(); 15 this.maxLineLength = job.getInt("mapred.linerecordreader.maxlength", 16 Integer.MAX_VALUE); 17 start = split.getStart(); 18 end = start + split.getLength(); 19 final Path file = split.getPath(); 20 compressionCodecs = new CompressionCodecFactory(job); 21 codec = compressionCodecs.getCodec(file); 22 23 // open the file and seek to the start of the split 24 FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job); 25 FSDataInputStream fileIn = fs.open(split.getPath()); 26 27 if (isCompressedInput()) { 28 decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec); 29 if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) { 30 final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn = 31 ((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream( 32 fileIn, decompressor, start, end, 33 SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK); 34 in = new LineReader(cIn, job); 35 start = cIn.getAdjustedStart(); 36 end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd(); 37 filePosition = cIn; 38 } else { 39 in = new LineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn, decompressor), 40 job); 41 filePosition = fileIn; 42 } 43 } else { 44 fileIn.seek(start); 45 in = new LineReader(fileIn, job); 46 filePosition = fileIn; 47 } 48 // If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record 49 // because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in 50 // next() method. 51 if (start != 0) { 52 start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start)); 53 } 54 this.pos = start; 55 } 56 @Override 57 public LongWritable getCurrentKey() { 58 return key; 59 } 60 61 @Override 62 public Text getCurrentValue() { 63 return value; 64 }
65
7-8行可看到类的字段key和value。使用initialize()方法初始化,读取分片中的数据到key/value由nextKeyValue()方法完成:
1 public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException { 2 if (key == null) { 3 key = new LongWritable(); 4 } 5 key.set(pos);//以记录的偏移量为key 6 if (value == null) { 7 value = new Text(); 8 } 9 int newSize = 0; 10 // We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper 11 // split limit i.e. (end - 1) 12 while (getFilePosition() <= end) { 13 //获取value值,调用了很多的函数 14 newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, 15 Math.max(maxBytesToConsume(pos), maxLineLength)); 16 if (newSize == 0) { 17 break; 18 } 19 pos += newSize;//更新pos 20 if (newSize < maxLineLength) { 21 break; 22 } 23 24 // line too long. try again 25 LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " + 26 (pos - newSize)); 27 } 28 if (newSize == 0) { 29 key = null; 30 value = null; 31 return false; 32 } else { 33 return true; 34 } 35 }
7.初始化记录读取器input(例如LineRecordReader.initialize())
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
8.调用Mapper类的run()方法:
mapper.run(mapperContext);
Mapper类结果如下所示:

Mapper有一个内部类Context。通过run()方法调用这几个方法,run()的实现如下所示:
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { setup(context); try { while (context.nextKeyValue()) { map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); } } finally { cleanup(context); } }
从MapTask的角度分析下Mapper中的run()方法内的context.nextkeyValue(),流程图如下所示:
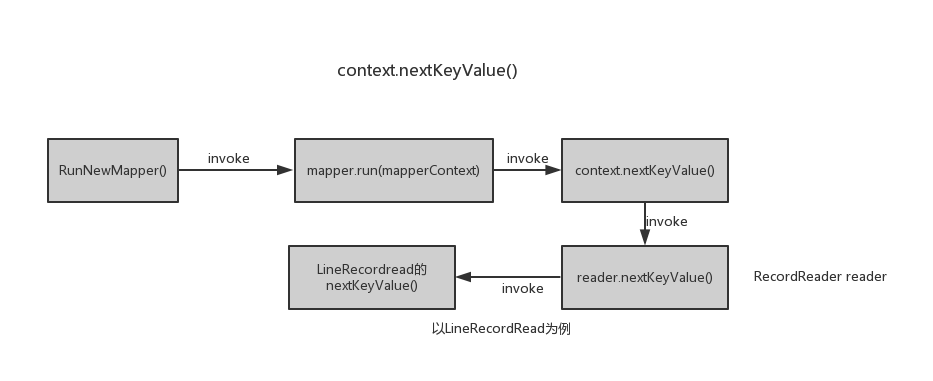
上面已经给出了LineRecordRead的源码,以下做简要分析:
LineRecordRead有3个核心字段,分别是pos,key,value。pos就是读取的字段在文件中的偏移量,每次通过nextKeyValue()方法中读取分片中一个记录,并将pos设置为此记录的key,然后再将此记录存储在value中,最后更新pos的值,作为下个字段的偏移量。最后,nextKeyValue方法返回一个布尔值,true表示成功读取到一条记录,否则,表示此分片中已没有记录。
然后执行map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context),其中context.getCurrentKey()调用了LineRecordRead的方法getCurrentKey()直接返回当前key,context.getCurrentValue()也是同样。
2)基于以上的分析,MapTask的任务逻辑图如下所示:

其中输入分片就是由上述的第2、3完成的。RecordReader就对应了第4步的记录读取器input对象。OutputCollector对应第5步中的输出收集器对象output。第8步就对应了上图中的Mapper,接下来就分析Mapper之后发生了什么,这就要进入到Mapper类的map()方法内部:
用户要重写Mapper的map方法,这里以WordCount为例进行分析。重写的map方法如下所示;
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { word.set(itr.nextToken()); context.write(word, one); } }
关注最后一行代码:context.write(word,one),一直Context是Mapper的内部类,继承自MapContext类,那么这个write方法究竟做了什么呢?以下是整个调用过程:
context.write(word, one);
Context类只是简单的继承了MapContext类,并没有write方法,查看MapContext有没有write方法,结果MapContext也没有write方法,继续查看MapContext的父类TaskInputOutputContext,其中write方法源码为:
public void write(KEYOUT key, VALUEOUT value ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { output.write(key, value); }
output是此类的一个字段,定义如下:
private RecordWriter<KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> output;
而RecordWriter是一个抽象类,没有字段,只有未实现的抽象方法write和close,Context通过继承机制,获得了output字段,这个字段肯定是RecordWriter的某个具体实现类,到底是哪个类呢?转了一圈,我们看看context对象的来源:就是在RunNewMapper中(对应第8步)
mapper.run(mapperContext);
mapper就是一个Mapper对象,调用其run方法:
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { setup(context); try { while (context.nextKeyValue()) { map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); } } finally { cleanup(context); } }
将mapperContext对象赋值给了context对象,也就是context的来源是mapperContext对象,那我们就需要看看mapperContext是怎么来的:
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context mapperContext = null;
mapperContext = contextConstructor.newInstance(mapper, job, getTaskID(),input, output, committer,reporter, split);
首先mapperContext对象是Context类型,然后就是第二行代码的作用就相当于使用new Context(....)创建新对象。是时候上图了:

super就是调用父类的构造函数。再次贴上mapperContext创建的代码:
mapperContext = contextConstructor.newInstance(mapper, job, getTaskID(),input, output, committer,reporter, split);
job就对应于conf,getTaskID()就对应于taskid,input对应reader,output对应writer,...。通过观察这三个类的构造函数,不能看出最终output对象传值给了TaskInputOutputContext类中的RecordReader output对象。再回到这个output的定义:
// get an output object if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {//reduce数量如果是0 output = new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter); } else { output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter); }
这样我们就可以确定TaskInputOutputContext中字段output的类型是NewOutputCollector类型(RecordWriter抽象类的一个实现)。
当然,context继承了TaskInputOutputContext这个output字段,更重要的还有其write方法。对Context类做个小结,到目前为止所知道的它的字段和方法如下:

再回到map方法:
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { word.set(itr.nextToken()); context.write(word, one); } }
可以看到context.write()方法其实就是调用了NewOutputCollector类的write方法,这个类部分声明:
private final MapOutputCollector<K,V> collector;//map的输出内存缓冲区。 private final org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V> partitioner;//作业所使用的分区(Partitioner)类型(默认的Partitioner就是HashPartitioner) private final int partitions;//reduce的数量 NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext, JobConf job, TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical, TaskReporter reporter ) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { collector = new MapOutputBuffer<K,V>(umbilical, job, reporter);//创建collector对象 partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();//获得reduce的数量。 if (partitions > 0) { partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);//获得作业所使用的分区(Partitioner)类型(默认的Partitioner就是HashPartitioner) } else { partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() { @Override public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) { return -1; } }; } } public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException { collector.collect(key, value, partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions)); }
NewOutputCollector有三个数据成员:collector、partitioner和partitions,这三个字段都在构造函数内完成初始化,collector是MapOutputBuffer类的对象,是本类的核心字段,partitioner是Partitioner类的对象,用于指示本次map所使用的分区类型,所谓的对key/value分区的过程其实也就是调用getPartition(key,value,reduceNums)方法返回一个整数作为此键值对的分区号,用户可以自定义分区类,其实也就是自定义getPartition(key,value,reduceNums)方法。不过分区只是根据key将map的输出分成不同的区(以0,1,2,3等数字作为分区号),每个区用一个reduce处理。默认的分区方法是HashPartitioner,首先将key的哈希值和Integer类型最大值进行与运算,然后将结果对作业的reduce数量取模值,将这个模值作为此key/value对应的分区号,可见键值对的分区号只是与key有关,其原型如下:
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> { /** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */ public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numReduceTasks) { return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks; }
接下来查看到NewOutputCollector的write方法又调用了collector.collect(key,value)方法:
public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException { collector.collect(key, value, partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions)); }
不深入collect方法内部看的话,看到此方法的第一印象就是colllector将key、value、partition(对应的分区号)一起存入内存缓冲区。接下来分析map阶段的spill过程。
参考:
http://zheming.wang/hadoop-mapreduce-zhi-xing-liu-cheng-xiang-jie.html