1. 背景:
1.1 最早是由 Vladimir N. Vapnik 和 Alexey Ya. Chervonenkis 在1963年提出
1.2 目前的版本(soft margin)是由Corinna Cortes 和 Vapnik在1993年提出,并在1995年发表
1.3 深度学习(2012)出现之前,SVM被认为机器学习中近十几年来最成功,表现最好的算法
2. 机器学习的一般框架:
训练集 => 提取特征向量 => 结合一定的算法(分类器:比如决策树,KNN)=>得到结果
3. 介绍:
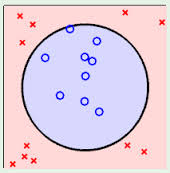
3.1 例子:
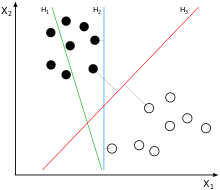
两类?哪条线最好?
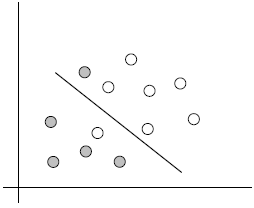
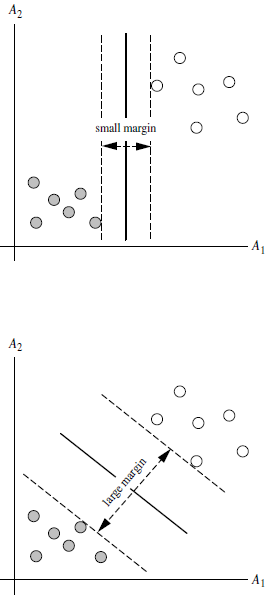
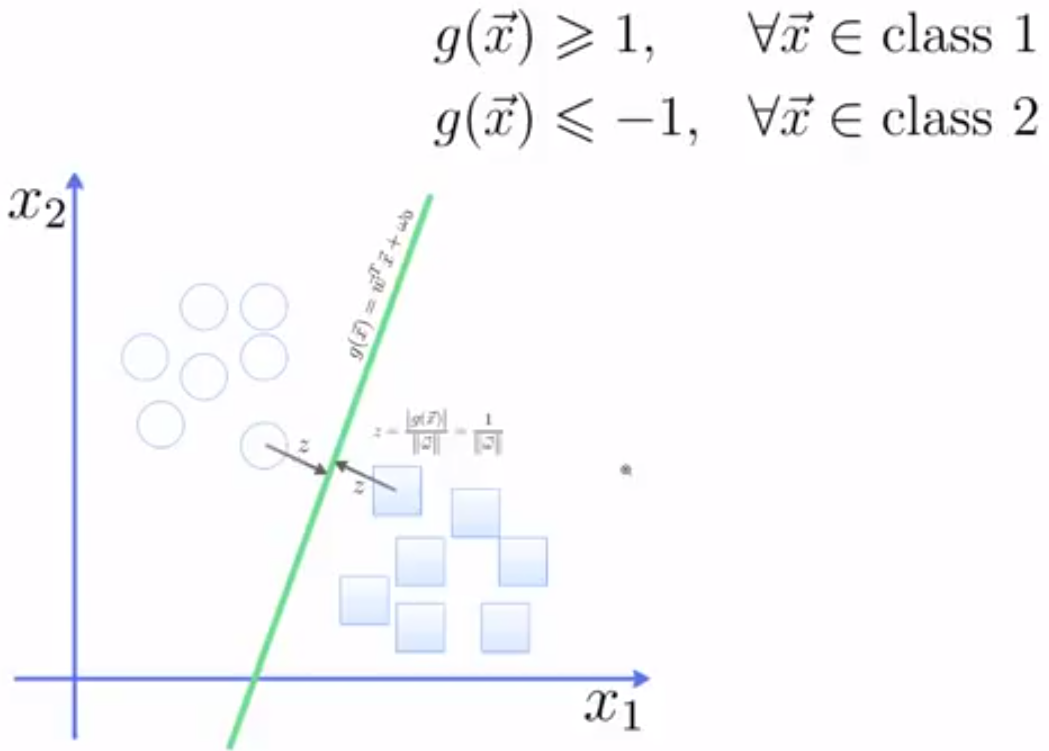
3.2 SVM寻找区分两类的超平面(hyper plane), 使边际(margin)最大
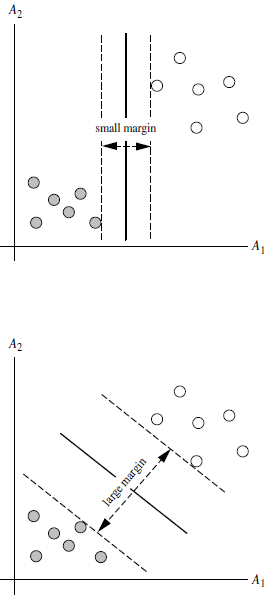
总共可以有多少个可能的超平面?无数条
如何选取使边际(margin)最大的超平面 (Max Margin Hyperplane)?
超平面到一侧最近点的距离等于到另一侧最近点的距离,两侧的两个超平面平行
3.3. 线性可区分(linear separable) 和 线性不可区分 (linear inseparable)
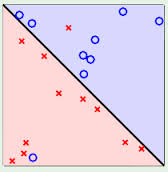
4. 定义与公式建立
超平面可以定义为:

W: weight vector, ![]()
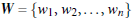
n :是特征值的个数
X: 训练实例
b: bias
4.1 假设2维特征向量:X = (x1, X2)
把 b 想象为额外的 wight
超平面方程变为:
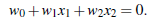
所有超平面右上方的点满足:![]()

所有超平面左下方的点满足:
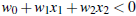
调整weight,使超平面定义边际的两边:
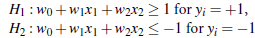
综合以上两式,得到:
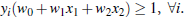
所有坐落在边际两边的超平面上的点被称作”支持向量(support vectors)"
分界的超平面和H1或H2上任意一点的距离为 

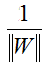

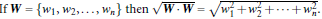
所以,最大边际距离为:

5. 求解
5.1 SVM如何找出最大边际的超平面呢(MMH)?
利用一些数学推倒,以上公式 (1)可变为有限制的凸优化问题(convex quadratic optimization)
利用 Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT)条件和拉格朗日公式,可以推出MMH可以被表示为以下“决定边 界(decision boundary)” 

其中,
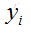
是支持向量点

(support vector)的类别标记(class label)
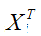
是要测试的实例
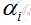
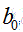
都是单一数值型参数,由以上提到的最有算法得出

是支持向量点的个数
5.2 对于任何测试(要归类的)实例,带入以上公式,得出的符号是正还是负决定
6. 实例一:
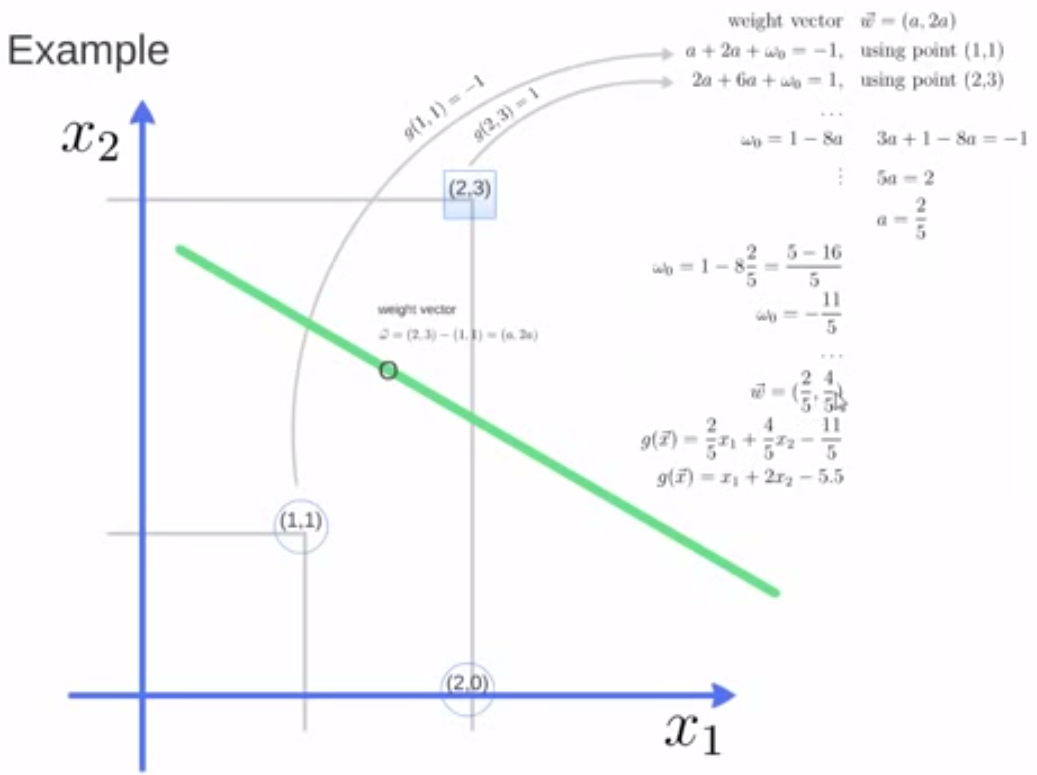
调用Python中库函数实现
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from sklearn import svm
x = [[2,0],[1,1],[2,3]]
#python中的两类问题分类标签
y = [0,0,1]
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf.fit(x,y)
print(clf)
#get support vectors 支持向量
print(clf.support_vectors_)
#get index of support vectors 支持向量的下标
print(clf.support_)
#get number of support vectors for each class
print(clf.n_support_)
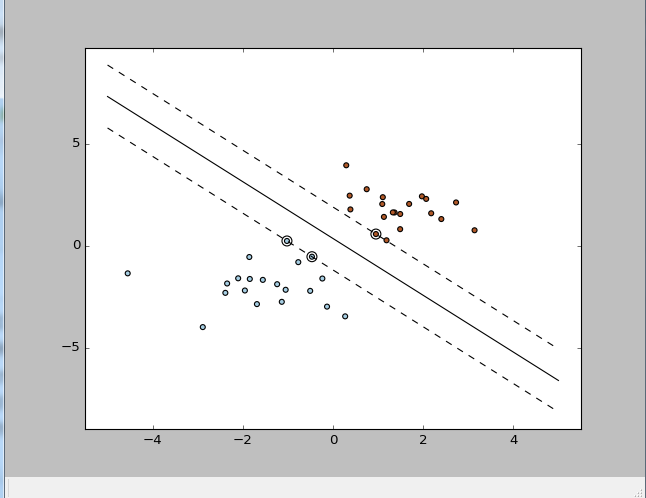
结果
SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape=None, degree=3, gamma='auto', kernel='linear',
max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True,
tol=0.001, verbose=False)
[[ 1. 1.]
[ 2. 3.]]
[1 2]
[1 1]
7.实例二
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from sklearn import svm
#we create 40 separable points
np.random.seed(0)#控制每次的数据相同
#- [2,2] + [2,2] 是为了使得两组正态分布的数据呈线性上下分开
X = np.r_[np.random.randn(20,2) - [2,2], np.random.randn(20,2) + [2,2]]
Y = [0]*20 + [1]*20 #类标签
#fit the model
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf.fit(X ,Y)
#get the separating hyperplane
w = clf.coef_[0]
a = -w[0] / w[1] #斜率
xx = np.linspace(-5,5) #[-5,-4,-3,...,5]
#clf.intercept_[0]) 为w[3]
yy = a * xx - (clf.intercept_[0]) / w[1]
# plot the parallels to the separating hyperplane that pass through the support vectors
b = clf.support_vectors_[0]#取出第一个支持向量
yy_down = a * xx + (b[1] - a*b[0]) #(b[1] - a*b[0])下面直线的截距
b = clf.support_vectors_[-1]#最后一个支持向量
yy_up = a * xx + (b[1] - a*b[0])
print("w: ", w)
print("a: ", a)
# print "xx: ", xx
# print "yy: ", yy
print("support_vectors_: ", clf.support_vectors_)
print("clf.coef_: ", clf.coef_)
# switching to the generic n-dimensional parameterization of the hyperplan to the 2D-specific equation
# of a line y=a.x +b: the generic w_0x + w_1y +w_3=0 can be rewritten y = -(w_0/w_1) x + (w_3/w_1)
# plot the line, the points, and the nearest vectors to the plane
pl.plot(xx, yy, 'k-')
pl.plot(xx, yy_down, 'k--')
pl.plot(xx, yy_up, 'k--')
pl.scatter(clf.support_vectors_[:, 0], clf.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=80, facecolors='none')
pl.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, cmap=pl.cm.Paired)
pl.axis('tight')
pl.show()
结果
w: [ 0.90230696 0.64821811]
a: -1.39198047626
support_vectors_: [[-1.02126202 0.2408932 ]
[-0.46722079 -0.53064123]
[ 0.95144703 0.57998206]]
clf.coef_: [[ 0.90230696 0.64821811]]