(function(modules) {
// 缓存已经加载过的 module 的 exports
var installedModules = {};
// _webpack_require 与 commonjs 的 require类似,它是 webpack加载函数,用来加载webpack定义的模块,返回exports导出对象
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// 如果缓存中存在当前模块就直接返回
if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
}
//第一次加载时, 初始化时模块对象,并将当前模块进行缓存
var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId, // 模块id
l: false, // 是否已加载
exports: {} // 模块导出对象
};
// module.exports 模块导出对象引用,改变模块包裹函数内部的this指向,module当前模块对象的引用,module.exports 模块导出对象的引用,__webpack_require__ 用于在模块中加载其他模块
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
// 标记是否已加载
module.l = true;
// 返回模块导出对象引用
return module.exports;
}
// 加载入口模块并返回入口模块的exports
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./src/index.js");
})
({
"./src/a.js":
(function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
eval("let b = __webpack_require__(/*! ./base.js/b */ "./src/base.js/b.js")
module.exports = 'a' + b
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/a.js?");
}),
"./src/base.js/b.js":
(function(module, exports) {
eval("module.exports = 'b'
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/base.js/b.js?");
}),
"./src/index.js":
(function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
eval("let str = __webpack_require__(/*! ./a.js */ "./src/a.js")
console.log(str)
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/index.js?");
})
});
上面代码的核心骨架其实就是一个IIFE (立即调用函数表达式)
这个立即执行函数接受一个对象 modules 作为参数,key 为依赖文件路径, value 是一个简单处理过后的函数,函数内部的代码不完全等同于是我们编写的源码,而是被webpack包裹后的内容。 这就是modules接收到的数据。
需要将require方法改写成__webpack_require__方法,因为浏览器端不支持require方法。
大致结构是这样的
先在package.json文件里配置打包命令
package.json
{
"name": "self-webpack",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"bin": {
"self-pack": "./bin/self-pack.js"
},
"scripts": {
"test": "echo "Error: no test specified" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
在self-webpack文件里写我们的打包流程
self-webpack.js
//通过此文件,需要解析编译用户配置的webpack.config.js文件
//1.需要找到当前执行名的路径 拿到webpack.config.js
//1.1拿到文件路径
let path = require('path')
//1.2config配置文件
let config = require(path.resolve(__dirname))
//1.3编译配置文件
let Compiler = require('./lib/Compiler')
let compiler = new Compiler(config)
//1.4运行
compiler.run()
在Compiler文件中写主要的打包逻辑,拿到webpack.config.js里面的配置信息,解析入口,解析文件依赖关系,发射文件。
Compiler.js
class Complier{
constructor(config){
this.config = config
//需要保存入口文件的路径
this.entryId //主模块路径 "./src/index.js"
//需要保存所有模块的依赖
this.module = {}
//入口路径
this.entry = config.entry
//工作目录 是指执行打包命令的文件夹地址 比如在d:/aa/b目录下执行 npm run build 那么cwd就是d:/aa/b
this.root = process.cwd()
}
buildModule(modulePath,isEntry){
}
emitFile(){
}
run(){
//创建模块的依赖关系
this.buildModule(path.resolve(this.root,this.entry),true) //true表示是主模块
//发射一个文件 打包后的文件
this.emitFile()
}
}
module.exports = Complier
大概流程就是这样,构建模块时,我们需要拿到模块的内容(我们编写的源码)。这个通过getSource函数拿到即可。我们还需要拿到模块id
接下来构建路径对应的模块内容
getSource(modulePath){
//拿到模块内容
let content = fs.readFileSync(modulePath,'utf8')
return content
}
//构建模块
buildModule(modulePath,isEntry){
//拿到路径对应的内容
let source = this.getSource(modulePath)
//模块id
let moduleName = './'+path.relative(this.root, modulePath)
console.log(sorce,moduleName) //sorce: let str = require('./a.js') console.log(str) moduleName: './src/index.js'
}
emitFile(){
}
run(){
//创建模块的依赖关系
this.buildModule(path.resolve(this.root,this.entry),true) //true表示是主模块
//发射一个文件 打包后的文件
this.emitFile()
}
console.log(sorce,moduleName)对应的内容
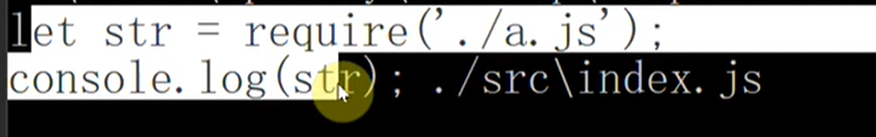
接下来要做的就是解析入口文件里面的文件依赖,解析依赖文件的依赖,递归解析出所有文件的依赖。
//解析源码
parse(source,parentPath){ //AST解析语法树
console.log(source,parentPath)
}
//构建模块
buildModule(modulePath,isEntry){
//拿到路径对应的内容
let source = this.getSource(modulePath)
//模块id 'src/index.js'
let moduleName = './'+path.relative(this.root, modulePath)
console.log(sorce,moduleName) //sorce: let str = require('./a.js') console.log(str) moduleName: './src/index.js'
if(isEntry){
this.entryId = moduleName //保存入口文件名字
}
//解析需要把source源码进行改造 返回一个依赖列表 比如index.js文件里面引入了a.js,需要把这个a.js进行解析,a.js里面要是再引入b.js也要把b.js对应的内容解析
let {sourceCode,dependencies} = this.parse(source,path.dirname(moduleName)) // path.dirname(moduleName)取父路径 .src
//把模块路径和模块中的内容对应起来
this.modules[moduleName] = sourceCode
}
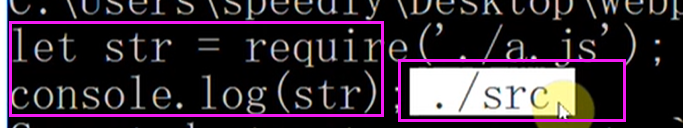
下面需要把let str = require('./a.js') 这种,/a.js转换成 './src/a.js' ,还有一个是将require方法改成 __webpack_require__console.log,这就是解析语法树的工作
parse方法需要安装几个包来解析,还需要看看ast的结构
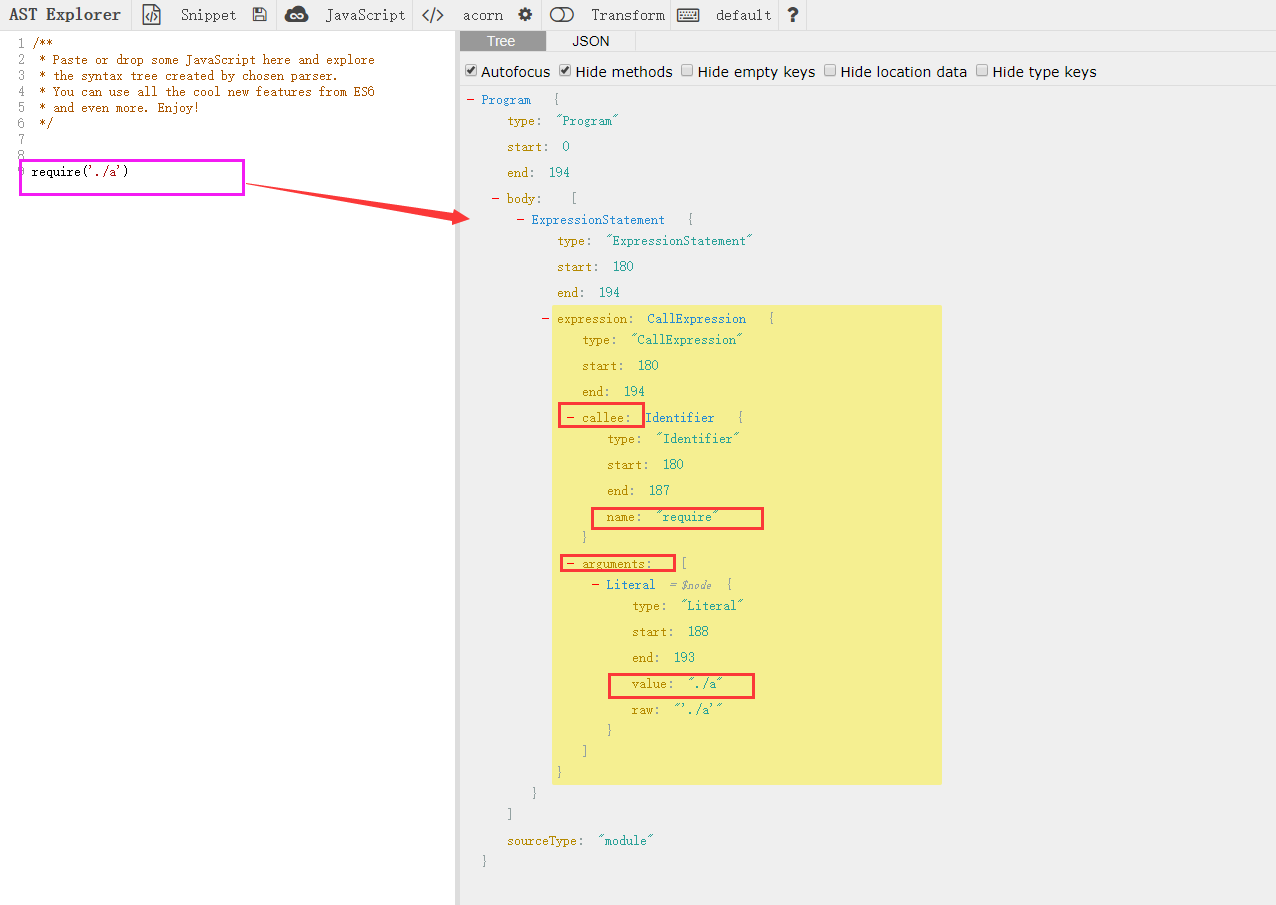
require('./a') 对应的ast的结构
下面就开始解析
//解析源码
//babylon 把源码转换成ast
// @babel/traverse
//@babel/types
//@babel/generator
parse(source,parentPath){ //AST解析语法树
console.log(source,parentPath)
let ast = babylon.parse(source)
let dependencies = [] //存放依赖模块
traverse(ast,{
CallExpression(p){
let node = p.node //对应的节点
if(node.callee.name === 'require') {
node.callee.name = "__webpack_require__" //改require名字
let moduleName = node.arguments[0].value //取到引用模块的名字 a
moduleName = moduleName + (path.extname(moduleName)?'': '.js') //拼接成./a.js
moduleName = './'+path.join(parentPath,moduleName) // ./src/a.js
dependencies.push(moduleName) //将这个依赖模块存入数组
node.arguments = [traverse.stringLiteral(moduleName)] //改源码
}
}
})
let sourceCode = generator(ast).code
return {sourceCode,dependencies}
}
//构建模块
buildModule(modulePath,isEntry){
//拿到路径对应的内容
let source = this.getSource(modulePath)
//模块id 'src/index.js'
let moduleName = './'+path.relative(this.root, modulePath)
console.log(sorce,moduleName) //sorce: let str = require('./a.js') console.log(str) moduleName: './src/index.js'
if(isEntry){
this.entryId = moduleName //保存入口文件名字
}
//解析需要把source源码进行改造 返回一个依赖列表 比如index.js文件里面引入了a.js,需要把这个a.js进行解析,a.js里面要是再引入b.js也要把b.js对应的内容解析
let {sourceCode,dependencies} = this.parse(source,path.dirname(moduleName)) // path.dirname(moduleName)取父路径 .src
console.log(sourceCode,dependencies)
//把模块路径和模块中的内容对应起来
this.modules[moduleName] = sourceCode
//若依赖模块里面又依赖别的模块就需要递归解析
dependencies.forEach(dep=>{
this.buildModule(path.join(this.root,dep),false) //false表示不是主模块
})
}
emitFile(){
}
run(){
//创建模块的依赖关系
this.buildModule(path.resolve(this.root,this.entry),true) //true表示是主模块
console.log(this.modules,this.entryId)
//发射一个文件 打包后的文件
this.emitFile()
}


接下来看看发射文件,需要准备一个webpack打包后的模板,并且增加一个渲染引擎,这里我选择 ejs
其实就是写一个模板,然后将我们拿到的模块id和对应的内容渲染到模板,再发射出去这个文件
首先需要一个ejs模板
(function (modules) { // webpackBootstrap
// The module cache
var installedModules = {};
// The require function
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// Check if module is in cache
if (installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
}
// Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId,
l: false,
exports: {}
};
// Execute the module function
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
// Flag the module as loaded
module.l = true;
// Return the exports of the module
return module.exports;
}
// Load entry module and return exports
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "<%-entryId%>");
})
/************************************************************************/
({
<% for(let key in modules){ %>
"<%- key %>":
(function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
eval(`<%- modules[key] %>`)
}),
<% } %>
})
开始渲染,将拿到的模块id以及模块内容渲染到模板中,在发射到一个文件即可
emitFile(){
//将打包好的资源放到哪个目录下
let main = path.join(this.config.output.path,this.config.output.filename)
//模板路径 读取模板内容
let templateStr = this.getSource(path.join(__dirname,'main.ejs'))
//渲染
let code = ejs.render(templateStr,{entryId:this.entryId,modules:this.modules})
this.assets = {}
//路径对应的代码
this.assets[main] = code
fs.writeFileSync(main,this.assets[main])
}
完整版:
let fs = require('fs')
let path = require('path')
let babylon = require('babylon')
let traverse = require('@babel/traverse')
let types = require('@babel/types')
let generator = require('@babel/generator')
class Complier{
constructor(config){
this.config = config
//需要保存入口文件的路径
this.entryId //主模块路径 "./src/index.js"
//需要保存所有模块的依赖
this.module = {}
//入口路径
this.entry = config.entry
//工作目录 是指执行打包命令的文件夹地址 比如在d:/aa/b目录下执行 npm run build 那么cwd就是d:/aa/b
this.root = process.cwd()
}
getSource(modulePath){
//拿到模块内容
let content = fs.readFileSync(modulePath,'utf8')
return content
}
//解析源码
//babylon 把源码转换成ast
// @babel/traverse
//@babel/types
//@babel/generator
parse(source,parentPath){ //AST解析语法树
console.log(source,parentPath)
let ast = babylon.parse(source)
let dependencies = [] //存放依赖模块
traverse(ast,{
CallExpression(p){
let node = p.node //对应的节点
if(node.callee.name === 'require') {
node.callee.name = "__webpack_require__" //改require名字
let moduleName = node.arguments[0].value //取到引用模块的名字 a
moduleName = moduleName + (path.extname(moduleName)?'': '.js') //拼接成./a.js
moduleName = './'+path.join(parentPath,moduleName) // ./src/a.js
dependencies.push(moduleName) //将这个依赖模块存入数组
node.arguments = [traverse.stringLiteral(moduleName)] //改源码
}
}
})
let sourceCode = generator(ast).code
return {sourceCode,dependencies}
}
//构建模块
buildModule(modulePath,isEntry){
//拿到路径对应的内容
let source = this.getSource(modulePath)
//模块id 'src/index.js'
let moduleName = './'+path.relative(this.root, modulePath)
console.log(sorce,moduleName) //sorce: let str = require('./a.js') console.log(str) moduleName: './src/index.js'
if(isEntry){
this.entryId = moduleName //保存入口文件名字
}
//解析需要把source源码进行改造 返回一个依赖列表 比如index.js文件里面引入了a.js,需要把这个a.js进行解析,a.js里面要是再引入b.js也要把b.js对应的内容解析
let {sourceCode,dependencies} = this.parse(source,path.dirname(moduleName)) // path.dirname(moduleName)取父路径 .src
console.log(sourceCode,dependencies)
//把模块路径和模块中的内容对应起来
this.modules[moduleName] = sourceCode
//若依赖模块里面又依赖别的模块就需要递归解析
dependencies.forEach(dep=>{
this.buildModule(path.join(this.root,dep),false) //false表示不是主模块
})
}
emitFile(){
//将打包好的资源放到哪个目录下
let main = path.join(this.config.output.path,this.config.output.filename)
//模板路径 读取模板内容
let templateStr = this.getSource(path.join(__dirname,'main.ejs'))
//渲染
let code = ejs.render(templateStr,{entryId:this.entryId,modules:this.modules})
this.assets = {}
//路径对应的代码
this.assets[main] = code
fs.writeFileSync(main,this.assets[main])
}
run(){
//创建模块的依赖关系
this.buildModule(path.resolve(this.root,this.entry),true) //true表示是主模块
console.log(this.modules,this.entryId)
//发射一个文件 打包后的文件
this.emitFile()
}
}
module.exports = Complier
这样我们就能把我们写的代码进行打包,并且可以在浏览器端运行。后续工作就是添加loader和plugin
到这里, 我们就可以大概总结一下webpack的运作流程是这样的 :
- 获取配置参数
- 实例化Compiler, 通过run方法开启编译
- 根据入口文件, 创建依赖项, 并递归获取所有模块的依赖模块
- 把模块内容通过渲染模板渲染成代码块
- 输出文件到指定路径