HashMap的数据结构
数据+链表的形式======》jdk1.8 红黑树
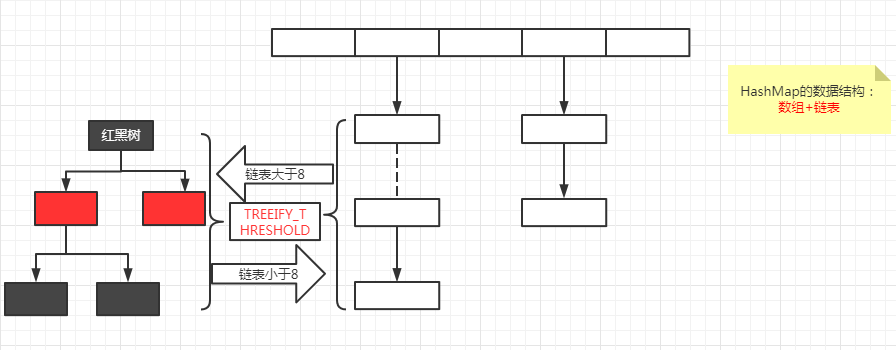
在链表的长度大于8的时候,链表会转换成红黑树(好处:红黑树的深度比较浅,遍历快)
单向链表,源码的表示:
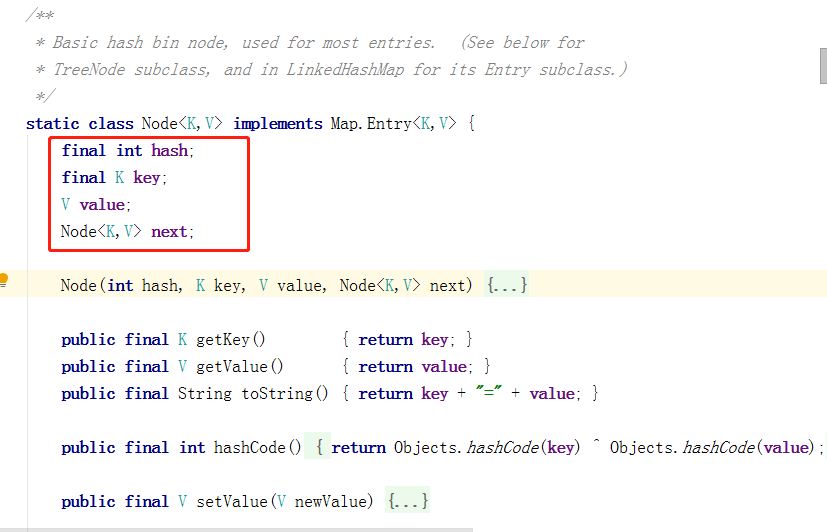
数组,源码的表示:(transient关键字意思为该数组不参与序列化)

数组的默认大小,源码表示:

数组的最大值,源码表示:

数组的大小可能不够用,当数组用到16时,对数组进行扩大,用16乘于该变量为对数组的扩大的标准

记录数组的大小,对它是否做扩展

链表的上限,源码表示:也就是说到达该上限就由链表转变成红黑树

(1)数组原本的位置为空
(2)数组原本的位置不为空,且下面是链表结构
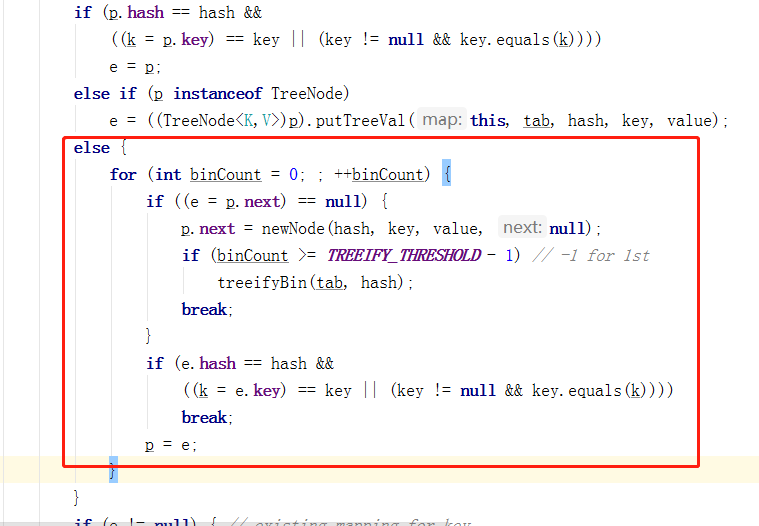
(3)数组原本的位置不为空,且下面是红黑树结构
![]()
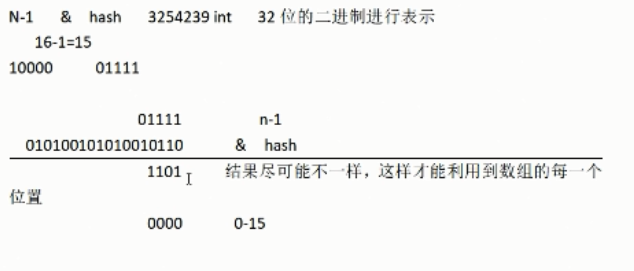
hash的算法:
n-1(15)&hash 《========》 hash%n(16) ======>0-15
“与”运算:运算规则:0&0=0;0&1=0;1&0=0;1&1=1;
源码分析:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//初始化数组
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//计算存储的索引位置,如果没有元素,直接赋值
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//覆盖旧值
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//判断是不是红黑树
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//判断是否转成红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
//记录数组长度
if (++size > threshold)
//对数组扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
面试题:
- HashMap的原理,内部数据结构?
- 底层使用哈希表(数组+链表),当链表过长,则转换为红黑树,时间复杂度为O(logn)
- HashMap的put过程?
- 对key求hash值,然后在计算下标
- 如果没有碰撞,则直接放入桶
- 如果碰撞,以链表的方式链接到后面如果链表长过阀值(TREEIFY_THRESHOLD == 8),就转换成红黑树
- 如果节点已经存在则替换旧值
- 如果桶满了(容量+加载因子),就扩容
- HashMap中hash函数怎么实现的,还有那些的实现方式
- 高16位不变,低16位和高16位做异或
- (n-1)&hash=====>得到下标
- HashMap怎样解决冲突,怎样扩容,如果一个值在原数组中,现在移动的新数组,位置肯定改变了,那是怎么定位到在这个新值数组中的位置
- 将新节点加到链表后
- 容量扩充为原来的两倍,然后对每个节点重新计算哈希值
- 这个值只可能在两个地方,一个是原下标的位置,另一个是在下标为《原下标+原容量》的位置
- HashMap,hash冲突有哪些解决方法
- 开放定址,链地址法
推荐文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41345773/article/details/92066554