一、Broadcast自动扩展
Expand和unsquee的结合,习惯性行是高维度,列是低维度

example:
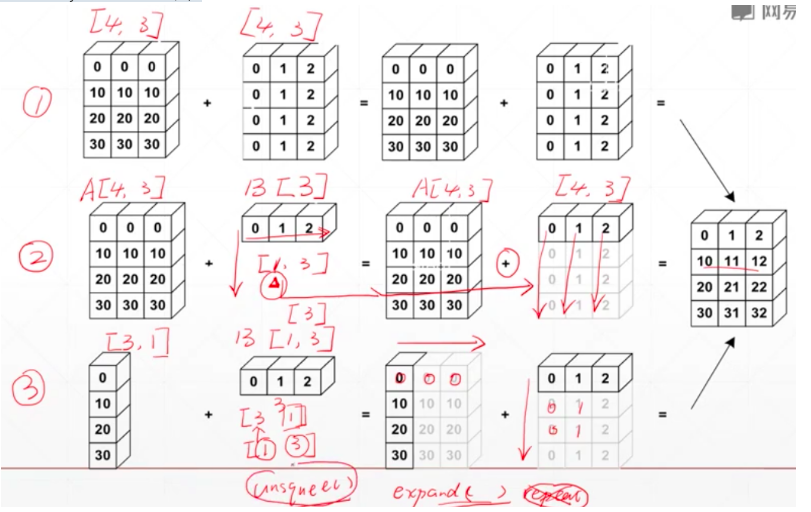
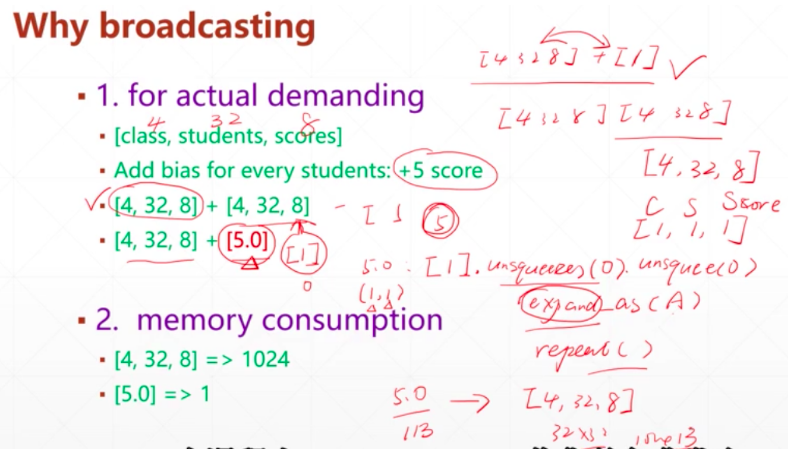
小维度指定,大维度随意


二、拼接与拆分
- Cat
- Stack:增加新的维度
- Split(按照长度进行拆分)
- Chunk(按照数量进行拆分)
torch.stack
torch.stack(sequence, dim=0)
参数:
- sqequence (Sequence) – 待连接的张量序列
- dim (int) – 插入的维度。必须介于 0 与 待连接的张量序列数之间。
沿着一个新维度对输入张量序列进行连接。 序列中所有的张量都应该为相同形状。
>>> a=torch.rand(32,8)
>>> b=torch.rand(32,8)
>>> c=torch.rand(32,8)
>>> torch.stack([a,b,c],dim=0).shape
torch.Size([3, 32, 8])
>>> torch.stack([a,b,c],dim=1).shape #a,b,c的维度需完全一样
torch.Size([32, 3, 8])
torch.split
torch.split(tensor, split_size, dim=0)
参数:
- tensor (Tensor) – 待分割张量
- split_size (int) – 单个分块的形状大小
- dim (int) – 沿着此维进行分割
将输入张量分割成相等形状的chunks(如果可分)。 如果沿指定维的张量形状大小不能被split_size 整分, 则最后一个分块会小于其它分块。
torch.chunk
torch.chunk(tensor, chunks, dim=0)
参数:
- tensor (Tensor) :待分块的输入张量
- chunks (int) : 分块的个数
- dim (int) :沿着此维度进行分块
>>> b=torch.rand(32,8)
>>> a=torch.rand(32,8)
>>> c=torch.stack([a,b],0)
>>> c.shape
torch.Size([2, 32, 8])
>>> aa,bb=c.split([1,1],dim=0)#具体有两个块,每个块的len由[1,1]指定
>>> aa.shape,bb.shape
(torch.Size([1, 32, 8]), torch.Size([1, 32, 8]))
>>> aa,bb=c.split(1,dim=0) #每个块的len为1
>>>
>>> aa.shape,bb.shape
(torch.Size([1, 32, 8]), torch.Size([1, 32, 8]))
>>> aa,bb=c.split(2,dim=0) #只能拆成一个tensor,不能用两个tensor接受
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: not enough values to unpack (expected 2, got 1)
>>> aa,bb=c.chunk(2,dim=0) #快数为2
>>> aa.shape,bb.shape
(torch.Size([1, 32, 8]), torch.Size([1, 32, 8]))
ctorch.Cat
torch.cat(inputs, dimension=0) → Tensor
参数:
- inputs (sequence of Tensors) :可以是任意相同Tensor 类型的python 序列
- dimension (int, optional) :沿着此维度连接张量序列。
在给定维度上对输入的张量序列seq 进行连接操作。torch.cat()可以看做 torch.split() 和 torch.chunk()的反操作。

>>> a=torch.rand(4,32,8)
>>> b=torch.rand(5,32,8)
>>> torch.cat([a,b],dim=0).shape
torch.Size([9, 32, 8])
>>> x = torch.randn(2,3)
>>> x
tensor([[-0.1026, 0.9607, -0.5655],
[-0.0174, 2.6582, 2.0188]])
>>> torch.cat((x,x,x),0)
tensor([[-0.1026, 0.9607, -0.5655],
[-0.0174, 2.6582, 2.0188],
[-0.1026, 0.9607, -0.5655],
[-0.0174, 2.6582, 2.0188],
[-0.1026, 0.9607, -0.5655],
[-0.0174, 2.6582, 2.0188]])
>>> torch.cat((x,x,x),1)
tensor([[-0.1026, 0.9607, -0.5655, -0.1026, 0.9607, -0.5655, -0.1026, 0.9607,
-0.5655],
[-0.0174, 2.6582, 2.0188, -0.0174, 2.6582, 2.0188, -0.0174, 2.6582,
2.0188]])
#####cat和stack
>>> a.shape
torch.Size([32, 8])
>>> b=torch.rand([30,8])
>>> torch.stack([a,b],dim=0) #stack作拼接是增加新的维度,需要a b两个张量的维度形状完全一致
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
RuntimeError: invalid argument 0: Sizes of tensors must match except in dimension 0. Got 32 and 30 in dimension 1 at /pytorch/aten/src/TH/generic/THTensor.cpp:689
>>> torch.cat([a,b],dim=0).shape#cat是在指定维度上作拼接
torch.Size([62, 8])


torch.gather
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None) → Tensor
参数:
- input (Tensor) – 源张量
- dim (int) – 索引的轴
- index (LongTensor) – 聚合元素的下标
- out (Tensor, optional) – 目标张量
沿给定轴dim,将输入索引张量index指定位置的值进行聚合。
对一个3维张量,输出的定义:
out[i][j][k] = tensor[index[i][j][k]][j][k] # dim=0,行
out[i][j][k] = tensor[i][index[i][j][k]][k] # dim=1,列
out[i][j][k] = tensor[i][j][index[i][j][k]] # dim=3
example:
>>> t=torch.Tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
>>> t.shape
torch.Size([2, 2])
>>> torch.gather(t,1,torch.LongTensor([[0,0],[1,0]]))
tensor([[1., 1.],
[4., 3.]])
>>> torch.gather(t,1,torch.LongTensor([[0,1],[1,0]]))
tensor([[1., 2.],
[4., 3.]])
>>> torch.gather(t,0,torch.LongTensor([[0,1],[1,0]]))
tensor([[1., 4.],
[3., 2.]])
>>> torch.gather(t,0,torch.LongTensor([[0,0],[1,0]]))
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 2.]])
三、数学运算
- Add/minus/multiply/divide
- Matmul(矩阵式相乘)
- Pow
- Sqrt/rsqrt
- Round
basic(+ - * / add sub mul div)
建议直接使用运算符
>>> a=torch.rand(3,4)
>>> b=torch.rand(4) #broadingcast机制
>>> a+b
tensor([[0.2349, 1.7635, 1.4385, 0.5826],
[0.7362, 0.9101, 0.9326, 0.7863],
[0.2260, 1.1575, 0.4948, 0.4016]])
>>> torch.add(a,b)
tensor([[0.2349, 1.7635, 1.4385, 0.5826],
[0.7362, 0.9101, 0.9326, 0.7863],
[0.2260, 1.1575, 0.4948, 0.4016]])
>>> torch.all(torch.eq(a-b,torch.sub(a,b)))
tensor(True)
>>> torch.all(torch.eq(a*b,torch.mul(a,b)))
tensor(True)
>>> torch.all(torch.eq(a/b,torch.div(a,b)))
tensor(True)
matmul
- Torch.mm(only for 2d 不推荐)
- Torch.matmul(推荐)
- @
注意:①*是element-wise,对应元素相乘;②.matmul是矩阵相乘

Example:
>>> a=torch.rand(4,784)
>>> x=torch.rand(4,784)
>>> w=torch.rand(512,784) #pytorch写法:第一个维度为ch-out(降维的维度),第二个维度为ch-in()
>>> (x@w.t()).shape #w若是高维矩阵,则使用transpose进行转置
torch.Size([4, 512])
#### matiple dims(支持多个矩阵并行相乘)
>>> a=torch.rand(4,3,28,64)
>>> b=torch.rand(4,3,64,32)
>>> torch.matmul(a,b).shape
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 32])
>>> b=torch.rand(4,1,64,32) #broadingcast和矩阵相乘相结合
>>> torch.matmul(a,b).shape
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 32])
>>> b=torch.rand(4,64,32)
>>> torch.matmul(a,b).shape
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (3) must match the size of tensor b (4) at non-singleton dimension 1
Power
>>> a=torch.full([2,2],3)
>>> a.pow(2)
tensor([[9., 9.],
[9., 9.]])
>>> a**2
tensor([[9., 9.],
[9., 9.]])
>>> aa=a**2
>>> aa.sqrt()
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
>>> aa.rsqrt() ##倒数
tensor([[0.3333, 0.3333],
[0.3333, 0.3333]])
>>> aa**0.5
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
>>> aa**0.25
Exp log

近似值
- .floor(向下取整).ceil(向上取整)
- .round(四舍五入)
- .trunc(整数部分).frac(小数部分)

torch.clamp
- gradient clipping
- (min)
- (min,max)
>>> grad=torch.rand(2,3)*15
>>> grad.max()
tensor(11.2428)
>>> grad.median()
tensor(3.1227)
>>> grad.clamp(10) #小于10的数用10代替
tensor([[10.0000, 10.0000, 10.0000],
[10.0000, 10.0000, 11.2428]])
>>> grad
tensor([[ 3.5420, 8.3126, 1.7083],
[ 0.2245, 3.1227, 11.2428]])
>>> grad.clamp(0,10)#返回一个在0到10之间的张量,大于10的用10代替
tensor([[ 3.5420, 8.3126, 1.7083],
[ 0.2245, 3.1227, 10.0000]])
四、统计属性(statistics)
- norm
- mean sum
- prod
- max min argmin(最小值的index) argmax(最大值的index)
- kthvalue,topk
norm
- vs normalize/batch_norm
- matrix norm vs vector norm

norm-p

>>> a=torch.full([8],1)
>>> b=a.view(2,4)
>>> c=a.view(2,2,2)
>>> b
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
>>> b.norm(1,dim=1)
tensor([4., 4.])
>>> b.norm(1,dim=0)
tensor([2., 2., 2., 2.])
>>>
>>> c.norm(1,dim=0)
tensor([[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]])
>>> c.norm(2,dim=0)
tensor([[1.4142, 1.4142],
[1.4142, 1.4142]])
>>> c.norm(1,dim=1)
tensor([[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]])

argmin argmax
>>> a=torch.randn(4,10)
>>> a.argmax()
tensor(19)
>>> a.argmax(dim=1)
tensor([9, 9, 7, 2])
dim keepdim

Top-k(排在前k的)/k-thvalue(第k小的值)
>>> a=torch.rand(4,10)
>>> a
tensor([[0.0558, 0.5948, 0.5399, 0.1482, 0.6319, 0.7229, 0.3600, 0.1825, 0.7594,
0.8119],
[0.2995, 0.2717, 0.0817, 0.2484, 0.3984, 0.6939, 0.5643, 0.2380, 0.5323,
0.1330],
[0.3299, 0.8043, 0.6704, 0.8987, 0.7656, 0.5682, 0.3257, 0.7047, 0.5247,
0.3946],
[0.7960, 0.7122, 0.8428, 0.7559, 0.2872, 0.1691, 0.1877, 0.4244, 0.7347,
0.9397]])
>>> a.topk(3,dim=1)
torch.return_types.topk(
values=tensor([[0.8119, 0.7594, 0.7229],
[0.6939, 0.5643, 0.5323],
[0.8987, 0.8043, 0.7656],
[0.9397, 0.8428, 0.7960]]),
indices=tensor([[9, 8, 5],
[5, 6, 8],
[3, 1, 4],
[9, 2, 0]]))
>>> a.topk(3,dim=1,largest=False)
torch.return_types.topk(
values=tensor([[0.0558, 0.1482, 0.1825],
[0.0817, 0.1330, 0.2380],
[0.3257, 0.3299, 0.3946],
[0.1691, 0.1877, 0.2872]]),
indices=tensor([[0, 3, 7],
[2, 9, 7],
[6, 0, 9],
[5, 6, 4]]))
>>> a.kthvalue(8,dim=1) #第8小的值,也就是第三大的值
torch.return_types.kthvalue(
values=tensor([0.7229, 0.5323, 0.7656, 0.7960]),
indices=tensor([5, 8, 4, 0]))
>>> a.kthvalue(3)
torch.return_types.kthvalue(
values=tensor([0.1825, 0.2380, 0.3946, 0.2872]),
indices=tensor([7, 7, 9, 4]))
>>> a.kthvalue(3,dim=1)
torch.return_types.kthvalue(
values=tensor([0.1825, 0.2380, 0.3946, 0.2872]),
indices=tensor([7, 7, 9, 4]))
compare
>、>=、<、<=、!=、==- torch.eq(a,b)
- torch.equal(a,b)
>>> a.shape
torch.Size([4, 10])
>>> a
tensor([[0.0558, 0.5948, 0.5399, 0.1482, 0.6319, 0.7229, 0.3600, 0.1825, 0.7594,
0.8119],
[0.2995, 0.2717, 0.0817, 0.2484, 0.3984, 0.6939, 0.5643, 0.2380, 0.5323,
0.1330],
[0.3299, 0.8043, 0.6704, 0.8987, 0.7656, 0.5682, 0.3257, 0.7047, 0.5247,
0.3946],
[0.7960, 0.7122, 0.8428, 0.7559, 0.2872, 0.1691, 0.1877, 0.4244, 0.7347,
0.9397]])
>>> a>0
tensor([[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True]])
>>> torch.gt(a,0)
tensor([[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True]])
>>> a!=0
tensor([[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True]])
>>> a=torch.ones(2,3)
>>> b=torch.randn(2,3)
>>> torch.eq(a,b)
tensor([[False, False, False],
[False, False, False]])
>>> torch.eq(a,a)
tensor([[True, True, True],
[True, True, True]])
>>> torch.equal(a,a)
True
五、高阶OP
Tensor advanceed operation
- where
- Gather
whree


gather


