一、@Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
1、Caching接口源码:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Inherited @Documented public @interface Caching { Cacheable[] cacheable() default {}; CachePut[] put() default {}; CacheEvict[] evict() default {}; }
2、@Caching使用案例:
在上节的基础上service添加一个根据lastName查询employee的方法
@Caching( cacheable = { @Cacheable(value = "emp",key = "#lastName") }, put = { @CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.id"), @CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.email") } ) //此时会将id、email、lastname分别作为key的之后的数据都加载缓存中 /*但这个根据lastName查询employee的方法每次查询都会执行,不会从缓存中取; 因为有@CachePut;CachePut是把方法执行后的结果放入缓存;所以方法必须执行*/ public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){ Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName); return emp; }
employeeMapper中添加相应的sql映射
@Select("select * from employee where last_name = #{lastName}")
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName);
employeeController中定义方法
@RestController public class EmployeeController { @Autowired EmployeeService employeeService; @GetMapping("/emp/{id}") public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ Employee emp = employeeService.getEmp(id); return emp; } @GetMapping("/emp") public Employee updateEmployee(Employee employee){ Employee emp = employeeService.updateEmp(employee); return emp; } @GetMapping("/delEmp") public String deleteEmployee(Integer id){ employeeService.deleteEmp(id); return "success"; } @GetMapping("/emp/lastName/{lastName}") public Employee getEmpByLastName(@PathVariable("lastName") String lastName){ Employee emp = employeeService.getEmpByLastName(lastName); return emp; } }
测试步骤:
重启项目,先在浏览器访问根据lastName查询的链接
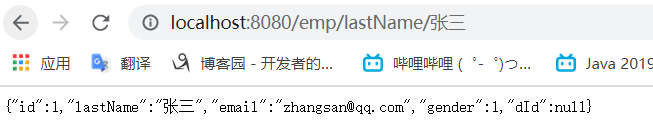
发出sql进行查询(此时将id、email、lastname分别作为key的之后的数据都加载缓存中)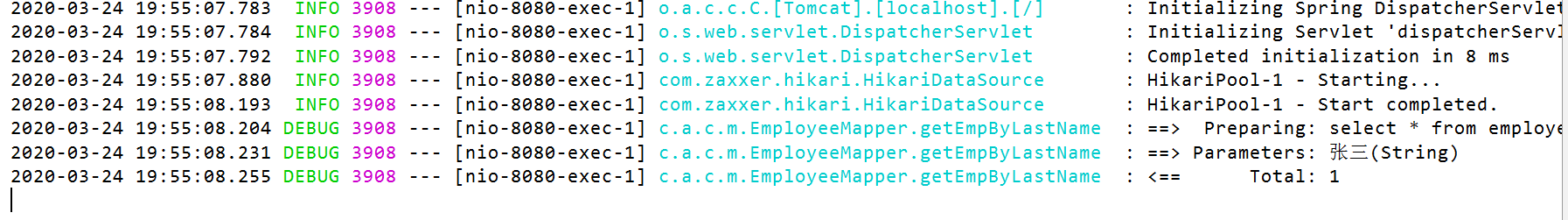
再根据id查询张三这个员工:(此时控制台没有发出sql,说明是从缓存中查询的)

但是我们再根据lastName为张三进行查询,还是发出了sql进行查询,不会从缓存中取;因为有配置了@CachePut;CachePut是把方法执行后的结果放入缓存;所以方法必须执行
二、@CacheConfig:指定某个类中缓存的公共配置,就不用一个一个方法配置
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface CacheConfig { String[] cacheNames() default {}; String keyGenerator() default ""; String cacheManager() default ""; String cacheResolver() default ""; }
在类上中进行配置:
