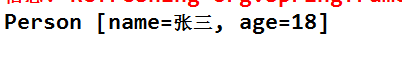1、创建Person类
public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person() { super(); } public Person(String name, Integer age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
2、spring配置类中注入Person
/** * 测试bean的属性赋值的配置 */ @Configuration public class MainConfigOfPropertyValue { @Bean("person") public Person person() { return new Person(); } }
3、创建测试方法测试
@Test public void test01() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfPropertyValue.class); Object bean = applicationContext.getBean("person"); System.out.println(bean); }
得到结果:

4、此时我们利用@Value进行赋值,修改Person类
public class Person { /* * 使用@Value赋值: * 1、基本数值 * 2、可以写SpEl;#{} * 3、可以写${}、取出配置文件中(例如properties文件)的值(运行环境变量里面的值) */ @Value("张三") private String name; @Value("#{20-2}") private Integer age; public Person() { super(); } public Person(String name, Integer age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
再次运行测试方法得到: