2019-10-29 18:53:13
一丶概览
json-simp是一个方便java的json处理,提供了解码或编码json的功能
二丶功能
. 使用轻量级的库来解码/解析和转换JSON文本
. 灵活,简单并且易于被Map和List接口重用;
. 支持流式的JSON文本输出;
. 高性能;
. 不依赖其它的库;
. 所有的代码和执行文件都和JDK 1.2兼容
.支持json数组的解码和编码
三丶使用
1.创建一个java工程
.在工程中导入json-simple的jar包
.右键工程选build path

然后点configure....
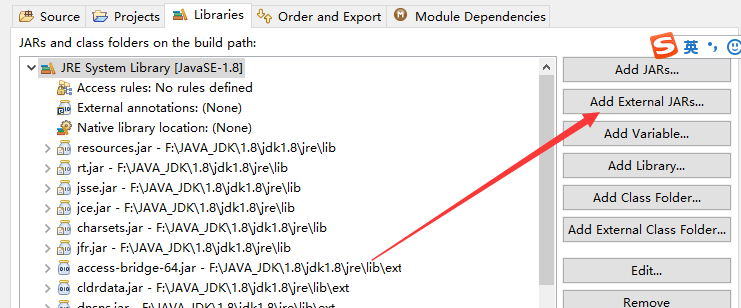
.或者直接使用maven导入
<dependency>
<groupId>com.googlecode.json-simple</groupId>
<artifactId>json-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
2.解析json数据
. 普通json解析
package com.lxl.learn.json; import org.json.simple.JSONObject; import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser; public class json { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String test_json = "{"temp":"27.9度","city":"北京","weather":"多云转阴","WS":"小于3级","temp2":"31℃","WD":"南风","temp1":"18℃"}"; JSONObject json = (JSONObject) new JSONParser().parse(test_json); System.out.println("城市:"+json.get("city").toString()); System.out.println("温度:"+json.get("temp").toString()); /* 输出 * 城市:北京 * 温度:27.9度 */ } }
. json数组解析
package com.lxl.learn.json; import org.json.simple.JSONArray; import org.json.simple.JSONObject; import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser; public class json { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String data = ""+ "[ " + "{"city":"北京","temp":"27.9","WD":"南风","WS":"小于3级","temp1":"18℃","temp2":"31℃","weather":"多云转阴"}, " + "{"city":"广州","temp":"26.6","WD":"东南风","WS":"小于3级","temp1":"26℃","temp2":"29℃","weather":"阵雨转暴雨"}, " + "{"city":"广元","temp":"24.8","WD":"北风","WS":"小于3级","temp1":"16℃","temp2":"28℃","weather":"阴转多云"}, " + "{"city":"达州","temp":"20.2","WD":"南风","WS":"小于3级","temp1":"17℃","temp2":"27℃","weather":"阵雨转多云"} " + "]"; //json解析数组 JSONArray dataArr = (JSONArray) new JSONParser().parse(data); //得到数组下标0,这里得到的数据可以直接强转换为JSONObject(特此记一下) JSONObject firstData = (JSONObject) dataArr.get(0); System.out.println("城市:"+firstData.get("city").toString()); System.out.println("温度:"+firstData.get("temp").toString()); /* 输出 * 城市:北京 * 温度:27.9 */ } }
.json的多级解析,(更多级类似)
package com.lxl.learn.json; import org.json.simple.JSONArray; import org.json.simple.JSONObject; import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser; public class json { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String data = "{"data":[ " + "{"city":"北京","temp":"27.9","WD":"南风","WS":"小于3级","temp1":"18℃","temp2":"31℃","weather":"多云转阴"}, " + "{"city":"广州","temp":"26.6","WD":"东南风","WS":"小于3级","temp1":"26℃","temp2":"29℃","weather":"阵雨转暴雨"} " + "]}"; //转换json JSONObject json_data = (JSONObject) new JSONParser().parse(data); //得到data的数组 JSONArray dataArr = (JSONArray) json_data.get("data"); //得到数组下标0 JSONObject firstData = (JSONObject) dataArr.get(0); System.out.println("城市:"+firstData.get("city").toString()); System.out.println("温度:"+firstData.get("temp").toString()); /* 输出 * 城市:北京 * 温度:27.9 */ } }
3.编码数据
.构造普通json
package com.lxl.learn.json; import org.json.simple.JSONObject; public class json { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { JSONObject json = new JSONObject(); json.put("city", "北京"); json.put("temp", "27.9度"); System.out.println(json.toJSONString());
/*
* 输出: {"temp":"27.9度","city":"北京"}
*
*/
} }
.构造数组json
package com.lxl.learn.json; import org.json.simple.JSONArray; import org.json.simple.JSONObject; public class json { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { JSONArray dataArr = new JSONArray(); //第一项数据 JSONObject json1 = new JSONObject(); json1.put("city", "北京"); json1.put("temp", "27.9度"); dataArr.add(json1); JSONObject json2 = new JSONObject(); json2.put("city", "广州"); json2.put("temp", "19.5度"); dataArr.add(json2); System.out.println(dataArr.toJSONString()); /* * 输出 * [{"temp":"27.9度","city":"北京"},{"temp":"19.5度","city":"广州"}] */ } }
.使用Map构造json
package com.lxl.learn.json; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.json.simple.JSONValue; public class json { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Map json1 = new LinkedHashMap(); json1.put("city", "北京"); json1.put("temp", "27.9度"); json1.put("temp1", "13度"); json1.put("temp2", "30度"); String data = new JSONValue().toJSONString(json1); System.out.println(data); /* * 输出 * {"city":"北京","temp":"27.9度","temp1":"13","temp2":"30度"} */ } }
.使用List构造json数组
package com.lxl.learn.json; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import org.json.simple.JSONObject; import org.json.simple.JSONValue; public class json { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //这里使用map构造普通json也一样 JSONObject obj1 = new JSONObject(); obj1.put("city", "北京"); obj1.put("temp", "29.7"); JSONObject obj2 = new JSONObject(); obj2.put("city", "广州"); obj2.put("temp", "19"); List li = new LinkedList(); li.add(obj1.toJSONString()); li.add(obj2.toJSONString()); String json = new JSONValue().toJSONString(li); System.out.println(json); /* * 输出 * ["{"temp":"29.7","city":"北京"}","{"temp":"19","city":"广州"}"] */ } }
四丶其他
只是对json的简单使用,里面还有合并json数组或者json。分别调用putall方法即可