学习目标:学习V4L2(V4L2:vidio for linux version 2)摄像头驱动框架,分析vivi.c(虚拟视频硬件相关)驱动源码程序,总结V4L2硬件相关的驱动的步骤;
一、V4L2架构
1. 字符类驱动
V4L2(V4L2:vidio for linux version 2)摄像头驱动属于字符类驱动,
对于一般的字符类驱动程序,其编写步骤一般分为:
1)构造一个file_operations: 编写open=drv_open .read=drv_read
2)注册设备,告诉内核:register_chrdev(主设备号,名字,&file_operations)
3)入口函数:调用register_chrdev
4)出口函数:卸载
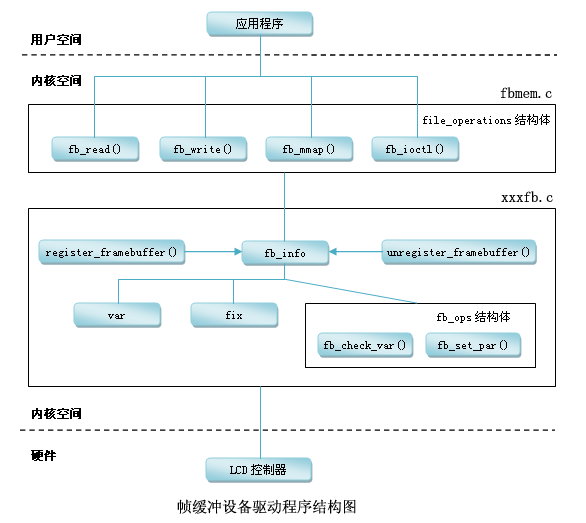
对于复杂的字符类驱动程序,其程序是一种分层结构。例如LCD驱动程序。如下图所示。
--> 上层为核心层(内核已经做好的),在fbmem.c中 ,主要的作用为:
1)构造file_operations(open read write 函数);2)注册;3)入口、出口。
--> 硬件相关层(用户需要做的),供核心层的file_operations调用,主要完成:
1) 分配一个fb_info 结构体;2) 设置fb_info 结构体等;3) 注册;4) 硬件相关的操作。
2. V4L2驱动架构
由以上字符类设备驱动架构可知,摄像头驱动也是分层结构的。
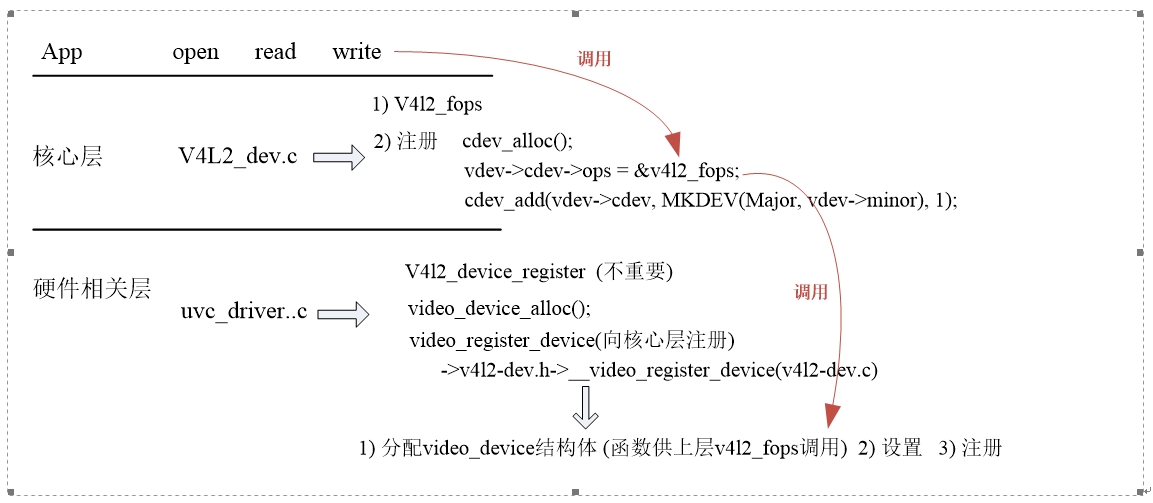
其中,ucv_driver.c中,定义了uvc_driver结构体,根据ucv_ids查找匹配的设备,如果支持,则会进入probe函数
1 struct uvc_driver uvc_driver = { 2 .driver = { 3 .name = "uvcvideo", 4 .probe = uvc_probe, 5 .disconnect = uvc_disconnect, 6 .suspend = uvc_suspend, 7 .resume = uvc_resume, 8 .reset_resume = uvc_reset_resume, 9 .id_table = uvc_ids, 10 .supports_autosuspend = 1, 11 }, 12 };
二. vivi.c虚拟视频驱动程序架构
由于V4L2驱动程序是一种分层架构,用户只需要完成硬件相关驱动程序即可。这里主要以vivi虚拟视频驱动程序为例分析源码的调用过程和框架。
1. 进入入口的vivi_init(void)函数:
1 static int __init vivi_create_instance(int inst) 2 { 3 struct vivi_dev *dev; 4 struct video_device *vfd; //video_device结构体定义 5 struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *hdl; 6 struct vb2_queue *q; 7 int ret; 8 9 dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL); 10 if (!dev) 11 return -ENOMEM; 12 13 snprintf(dev->v4l2_dev.name, sizeof(dev->v4l2_dev.name), 14 "%s-%03d", VIVI_MODULE_NAME, inst); 15 ret = v4l2_device_register(NULL, &dev->v4l2_dev); 16 if (ret) 17 goto free_dev; 18 //摄像头相关属性设置 19 dev->fmt = &formats[0]; 20 dev->width = 640; 21 dev->height = 480; 22 hdl = &dev->ctrl_handler; 23 v4l2_ctrl_handler_init(hdl, 11); 24 dev->volume = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 25 V4L2_CID_AUDIO_VOLUME, 0, 255, 1, 200); 26 dev->brightness = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 27 V4L2_CID_BRIGHTNESS, 0, 255, 1, 127); 28 dev->contrast = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 29 V4L2_CID_CONTRAST, 0, 255, 1, 16); 30 dev->saturation = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 31 V4L2_CID_SATURATION, 0, 255, 1, 127); 32 dev->hue = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 33 V4L2_CID_HUE, -128, 127, 1, 0); 34 dev->autogain = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 35 V4L2_CID_AUTOGAIN, 0, 1, 1, 1); 36 dev->gain = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 37 V4L2_CID_GAIN, 0, 255, 1, 100);
55 /* initialize queue */ 56 q = &dev->vb_vidq; 57 memset(q, 0, sizeof(dev->vb_vidq)); 58 q->type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; 59 q->io_modes = VB2_MMAP | VB2_USERPTR | VB2_READ; 60 q->drv_priv = dev; 61 q->buf_struct_size = sizeof(struct vivi_buffer); 62 q->ops = &vivi_video_qops; 63 q->mem_ops = &vb2_vmalloc_memops; 64 65 vb2_queue_init(q); 66 67 mutex_init(&dev->mutex); 68 69 /* init video dma queues */ 70 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->vidq.active); 71 init_waitqueue_head(&dev->vidq.wq); 72 73 ret = -ENOMEM;
//分配video_device结构体 74 vfd = video_device_alloc(); 75 if (!vfd) 76 goto unreg_dev; 77 //设置 78 *vfd = vivi_template;
/******************************************************************
其中,以赋值的方式进行设置vfd,进入vivi_template:
.name = "vivi",
.fops = &vivi_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &vivi_ioctl_ops,
.release = video_device_release,
.current_norm = V4L2_STD_NTSC_M,
};
*******************************************************************// 79 vfd->debug = debug; 80 vfd->v4l2_dev = &dev->v4l2_dev; 81 set_bit(V4L2_FL_USE_FH_PRIO, &vfd->flags); 82 83 /* 84 * Provide a mutex to v4l2 core. It will be used to protect 85 * all fops and v4l2 ioctls. 86 */ 87 vfd->lock = &dev->mutex; 88 //注册 89 ret = video_register_device(vfd, VFL_TYPE_GRABBER, video_nr);
93 video_set_drvdata(vfd, dev); 94 95 /* Now that everything is fine, let's add it to device list */ 96 list_add_tail(&dev->vivi_devlist, &vivi_devlist); 97 101 dev->vfd = vfd; 102 v4l2_info(&dev->v4l2_dev, "V4L2 device registered as %s ", 103 video_device_node_name(vfd)); 104 return 0;
107 video_device_release(vfd);110 v4l2_device_unregister(&dev->v4l2_dev);114 }
vivi_init函数的调用结构如下:
vivi_init
-->vivi_create_instance
-->v4l2_device_register // 不是主要, 只是用于初始化一些东西,比如自旋锁、引用计数
vfd = video_device_alloc(); //分配video_device结构体
1. *vfd = vivi_template; // 设置
.fops = &vivi_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &vivi_ioctl_ops,
.release = video_device_release,
2. vfd->v4l2_dev = &dev->v4l2_dev;
3. 设置"ctrl属性"(用于APP的ioctl):
v4l2_ctrl_handler_init(hdl, 11);
dev->volume = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops,
V4L2_CID_AUDIO_VOLUME, 0, 255, 1, 200);
dev->brightness = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops,
V4L2_CID_BRIGHTNESS, 0, 255, 1, 127);
dev->contrast = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops,
V4L2_CID_CONTRAST, 0, 255, 1, 16);
4. video_register_device(vfd, VFL_TYPE_GRABBER, video_nr); //注册
--> __video_register_device(vdev, type, nr, 1, vdev->fops->owner);
-->vdev->cdev = cdev_alloc(); (v4l2.dev.c程序中)
vdev->cdev->ops = &v4l2_fops;
cdev_add(vdev->cdev, MKDEV(VIDEO_MAJOR, vdev->minor), 1);
2. vivi.c的open,read,write,ioctl过程
1 static const struct v4l2_file_operations vivi_fops = { 2 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 3 .open = v4l2_fh_open, 4 .release = vivi_close, 5 .read = vivi_read, 6 .poll = vivi_poll, 7 .unlocked_ioctl = video_ioctl2, /* V4L2 ioctl handler */ 8 .mmap = vivi_mmap, 9 };
1)open
app: open("/dev/video0",....)向下层调用
-------------------------------------------------------------------
drv: v4l2_fops.v4l2_open
vdev = video_devdata(filp); // 根据次设备号从数组中得到video_device
return video_device[iminor(file->f_path.dentry->d_inode)];
if (vdev->fops->open) //如果有open函数
if (video_is_registered(vdev))
ret = vdev->fops->open(filp);//调用open 函数
调用vivi.c 里的v4l2_fh_open函数
2)read
app: read("/dev/video0",....)向下层调用
-------------------------------------------------------------------
drv: v4l2_fops.v4l2_read
struct video_device *vdev = video_devdata(filp);
if (video_is_registered(vdev))
ret = vdev->fops->read(filp, buf, sz, off);
调用vivi.c 里的vivi_read
app: ioctl
----------------------------------------------------
drv: v4l2_fops.unlocked_ioctl => v4l2_ioctl
struct video_device *vdev = video_devdata(filp);
if (video_is_registered(vdev))
ret = vdev->fops->unlocked_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
调用vivi.c 里的video_ioctl2
video_usercopy(file, cmd, arg, __video_do_ioctl); //从用户空间把用户的命令cmd复制进来,调用__video_do_ioctl
__video_do_ioctl
struct video_device *vfd = video_devdata(file); //根据次设备号从数组中得到video_device
switch (cmd) { ..... // 根据APP传入的cmd来获得、设置"某些属性"
{
struct v4l2_queryctrl *p = arg;
if (vfh && vfh->ctrl_handler)
ret = v4l2_queryctrl(vfh->ctrl_handler, p);
else if (vfd->ctrl_handler) // 在video_register_device设置 vivi_create_instance-->hdl = &dev->ctrl_handler; v4l2_ctrl_handler_init(hdl, 11);
ret = v4l2_queryctrl(vfd->ctrl_handler, p); // 根据ID在ctrl_handler里找到v4l2_ctrl,返回它的值
1 hdl = &dev->ctrl_handler; 2 v4l2_ctrl_handler_init(hdl, 11); 3 dev->volume = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 4 V4L2_CID_AUDIO_VOLUME, 0, 255, 1, 200); 5 dev->brightness = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 6 V4L2_CID_BRIGHTNESS, 0, 255, 1, 127); 7 dev->contrast = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 8 V4L2_CID_CONTRAST, 0, 255, 1, 16); 9 dev->saturation = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 10 V4L2_CID_SATURATION, 0, 255, 1, 127); 11 dev->hue = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 12 V4L2_CID_HUE, -128, 127, 1, 0); 13 dev->autogain = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 14 V4L2_CID_AUTOGAIN, 0, 1, 1, 1); 15 dev->gain = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 16 V4L2_CID_GAIN, 0, 255, 1, 100);
三、怎么写v4l2驱动?
1. 分配、设置、注册:v4l2_device --》 v4l2_device_register()(辅助作用,提供自旋锁、引用计数等功能)
2. 分配一个video_device:video_device_alloc()
3. 设置
1)vfd->v4l2_dev
2) .fops 设置vfd的fops 里的open、read、write 被上层调用
.ioctl_ops 设置属性被上层调用
3)注册:video_register_device()
4. 接下来,应用层App可以通过ioctl来设置(获得)亮度等某些属性,在驱动程序里,谁来接收、存储、设置到硬件(提供这些信息)?
在驱动程序中抽象出来一个结构体v4l2_ctrl,每个Ctrl对应其中的一项(音量、亮度等等);
v4l2_ctrl_handler来管理他们,在vivi.c的vivi_create_instance函数中:
1.初始化
v4l2_ctrl_handler_init
2.设置
v4l2_ctrl_new_std
v4l2_ctrl_new_custom
这些函数就是创建各个属性,并且放入v4l2_ctrl_handler的链表
3.跟vdev关联
dev->v4l2_dev.ctrl_handler = hdl;
1 static int __init vivi_create_instance(int inst) 2 { 3 struct vivi_dev *dev; 4 struct video_device *vfd; 5 struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *hdl; //定义v4l2_ctrl_handler结构体 6 struct vb2_queue *q; 7 int ret; 8 9 dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL); 10 if (!dev) 11 return -ENOMEM; 12 13 snprintf(dev->v4l2_dev.name, sizeof(dev->v4l2_dev.name), 14 "%s-%03d", VIVI_MODULE_NAME, inst); 15 ret = v4l2_device_register(NULL, &dev->v4l2_dev); 16 if (ret) 17 goto free_dev; 18 19 dev->fmt = &formats[0]; 20 dev->width = 640; 21 dev->height = 480; 22 hdl = &dev->ctrl_handler; 23 v4l2_ctrl_handler_init(hdl, 11); //初始化 24 dev->volume = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, //创建一个属性设置其值,并且放入v4l2_ctrl_handler的链表 25 V4L2_CID_AUDIO_VOLUME, 0, 255, 1, 200); 26 dev->brightness = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 27 V4L2_CID_BRIGHTNESS, 0, 255, 1, 127); 28 dev->contrast = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 29 V4L2_CID_CONTRAST, 0, 255, 1, 16); 30 dev->saturation = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 31 V4L2_CID_SATURATION, 0, 255, 1, 127); 32 dev->hue = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 33 V4L2_CID_HUE, -128, 127, 1, 0); 34 dev->autogain = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 35 V4L2_CID_AUTOGAIN, 0, 1, 1, 1); 36 dev->gain = v4l2_ctrl_new_std(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_ops, 37 V4L2_CID_GAIN, 0, 255, 1, 100); 38 dev->button = v4l2_ctrl_new_custom(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_button, NULL); 39 dev->int32 = v4l2_ctrl_new_custom(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_int32, NULL); 40 dev->int64 = v4l2_ctrl_new_custom(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_int64, NULL); 41 dev->boolean = v4l2_ctrl_new_custom(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_boolean, NULL); 42 dev->menu = v4l2_ctrl_new_custom(hdl, &vivi_ctrl_menu, NULL);
45 dev->v4l2_dev.ctrl_handler = hdl;
.........
}