1.背景
网卡接收一个数据包的情况下,会经过三个阶段:
- 网卡产生硬件中断通知CPU有包到达
- 通过软中断处理此数据包
- 在用户态程序处理此数据包
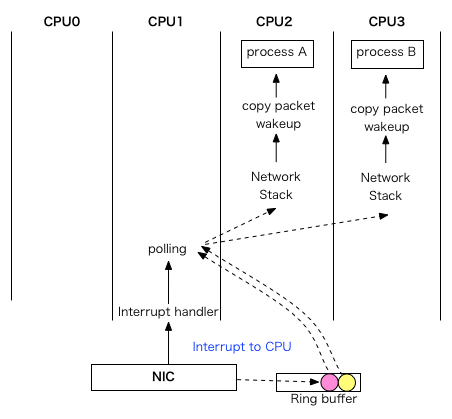
在SMP体系下,这三个阶段有可能在3个不同的CPU上处理,如下图所示:

而RFS的目标就是增加CPU缓存的命中率从而提高网络延迟。当使用RFS后,其效果如下:
2.实现原理
当用户程序调用 revmsg() 或者 sendmsg()的时候,RFS会将此用户程序运行的CPU id存入hash表;
而当有关用户程序的数据包到达的时候,RFS尝试从hash表中取出相应的CPU id, 并将数据包放置
到此CPU的队列,从而对性能进行优化。
3.重要数据结构

/* * The rps_sock_flow_table contains mappings of flows to the last CPU * on which they were processed by the application (set in recvmsg). */ struct rps_sock_flow_table { unsigned int mask; u16 ents[0]; }; #define RPS_SOCK_FLOW_TABLE_SIZE(_num) (sizeof(struct rps_sock_flow_table) + ((_num) * sizeof(u16)))
结构体 rps_sock_flow_table 实现了一个hash表,RFS会将其声明一个全局变量用于存放所有sock对应的CPU。

/* * The rps_dev_flow structure contains the mapping of a flow to a CPU, the * tail pointer for that CPU's input queue at the time of last enqueue, and * a hardware filter index. */ struct rps_dev_flow { u16 cpu; //此链路上次使用的cpu u16 filter; unsigned int last_qtail; //此设备队列入队的sk_buff的个数 }; #define RPS_NO_FILTER 0xffff /* * The rps_dev_flow_table structure contains a table of flow mappings. */ struct rps_dev_flow_table { unsigned int mask; struct rcu_head rcu; struct rps_dev_flow flows[0]; //实现hash表 }; #define RPS_DEV_FLOW_TABLE_SIZE(_num) (sizeof(struct rps_dev_flow_table) + ((_num) * sizeof(struct rps_dev_flow)))
结构体 rps_dev_flow_table 是针对一个设备队列
4.具体实现
用户程序使用revmsg() 或者 sendmsg()的时候 设置CPU id。

int inet_recvmsg(struct kiocb *iocb, struct socket *sock, struct msghdr *msg, size_t size, int flags) { struct sock *sk = sock->sk; int addr_len = 0; int err; sock_rps_record_flow(sk); //设置CPU id err = sk->sk_prot->recvmsg(iocb, sk, msg, size, flags & MSG_DONTWAIT, flags & ~MSG_DONTWAIT, &addr_len); if (err >= 0) msg->msg_namelen = addr_len; return err; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(inet_recvmsg);
当有数据包进行了响应后,会调用get_rps_cpu()选择合适的CPU id。其关键代码如下:

3117 hash = skb_get_hash(skb); 3118 if (!hash) 3119 goto done; 3120 3121 flow_table = rcu_dereference(rxqueue->rps_flow_table); //设备队列的hash表 3122 sock_flow_table = rcu_dereference(rps_sock_flow_table); //全局的hash表 3123 if (flow_table && sock_flow_table) { 3124 u16 next_cpu; 3125 struct rps_dev_flow *rflow; 3126 3127 rflow = &flow_table->flows[hash & flow_table->mask]; 3128 tcpu = rflow->cpu; 3129 3130 next_cpu = sock_flow_table->ents[hash & sock_flow_table->mask]; //得到用户程序运行的CPU id 3131 3132 /* 3133 * If the desired CPU (where last recvmsg was done) is 3134 * different from current CPU (one in the rx-queue flow 3135 * table entry), switch if one of the following holds: 3136 * - Current CPU is unset (equal to RPS_NO_CPU). 3137 * - Current CPU is offline. 3138 * - The current CPU's queue tail has advanced beyond the 3139 * last packet that was enqueued using this table entry. 3140 * This guarantees that all previous packets for the flow 3141 * have been dequeued, thus preserving in order delivery. 3142 */ 3143 if (unlikely(tcpu != next_cpu) && 3144 (tcpu == RPS_NO_CPU || !cpu_online(tcpu) || 3145 ((int)(per_cpu(softnet_data, tcpu).input_queue_head - 3146 rflow->last_qtail)) >= 0)) { 3147 tcpu = next_cpu; 3148 rflow = set_rps_cpu(dev, skb, rflow, next_cpu); 3149 } 3150 3151 if (tcpu != RPS_NO_CPU && cpu_online(tcpu)) { 3152 *rflowp = rflow; 3153 cpu = tcpu; 3154 goto done; 3155 } 3156 }
上面的代码中第3145行比较难理解,数据结构 softnet_data用于管理进出的流量,他有两个关键的变量:

2374 #ifdef CONFIG_RPS 2375 /* Elements below can be accessed between CPUs for RPS */ 2376 struct call_single_data csd ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp; 2377 struct softnet_data *rps_ipi_next; 2378 unsigned int cpu; 2379 unsigned int input_queue_head; //队列头,也可以理解为出队的位置 2380 unsigned int input_queue_tail; //队列尾,也可以理解为入队的位置 2381 #endif
表达式 (int)(per_cpu(softnet_data, tcpu).input_queue_head 求出了在tcpu 这个CPU上的出队数目,而rflow->last_qtail
代表设备队列上此sock对应的最后入队的位置,如果出队数目大于入队数目,那么说明这一链路上的包都处理完毕,不会
出现乱序处理的包。第3143的if 语句就是为了防止乱序包的出现,假如是多进程或者多线程同时处理一个socket,那么此
socket对应的CPU id就会不停变化。
参考文献:
