1123 Is It a Complete AVL Tree(30 分)
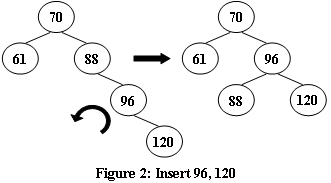
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
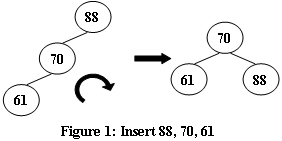 |  |
|---|---|
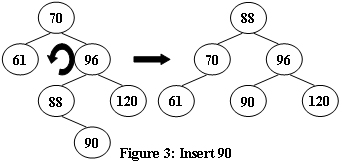 |
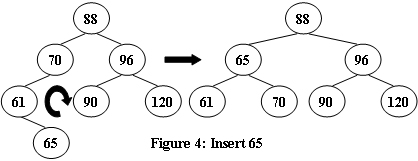 |
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 20). Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, insert the keys one by one into an initially empty AVL tree. Then first print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line. Then in the next line, print YES if the tree is complete, or NO if not.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 63 65
Sample Output 1:
70 63 88 61 65
YES
Sample Input 2:
8
88 70 61 96 120 90 65 68
Sample Output 2:
88 65 96 61 70 90 120 68
NO判断是否完全二叉树:
层序遍历时,若前面已经出现过空子树,而后面又发现了非空子树,则不是完全二叉树。
平衡二叉树的旋转:
1、右单旋
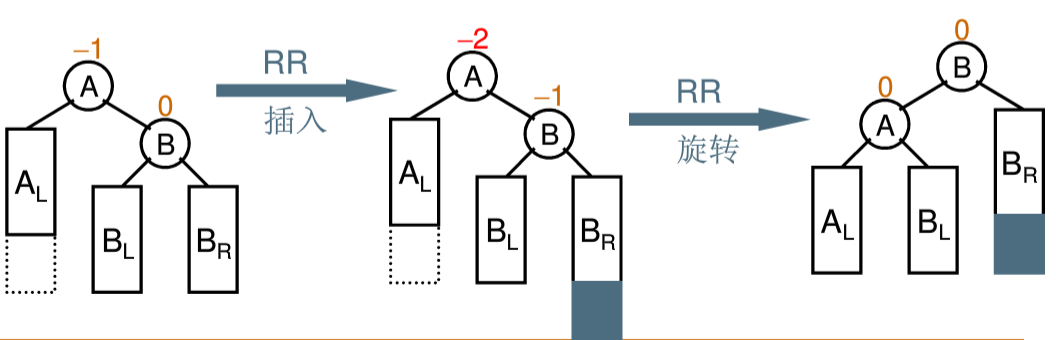
2、左单旋
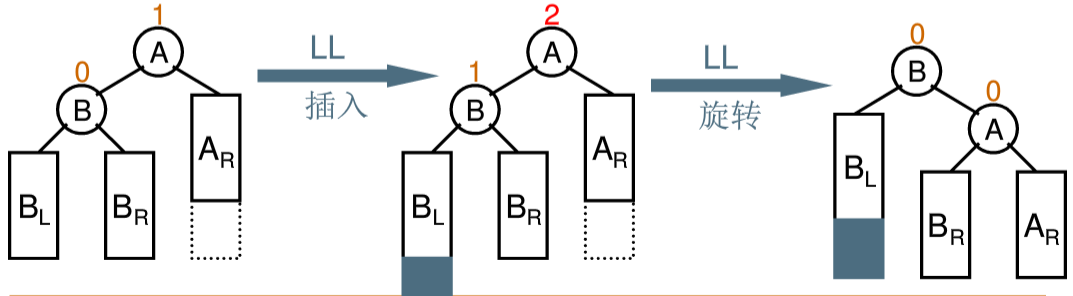
3、左右双旋
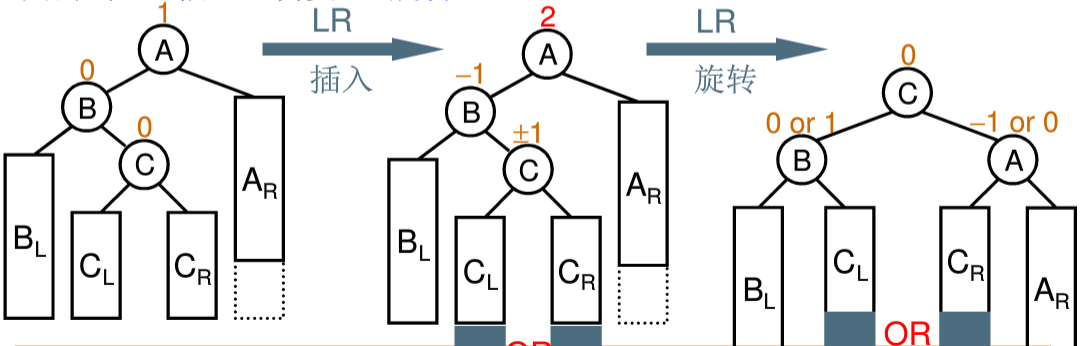
4、右左双旋
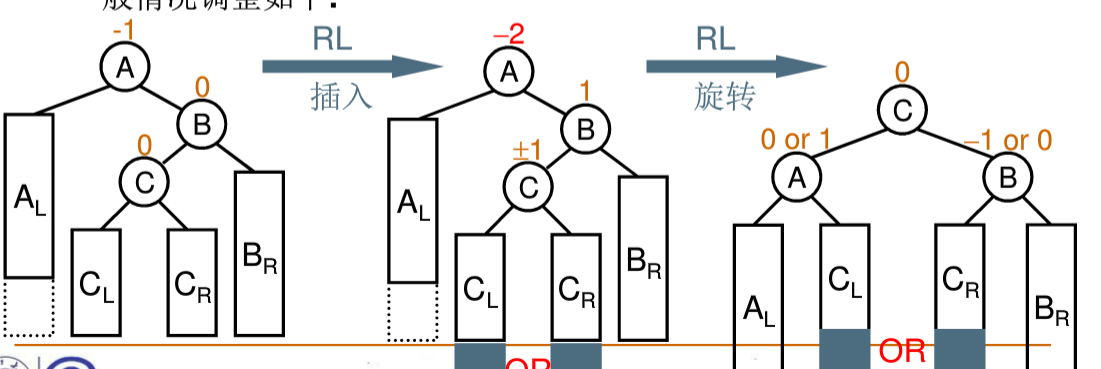
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <queue> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 typedef struct Node *Tree; 7 struct Node 8 { 9 int data; 10 Tree left; 11 Tree right; 12 }; 13 14 Tree insert(Tree T, int data); 15 int getHeight(Tree T); 16 Tree LL(Tree T); 17 Tree LR(Tree T); 18 Tree RR(Tree T); 19 Tree RL(Tree T); 20 vector<int> levelOrder(Tree T, bool& isComplete); 21 22 int main() 23 { 24 int N, i, t; 25 cin >> N; 26 Tree root = NULL; 27 for (i = 0; i < N; i++) 28 { 29 cin >> t; 30 root = insert(root, t); 31 } 32 bool isComplete; 33 vector<int> v = levelOrder(root, isComplete); 34 cout << v[0]; 35 for (i = 1; i < v.size(); i++) 36 cout << " " << v[i]; 37 printf(" %s", isComplete ? "YES" : "NO"); 38 return 0; 39 } 40 41 Tree insert(Tree T, int data) 42 { 43 if (T == NULL) 44 { 45 T = new Node; 46 T->data = data; 47 T->left = T->right = NULL; 48 } 49 else if (data < T->data) 50 { 51 T->left = insert(T->left, data); 52 if (getHeight(T->left) - getHeight(T->right) == 2) 53 { 54 if (data < T->left->data) 55 T = LL(T); 56 else 57 T = LR(T); 58 } 59 } 60 else 61 { 62 T->right = insert(T->right, data); 63 if (getHeight(T->right) - getHeight(T->left) == 2) 64 { 65 if (data > T->right->data) 66 T = RR(T); 67 else 68 T = RL(T); 69 } 70 } 71 return T; 72 } 73 74 int getHeight(Tree T) 75 { 76 if (T == NULL) return 0; 77 int a = getHeight(T->left); 78 int b = getHeight(T->right); 79 return (a > b) ? (a + 1) : (b + 1); 80 } 81 82 Tree LL(Tree T) 83 { 84 Tree tmp = T->left; 85 T->left = tmp->right; 86 tmp->right = T; 87 return tmp; 88 } 89 90 Tree LR(Tree T) 91 { 92 T->left = RR(T->left); 93 return LL(T); 94 } 95 96 Tree RR(Tree T) 97 { 98 Tree tmp = T->right; 99 T->right = tmp->left; 100 tmp->left = T; 101 return tmp; 102 } 103 104 Tree RL(Tree T) 105 { 106 T->right = LL(T->right); 107 return RR(T); 108 } 109 110 vector<int> levelOrder(Tree T, bool& isComplete) 111 { 112 vector<int> v; 113 isComplete = true; 114 queue<Tree> q; 115 q.push(T); 116 bool hasEmpty = false; 117 while (!q.empty()) 118 { 119 Tree T = q.front(); 120 q.pop(); 121 v.push_back(T->data); 122 if (T->left != NULL) 123 { 124 q.push(T->left); 125 //已经出现过空子树但是现在子树又不空,那么不是完全二叉树 126 if (hasEmpty) isComplete = false; 127 } 128 else 129 hasEmpty = true; 130 if (T->right != NULL) 131 { 132 q.push(T->right); 133 if (hasEmpty) isComplete = false; 134 } 135 else 136 hasEmpty = true; 137 } 138 return v; 139 }