考虑场景:
- 我们的自动化用例需要支持在不同测试环境运行,有时候在dev环境运行,有时候在test环境运行;
- 有时候需要根据某个参数不同的参数值,执行不同的业务逻辑;
上面的场景我们都可以通过“在命令行中输入参数,然后用例中接收这个参数,通过判断这个参数的值来做不同的逻辑”来实现。那么我们的需求就变为pytest中如何自定义一个命令行参数呢?这时候我们就需要用到pytest的钩子函数:pytest_addoption
通过conftest.py配置
新建一个conftest.py文件,然后在conftest.py文件中通过pytest_addoption方法来添加命令行参数,通过定义的fixture来获得参数的值。
# file_name: conftest.py import pytest def pytest_addoption(parser): parser.addoption( "--cmdopt", action="store", default="type1", help="my option: type1 or type2" ) parser.addoption( "--env", action="store", default="dev", help="env:表示测试环境,默认dev环境" ) @pytest.fixture() def cmdopt(pytestconfig): return pytestconfig.getoption("cmdopt") @pytest.fixture() def env(request): return request.config.getoption("--env")
上面conftest.py文件中新增了两个命令行参数:--cmdopt和--env;然后定义了两个fixture,在测试用例中想要获得参数--cmdopt的值,就可以调用cmdopt函数;调用env函数可以获取参数--env的值。
编写测试用例:
# file_name: test_option.py import pytest def test_option(env): if env == 'dev': print("当前测试环境为:{},域名切换为开发环境".format(env)) elif env == 'test': print("当前测试环境为:{},域名切换为测试环境".format(env)) else: print("环境错误,当前环境{}不存在".format(env)) if __name__ == '__main__': pytest.main(['-s', 'test_option.py'])
上面例子是获取env的值,针对env值的不同做不同的操作。
不带参数运行:
命令行中输入指令:pytest test_option.py -s,运行结果:
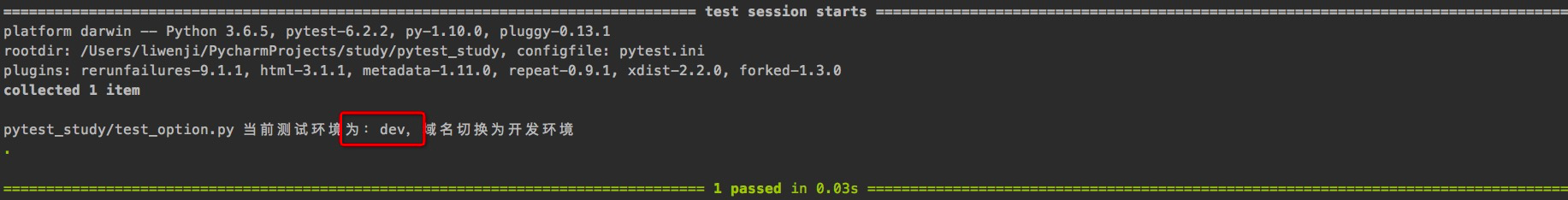
因为我们在conftest.py文件中定义的参数env的默认值为dev,所以当运行时命令行不传env参数,则使用默认值dev。
带参数运行:
命令行中输入指令:pytest test_option.py -s --env=test,运行结果:
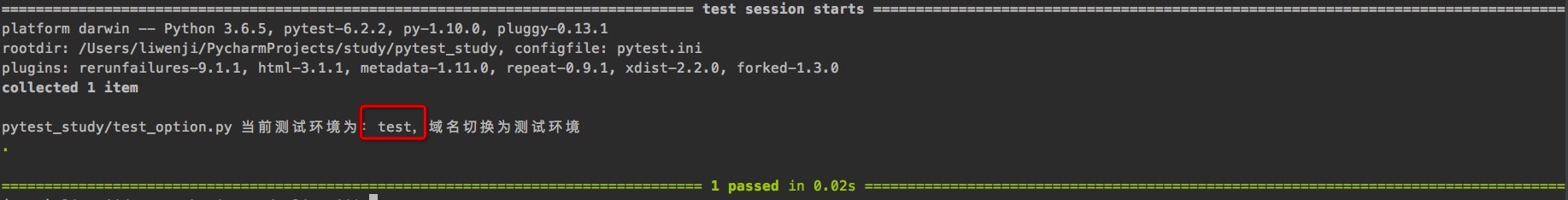
从结果中可以看到,命令行中输入参数env=test,在测试用例中获取到通过fixture获取到env的值为test。