http://www.php.cn/csharp-article-354819.html
1 indexer
[]声明的变量必须是固定长度的,即长度是静态的;object[] objectArray = new object[10];
objectArray是浅复制,即只在memory中给其赋一个地址值,此时每一item此时都是null引用;
应用举例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
AdjustablePanel[] adjustPanelArrays = new AdjustablePanel[12]; foreach (Control ultraControl in this.Controls) { if (ultraControl.GetType() == typeof(UltraGrid) || ultraControl.GetType() == typeof(UltraChart) || ultraControl.GetType() == typeof(Panel)) { //adjustPanelArrays[index]此时为null,因此会出现null引用bug adjustPanelArrays[index].Controls.Add(ultraControl); } } |
2 Array
提供创建、操作、搜索和排序数组的方法,因而在公共语言运行时用作所有数组的基类。长度是固定的,不能按需动态增加;Array 是抽象类,不能使用 new Array 创建;GetValue返回的是object类型。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
Array myArray = Array.CreateInstance(typeof(int),3);myArray.SetValue(1,0);myArray.SetValue(2,1);myArray.SetValue(3,2); //GetValue返回的是object类型,需要进行类型提升为intint val2 = (int)myArray.GetValue(2); |
3 ArrayList
使用大小可按需动态增加的数组实现 IList 接口,且是针对任意类型。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();al.Add("qaz");al.Add(1);al.Add(new List<object>()); string str = (string)al[0]; int intval = (int)al[1];List<object> objs = (List<object>)al[2]; |
总结
[], Array 编译前需要已知长度,是静态的,类型需要唯一确定的,Array是抽象类,创建需要Array.CreateInstance();
ArrayList 编译时长度未知,是动态的,并且添加的元素可以是不同的类型。
4 List-APIs
4-1 简介
List< T>是一个泛型类,实现了接口IList< T>,通过内部使用一个size动态调整的数组来显示外部的接口。
4-2 增加元素
实现添加一个元素
|
1
|
Add(obj) |
批量添加元素到列表中:
|
1
|
AddRange(objList) |
举例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
private List<int> intList = new List<int>(); public void AddApi(){ intList.Add(10); //添加1个元素 intList.AddRange(new List<int>() { 5, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 }); //批量添加元素} |
将集合中的某个元素插入指定索引处
|
1
|
void Insert(int index, T item); |
|
1
|
void InsertRange(int index, IEnumerable《T》 collection) |
4-3移除元素
假定intList是一个List类型,初始值为 {10,5,1,1,2,2,3}。执行:
|
1
|
intList.Remove(1); |
从intList中移除特定对象的第一个匹配项。移除元素1后,intList = {10,5,1,2,2,3};
移除一定范围的元素 :
|
1
|
intList.RemoveRange(0, 2); |
intList = {2,2,3};
移除所有重复元素后:intList = {3};
|
1
2
3
4
|
intList.RemoveAll(removeDuplicateElements);intList.RemoveAll(i =>{ List<int> elementList = intList.FindAll(r => r.Equals(i)); if (elementList != null && elementList.Count > 1) return true; return false;}); |
在以上判断某个元素是否存在时,比如移除某个元素时,需要用到相等比较器。如果类型T实现了IEquatable< T> 泛型接口,相等比较器就是 Equals(T) 方法; 否则, 默认的相等比较器是 Object.Equals(Object).
下面看一个不是默认的比较器,实现接口的例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public class MyObject{ public int Value { get; set; } public MyObject(int value) { this.Value = value; }} //实现接口IEquatable<MyObject>public class MyObjectCollection : IEquatable<MyObject>{ private List<MyObject> _myObjects = new List<MyObject>() { new MyObject(3), new MyObject(4), new MyObject(3), new MyObject(2), new MyObject(3) }; //删除所有重复的元素 public void RemoveDuplicates() { _myObjects.RemoveAll(Equals); } public List<MyObject> MyObjects { get { return _myObjects; } } public bool Equals(MyObject other) { MyObject duplicate = _myObjects.Find(r => r.Value == other.Value); if (duplicate != null && duplicate!=other) return true; return false; }} |
此处实现了Equals(object),但是Remove(test)暂时是失败的,以后找原因。
4-4查找元素
确定某元素是否在List 中。
|
1
|
bool Contains(obj) |
确定是否包含与指定谓词所定义的条件相匹配的元素。
|
1
|
bool Exists(Predicate<T> match) |
搜索与指定谓词所定义的条件相匹配的元素,并返回第一个匹配元素。
|
1
|
T Find(Predicate<T> match) |
检索与指定谓词定义的条件匹配的所有元素。
|
1
|
List<T> FindAll(Predicate<T> match) |
搜索与指定谓词所定义的条件相匹配的元素,并返回第一个匹配元素的从零开始的索引
|
1
|
int FindIndex(Predicate<T> match) |
搜索与指定谓词所定义的条件相匹配的元素,并返回从指定索引到最后一个元素的元素范围内第一个匹配项的从零开始的索引。
|
1
|
int FindIndex(int startIndex, Predicate<T> match) |
搜索与指定谓词所定义的条件相匹配的元素,并返回从指定的索引开始并包含指定元素数量的元素范围内的第一个匹配项的零始索引
|
1
|
int FindIndex(int startIndex, int count, Predicate<T> match) |
|
1
|
T FindLast(Predicate<T> match) |
|
1
|
int FindLastIndex(Predicate<T> match) |
|
1
|
int FindLastIndex(int startIndex, Predicate<T> match) |
|
1
|
int FindLastIndex(int startIndex, int count, Predicate<T> match) |
搜索指定的对象,并返回第一个匹配项的从零开始的索引
|
1
|
int IndexOf(T item) |
搜索指定的对象,并返回从指定索引到最后一个元素的元素范围内第一个匹配项的从零开始的索引
|
1
|
int IndexOf(T item, int index) |
|
1
|
int IndexOf(T item, int index, int count) |
搜索指定的对象,并返回最后一个匹配项的从零开始的索引。
|
1
|
int LastIndexOf(T item) |
|
1
|
int LastIndexOf(T item, int index) |
|
1
|
int LastIndexOf(T item, int index, int count) |
4-5二分查找
使用默认的比较器在整个已排序的List中搜索元素,并返回该元素从零开始的索引。
|
1
|
int BinarySearch(T item); |
使用指定的比较器在整个已排序的List中搜索元素,并返回该元素从零开始的索引。
|
1
|
int BinarySearch(T item, IComparer<T> comparer) |
|
1
|
int BinarySearch(int index, int count, T item, IComparer<T> comparer) |
4-6排序
使用默认比较器对整个List中的元素进行排序。
|
1
|
void Sort() |
使用指定的 System.Comparison 对整个 List中的元素进行排序。
|
1
|
void Sort(Comparison<T> comparison) |
使用指定的比较器对List中的元素进行排序。
|
1
|
void Sort(IComparer<T> comparer) |
|
1
|
void Sort(int index, int count, IComparer<T> comparer) |
4-7性能分析
| 操作 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| Add | O(1)或O(n) |
| Insert | O(n) |
| Remove | O(n) |
| GetAnItem | O(1) |
| Sort | O(nlogn),最坏O(n^2) |
| Find | O(n) |
4-8 附使用陷阱点:
1 list.Min() 和 list.Max() 和 Average()等Linq方法,当list元素个数为0,则会出现“序列不包含任何元素”的异常。
2 object.ToString() 使用前要检测object是否为null。
3 Foreach遍历时,迭代器是不允许增加或删除的。例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public List<MDevice> GetNormalDevices(List<MDevice> devices) { rtnDevices = devices; foreach (var device in devices) { var tmpdevices = bslMDevice.GetMDeviceByDeviceCode(device.DeviceCode); if (!devices[0].IsNormal) { //这是非法的,因为移除rtnDevices列表的一个元素,等价于移除devices列表。 rtnDevices.Remove(device); } } } |
5 SortedList
5-1 SortedList简介
Sorted表明了它内部实现自动排序,List表明了它有点像List,可以通过index访问集合中的元素。
5-2 内部实现机理
一个SortedList对象内部维护了2个数组,以此来存储元素,其中一个数组用来存放键(keys),另一个存放键关联的值(values)。每一个元素都是键值对(key/value pair)。key不能是null,value可以。
5-3 总结API
5-3-1 Capacity
一个SortedList对象的容量是SortedList能容纳的元素数,这个值是动态变化,自动调整的。如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SortedList mySL = new SortedList();mySL.Add("Third", "!");mySL.Add("Second", "World");mySL.Add("First", "Hello");Console.WriteLine( "mySL" );Console.WriteLine( " Capacity: {0}", mySL.Capacity ); |
此时Capacity: 16
如果添加到mySL中的元素增多,相应的Capacity会相应的自动变大。
5-3-2 访问元素
通过index访问
SortedList对象要想通过index访问,需要使用构造函数SortedList() 或 SortedList(IComparer icompared)。
|
1
2
3
4
|
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList();sortedList.Add(3,"gz");sortedList.Add(9, "lhx");sortedList.Add(3, "gz");object getByIndex = sortedList.GetByIndex(2); |
通过key访问
SortedList对象要想通过key访问,需要使用带有TKey,TValue的泛型构造函数。
|
1
2
3
|
SortedList<int,string> sortedList = new SortedList<int,string>();sortedList.Add(3,"gz");sortedList.Add(9, "lhx");object getByIndex = sortedList[3]; |
5-3-3排序
SortedList有一种默认的比较顺序,比如下面的代码:
|
1
2
3
|
SortedList<int,string> sortedList = new SortedList<int,string>();sortedList.Add(9,"gz");sortedList.Add(3, "lhx"); |
结果是 sortedList中第一个对是3,”lhx”
如果不想按照默认的排序顺序,需要自己在构造时定制一种排序顺序,如下面的代码:
实现排序接口
新建一个私有排序类,实现接口IComparer
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
private class ImplementICompare: IComparer<int> { public int Compare(int x, int y) { return x < y ? 1 : -1; } } |
构造SortedList
|
1
2
3
4
|
ImplementICompare impleCompare = new ImplementICompare();SortedList<int, string> sortedList = new SortedList<int, string>(impleCompare);sortedList.Add(9,"gz");sortedList.Add(3, "lhx"); |
按照键从大到小的顺序排序,结果是 sortedList中第一个对是9,”gz”
5-3-4 添加元素
用add接口实现添加某个元素到集合中,不允许重复添加相同键。
|
1
2
3
|
SortedList<int,string> sortedList = new SortedList<int,string>();sortedList.Add(9,"gz");sortedList.Add(3, "lhx"); |
5-3-5 移除元素
移除集合中指定元素Remove(object removedElement);指定index处移除元素RemoveAt(int index)。
Remove(object)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SortedList mySL = new SortedList();mySL.Add( "3c", "dog" );mySL.Add( "2c", "over" );mySL.Add( "3a", "the" );mySL.Add( "3b", "lazy" ); mySL.Remove( "3b" ); //sucessful to remove |
|
1
2
3
|
SortedList<int, string> sortedList = new SortedList<int, string>();sortedList.Add(9,"gz");sortedList.Add(3, "lhx");bool removedFlag = sortedList.Remove(3); //true |
|
1
2
3
4
|
ImplementICompare impleCompare = new ImplementICompare();SortedList<int, string> sortedList = new SortedList<int, string>(impleCompare);sortedList.Add(9,"gz");sortedList.Add(3, "lhx");bool removedFlag = sortedList.Remove(3); //false |
这是需要注意的一个地方,构造器带有impleCompare实现了排序接口时,好像不能移除某个元素,需要待确认。
RemoveAt(int index)
|
1
2
3
4
|
SortedList sorted = new SortedList();sorted.Add(9, "gz");sorted.Add(3, "lhx");sortedList.RemoveAt(1); //在排序后的位置移除,sortedList的一个对的键 为3,第二个对的键为9,因此移除了9这个键值对 |
5-4 性能
一个SortedList的操作相比Hashtable对象是要慢些的,由于它实现了排序功能。但是,SortedList提供了访问的方便性,由于既可以通过index,也可以通过key去访问元素。
6 .net容器相关接口
| 接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IEnumerable< T> | 实现foreach语句需要实现此接口,接口方法GetEnumerator返回枚举器。 |
| ICollection< T> | 方法:Count属性,CopyTo(Array),Add, Remove, Clear |
| IList< T> | 定义了indexer,Insert, RemoveAt方法,继承ICollection< T> |
| ISet< T> | 方法:求并集,交集,继承于ICollection< T> |
| IDictionary< TKey, TValue> | 有key和value的集合实现 |
| ILookup< TKey, TValue> | 类似上,允许multiple values with one key. |
| IComparer< T> | comparer实现,排序比较的规则 |
| IEqualityComparer< T> | 对象be compared for equality另一个对象 |
| IProducerConsumerCollection< T> | thread-safe collection classes |
7 接口UML
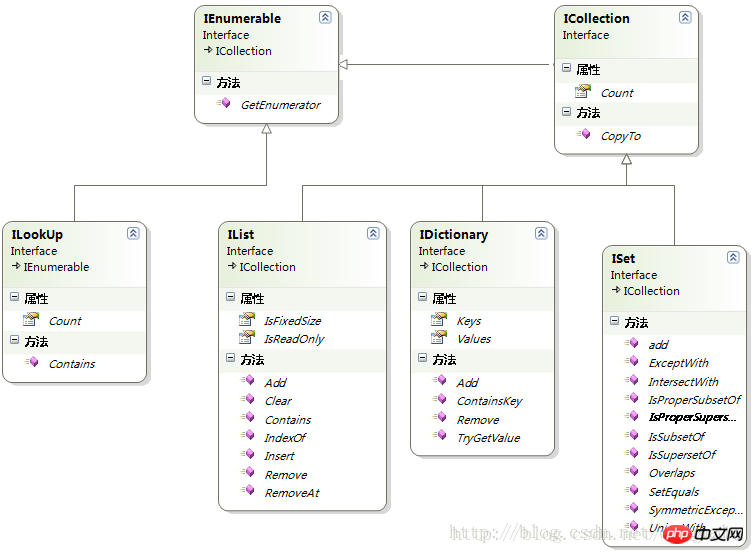
8 各个容器时间复杂度
| 集合类型 | Add | Insert | Remove | Item | Sort | Find |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List< T> | O(1)或O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(nlogn) | O(n) |
| Stack< T> | O(1)或O(n) | 不适用 | pop() O(1) | 不适用 | 不适用 | 不适用 |
| Queue< T> | O(1)或O(n) | 不适用 | O(1) | 不适用 | 不适用 | 不适用 |
| HashSet< T> | O(1)或O(n) | O(1)或O(n) | O(1) | 不适用 | 不适用 | 不适用 |
| LinkedList< T> | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | 不适用 | O(n) |
| Dictionary<, > | O(1)或O(n) | 不适用 | O(1) | O(1) | 不适用 | 不适用 |
| SortedDictionary<,> | O(logn) | 不适用 | O(logn) | O(logn) | 不适用 | 不适用 |
| SortedList<,> | O(logn) | 不适用 | O(n) | O(logn) | 不适用 | 不适用 |