RequestMappingHandlerMapping是SpringMvc中一个比较核心的类,查看下它的类结构图:
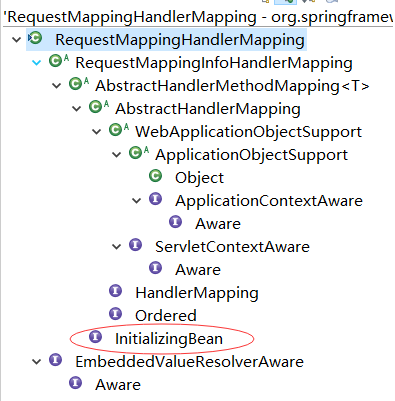
InitializingBean是个很神奇的接口,在Spring每个容器的bean构造方法、属性设置之后,会先调用InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法;
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法: 初始化了config对象,以及调用父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的afterPropertiesSet,父类方法afterPropertiesSet 逻辑是 initHandlerMethods,这也是SpringMvc初始化寻找Controller以及映射加载的核心逻辑;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch);
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
// 初始化config对象,主要属性就是pathMatcher; 以及调用父类 afterPropertiesSet 方法,这是SpringMvc映射关系加载的核心;
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的 initHandlerMethods代码:
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts 默认为false,代表不会检测SpringMvc父容器中的bean的映射关系
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//遍历容器中的beanName, 代理的对象跳过,获取当前bean的类型,调用isHandler判断是否是处理器(handlercontroller)
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { //isHandler方法判断是否是controller,判断逻辑下面有;
detectHandlerMethods(beanName); //加载Controller和请求映射关系
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); // 该方法是个空实现
}
isHandler方法: 判断当前bean的class属性,标注了Controller或者RequestMapping注解,就会去加载Controller和请求映射关系,如果不是handler,迭代下一个bean对象;
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
detectHandlerMethods方法:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());//之前传入handler为string类型,此处去容器获取handler的class
final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); //处理class为CGLIB生成class,如果是CGLIB的获取父类class
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>() {
@Override
public T inspect(Method method) {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
});
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);
}
for (Map.Entry<Method, T> entry : methods.entrySet()) {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
T mapping = entry.getValue();
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
}
}
MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(..)方法是个很全面的解析方法:注释写得很详细,☆方法处,metadataLookup.inspect方法,往上看,调用的就是getMappingForMethod方法获取RequestMappingInfo对象;
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {
final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<Method, T>();
Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>();
Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {
//handler class不是JDK代理生成的,加入到handlerTypes集合,specificHandlerType为当前handler class
handlerTypes.add(targetType);
specificHandlerType = targetType;
}
handlerTypes.addAll(Arrays.asList(targetType.getInterfaces())); /
/handler class实现的接口加入到handlerTypes
for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {
final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
//该工具类方法,遍历了该currentHandlerType本类中所有的方法
// 调用的是 getDeclaredMethods(),然后遍历method数组,调用doWith回调处理method方法
public void doWith(Method method) {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
// ☆ 核心!!! 这里处理了方法以及类上的映射关系,并且返回泛型T,实际类型是RequesMappingInfo
if (result != null) {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
// ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS是个methodFilter,作用是过滤方法是用户定义、且非桥接类型的方法;
}
return methodMap;
}
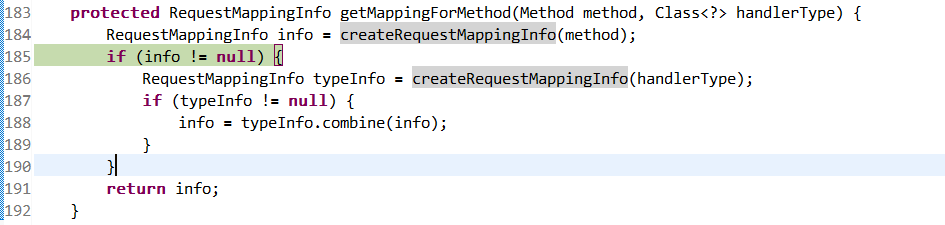
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的 getMappingForMethod 方法:先分析方法上的映射关系,再分析类所在方法上的映射关系,然后结合处理;
下面一点点记录我查看这个方法的发现;
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
// 解析类上RequestMapping注解
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);// 解析方法上@RequestMapping注解
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info); //方法上RequestMapping注解不为空,就需要结合分析
}
}
return info;
}
createRequestMappingInfo 方法:
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
//调用Spring注解工具类AnnotatedElementUtils获取方法上注解
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class<?> ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
//RequestMappingHandlerMapping两个方法都是返回null,空实现
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
具体的RequestMappingInfo的构造采用建造者模式还是其他模式的?
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, RequestCondition<?> customCondition) { //customCondition一般都为null
return RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))// @RequestMapping(path={....}) 将path属性设置上去
.methods(requestMapping.method()) // @RequestMapping(method={....}) 将method属性设置上去
.params(requestMapping.params()) // @RequestMapping(method={....}) 将method属性设置上去
.headers(requestMapping.headers()) // @RequestMapping(headers={....}) 将headers属性设置上去
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes()) // @RequestMapping(consumes={....}) 将consumes属性设置上去
.produces(requestMapping.produces()) // @RequestMapping(produces={....}) 将produces属性设置上去
.mappingName(requestMapping.name()) // @RequestMapping(name={....}) 将name属性设置上去
.customCondition(customCondition)
.options(this.config)
.build();
}
这里只分析一个开头、一个结尾这样;
RequestMappingInfo 的 paths 方法:
public static Builder paths(String... paths) { // paths是@RequestMapping的path属性,字符串数组,这里用可变参数来接收,效果一样
return new DefaultBuilder(paths);
}
Builder接口所有方法都返回Builder对象,DefaultBuilder持有一堆属性,可以看到都是@ReuqestMapping的属性;
paths方法就将注解的path属性注入到DefaultBuilder中,其他方法methods、params、headers、consumes、produces、mappingName、customCondition都是这个套路;
而 options注入的config属性 ,最开始 afterPropertiesSet 里 ,this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
就是将RequestMappingHandleMapping中的config作为DefaultBuilder的options注入; 最后就是build方法。
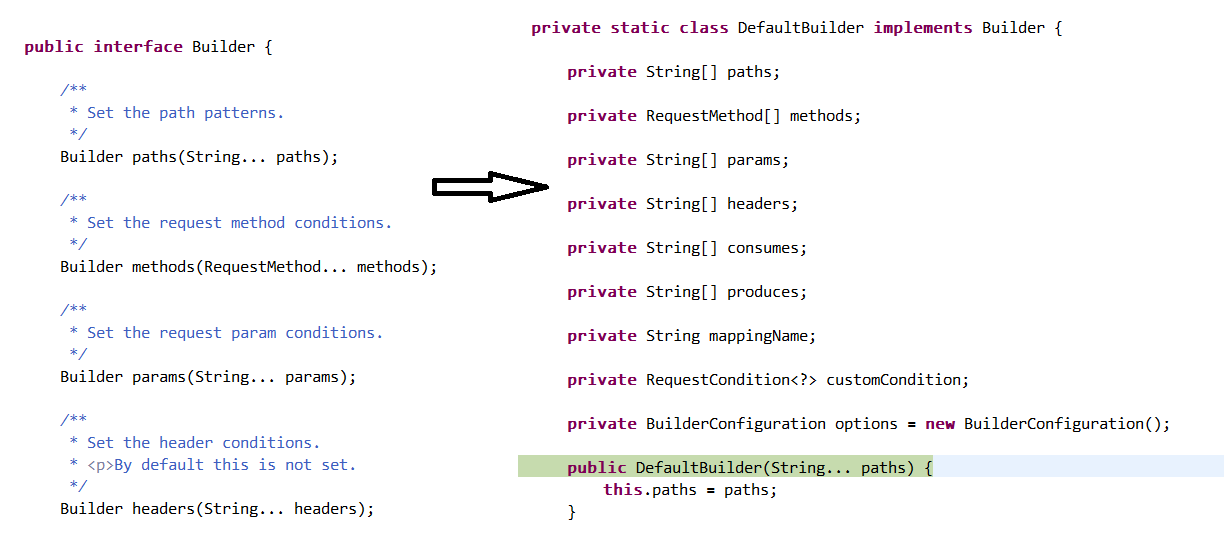
DefaultBuilder 的 build方法:
public RequestMappingInfo build() {
ContentNegotiationManager manager = this.options.getContentNegotiationManager();
// PatternsRequestCondition构造的主要属性就是paths,代表了映射的路径,不以/开头会添加 / 这个开头
PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition = new PatternsRequestCondition(
this.paths, this.options.getUrlPathHelper(), this.options.getPathMatcher(),
this.options.useSuffixPatternMatch(), this.options.useTrailingSlashMatch(),
this.options.getFileExtensions());
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.mappingName, patternsCondition,
new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(methods),
new ParamsRequestCondition(this.params),
new HeadersRequestCondition(this.headers),
new ConsumesRequestCondition(this.consumes, this.headers),
new ProducesRequestCondition(this.produces, this.headers, manager),
this.customCondition); // customCondition通常为null
}
build方法返回 RequestMappingInfo,其中构造入参都是XXXRequestCondition这种,他们都实现了RequestCondition接口;
private PatternsRequestCondition(Collection<String> patterns, UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper,
PathMatcher pathMatcher, boolean useSuffixPatternMatch, boolean useTrailingSlashMatch,
List<String> fileExtensions) {
//这里就是 prependLeadingSlash 会判断 @RequestMapping注解的 path属性,不是以 /开头会添加 /
this.patterns = Collections.unmodifiableSet(prependLeadingSlash(patterns));
this.pathHelper = (urlPathHelper != null ? urlPathHelper : new UrlPathHelper());
this.pathMatcher = (pathMatcher != null ? pathMatcher : new AntPathMatcher());
this.useSuffixPatternMatch = useSuffixPatternMatch;
this.useTrailingSlashMatch = useTrailingSlashMatch;
if (fileExtensions != null) {
for (String fileExtension : fileExtensions) {
if (fileExtension.charAt(0) != '.') {
fileExtension = "." + fileExtension;
}
this.fileExtensions.add(fileExtension);
}
}
}
private static Set<String> prependLeadingSlash(Collection<String> patterns) {
if (patterns == null) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<String>(patterns.size());
for (String pattern : patterns) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(pattern) && !pattern.startsWith("/")) { //URL不以 /开头就会自动添加 /
pattern = "/" + pattern;
}
result.add(pattern);
}
return result;
}
回到RequestMappingInfo的构造方法,将@RequestMapping的所有属性都以 RequestCondition的实现类 形式保存到 RequestMappingInfo对象中;
接口RequestCondition定义了三个方法,1.combine:一般用来 方法级别@RequestMapping与类级别@RequestMapping结合,返回新的(通常是RequestMappingInfo);
2.getMatchingCondition:检查request对象是否满足条件,返回一个新的满足条件的RequestMappingInfo实例(T泛型用都是RequestMappingInfo);
3.compareTo 用来多个匹配的情况排序挑选最合适的
public interface RequestCondition<T> {
T combine(T other);
T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request);
int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request);
}
至此 回到 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的 getMappingForMethod方法 ,第一个方法级别的createRequestMappingInfo方法分析完毕,下面两行解析了标注在 类上的 注解,并且返回 RequestMappingInfo对象,
第188行就是类上标注了@RequestMapping注解,和方法上同样标注@RequestMapping结合处理的步骤:调用类上的RequestMappingInfo的combine方法
查看RequestMappingInfo对象的combine方法:
public RequestMappingInfo combine(RequestMappingInfo other) {
// RequestMapping的name属性的处理方法,一般name属性很少写,处理方式:两个都不为空就返回this.name#other.name;有一个为空 就返回另外一个name
String name = combineNames(other);
//下面逻辑A分析 调用AntPathMatcher的combine方法,将类上URL和方法上URL组合并放入新PatternsRequestCondition
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.combine(other.patternsCondition);
//下面逻辑B分析,并且接下来的methods、params、headers等等实现方式大体一致
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.combine(other.methodsCondition);
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.combine(other.paramsCondition);
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.combine(other.headersCondition);
//!!comsume和produce判断逻辑不是相加,方法上的该属性优先级高于类级别上的
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.combine(other.consumesCondition);
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.combine(other.producesCondition);
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.combine(other.customConditionHolder);
return new RequestMappingInfo(name, patterns,//返回一个新的RequestMappingInfo对象,其中所有RequestCondition都是新创建的对象
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition());
}
逻辑A: PatternsRequestCondition 之前介绍过,其属性patterns 就是@RequestMapping的path / value 属性的集合,且判断 path是否以 / 开头,如果不是会自动补全 / 开头;
其实现了RequestCondition接口,查看其combine方法
public PatternsRequestCondition combine(PatternsRequestCondition other) {
// result作为新的请求路径集合
Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
//类上注解@RequestMapping path不为空,方法上注解注解@RequestMapping path不为空
//此处的AntPathMatcher就是RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象里的antPathMatcher对象
//@RequestMapping path属性是集合类型的,这类似笛卡尔积形式 调用AntPathMatcher的combine方式,进行URL组合 加入到result
if (!this.patterns.isEmpty() && !other.patterns.isEmpty()) {
for (String pattern1 : this.patterns) {
for (String pattern2 : other.patterns) {
result.add(this.pathMatcher.combine(pattern1, pattern2));
}
}
}
//已经说明有一方为空了,只要判断另外一方是否为空,不为空直接加入Set<String>
else if (!this.patterns.isEmpty()) {
result.addAll(this.patterns);
}
else if (!other.patterns.isEmpty()) {
result.addAll(other.patterns);
}
else {
result.add("");
} /返回了一个新的PatternsRequestCondition对象,patterns属性就是当前方法的请求路径
return new PatternsRequestCondition(result, this.pathHelper, this.pathMatcher, this.useSuffixPatternMatch,
this.useTrailingSlashMatch, this.fileExtensions); /
}
逻辑A-1:AntPathMatcher对象如何对请求路径进行结合combine?
| 类上path | 方法上path | 结合后path |
| null | null | |
| /hotels | null | /hotels |
| null | /hotels | /hotels |
| /hotels | /bookings | /hotels/bookings |
| /hotels | bookings | /hotels/bookings |
| /hotels/* | /bookings | /hotels/bookings |
| /hotels/** | /bookings | /hotels/**/bookings |
| /hotels | {hotel} | /hotels/{hotel} |
| /hotels/* | {hotel} | /hotels/{hotel} |
| /hotels/** | {hotel} | /hotels/**/{hotel} |
| /*.html | hotels.html | /hotels.html |
| /*.html | /hotels | /hotels.html |
| /*.html | /*.txt | IllegalArgumentException |
逻辑B:RequestMethodsRequestCondition 的 combine 方法,方法上注解@RequestMapping的method加入到类上注解的method属性里,然后返回一个全新的RequestMethodsRequestCondition,持有新的method集合;
public RequestMethodsRequestCondition combine(RequestMethodsRequestCondition other) {
Set<RequestMethod> set = new LinkedHashSet<RequestMethod>(this.methods);
set.addAll(other.methods);
return new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(set);
}
getMappingForMethod方法调用结束,返回结合后的RequestMappingInfo对象; 回到MethodIntrospector.selectMethods方法,第19行就是调用的getMappingForMethod方法,返回RequestMappingInfo对象result,result不为空之后,
会筛选不是桥接方法,存入methodMap这个Map对象,key-type是Method,value-type是RequestMappingInfo类型;
该方法selectMethods将Controller / Handler中所有方法都进行判断加载请求映射,返回methodMap对象;
1 public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {
2 final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<Method, T>();
3 Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>();
4 Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;
5
6 if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {
7 handlerTypes.add(targetType);
8 specificHandlerType = targetType;
9 }
10 handlerTypes.addAll(Arrays.asList(targetType.getInterfaces()));
11
12 for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {
13 final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);
14
15 ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
16 @Override
17 public void doWith(Method method) {
18 Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
19 T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
20 if (result != null) {
21 Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
22 if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
23 methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
24 }
25 }
26 }
27 }, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
28 }
29
30 return methodMap;
31 }
回到最开始的分析detectHandlerMethods方法:methods对象就是上面返回的methodMap,如果日志设置了DEBUG,每遍历一个controller都会输出日志;
![]()
1 protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
2 Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
3 getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
4 final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
5
6 Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
7 new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>() {
8 @Override
9 public T inspect(Method method) {
10 return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
11 }
12 });
13
14 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
15 logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);
16 }
17 for (Map.Entry<Method, T> entry : methods.entrySet()) {//遍历methods,并且调用registerHandlerMethod注册映射信息
18 Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
19 T mapping = entry.getValue();
20 registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
21 }
22 }
registerHandlerMethod:总结 :
|
RequestMappingHandlerMapping.mappingRegistry属性 |
key-type | value-type |
mappingLookup
|
RequestMappingInfo | HandlerMethod对象 |
urlLookup
|
请求路径URL | RequestMappingInfo |
| nameLookup | controller name中大写字母#方法名(如UC#test) | HandlerMethod对象 |
registry
|
RequestMappingInfo |
MappingRegistration对象(持有 |
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
} // this对象指RequestMappingHandlerMapping,mapping是RequestMappingInfo对象,handler是controler的name,method是当前@RequestMapping方法
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); //可重入锁 写锁上锁 这里不太明白为什么要上锁
try {
//创建新的HandlerMethod对象 下面逻辑C 介绍HandlerMethod 逻辑D 分析createHandlerMethod方法
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
//校验唯一性,一个RequestMappingInfo对应一个Handlermethod,如果根据RequestMappingInfo找到不同的hm 抛出异常
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
//INFO级别日志 比如Mapped "{[/user/test]}" onto public java.lang.String demo2.UserController.test(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest,javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse)
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped "" + mapping + "" onto " + handlerMethod);
}
//this指RequestMappingHandlerMapping.MappingRegistry,mappingLookup保存着RequestMappingInfo--HandlerMethod对象
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
//获取 mapping 的PatternsRequestCondition的patterns,也就是拼接的URL路径,并且路径不包含* ?的就加入到集合返回
, List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
//MappingRegistry的urlLookup保存着 url--RequestMappingInfo对象
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
//name属性感觉没用,如果@RequestMapping有name属性就是这个属性 如果没有就是 controller名字中的大写字母#方法名字,比如UC#test
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
//MappingRegistry的nameLookup保存着 name--HandlerMethod集合
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
//MappingRegistry的registry保存着RequestMappingInfo--MappingRegistration,MappingRegistration几乎有映射的所有信息
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<T>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); //可重入锁 写锁 释放锁
}
}
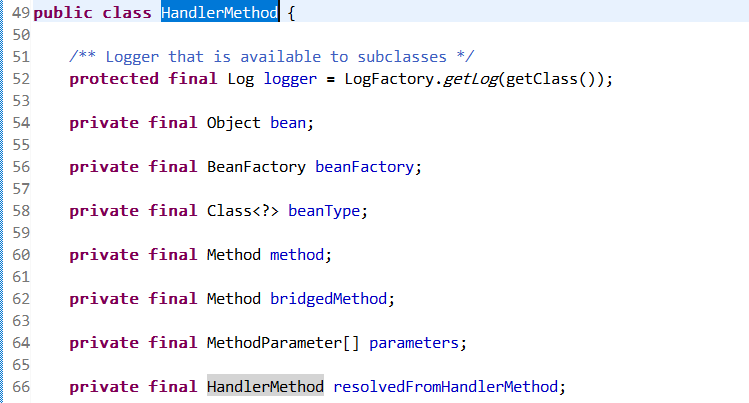
逻辑C:HandlerMethod对象 属性有bean,就是controller对象实例;beanFactory当前Spring容器;beanType就是controller的类型;method就是handler method;birdgeMethod是handler method的桥接方法;MethodParameter是handler method的方法参数,handlerMethod一般为null;
HandlerMethod,作用Spring给出了:一个handler method对象,包含了method以及controller对象,此外提供了便捷方式获取方法入参、返回值、注解等等;
逻辑D:createHandlerMethod方法只是调用了HandlerMethod的构造方法,构造方法中对方法入参进行了处理;
1 protected HandlerMethod createHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method) {
2 HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
3 if (handler instanceof String) {
4 String beanName = (String) handler;
5 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(beanName,
6 getApplicationContext().getAutowireCapableBeanFactory(), method);
7 }
8 else {
9 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(handler, method);
10 }
11 return handlerMethod;
12 }
13
14 public HandlerMethod(String beanName, BeanFactory beanFactory, Method method) {
15 Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name is required");
16 Assert.notNull(beanFactory, "BeanFactory is required");
17 Assert.notNull(method, "Method is required");
18 this.bean = beanName; //controller beanName
19 this.beanFactory = beanFactory; //当前controller所在Spring工厂
20 this.beanType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanFactory.getType(beanName)); //获取当前controller类型
21 this.method = method; //当前handler method
22 this.bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method); //查找method的桥接方法,没有桥接方法就是返回自身
23 this.parameters = initMethodParameters(); //初始化MethodParameter对象 设置了每个MethodParameter的method、parameterIndex属性 具体方法下图
24 this.resolvedFromHandlerMethod = null;
25 }
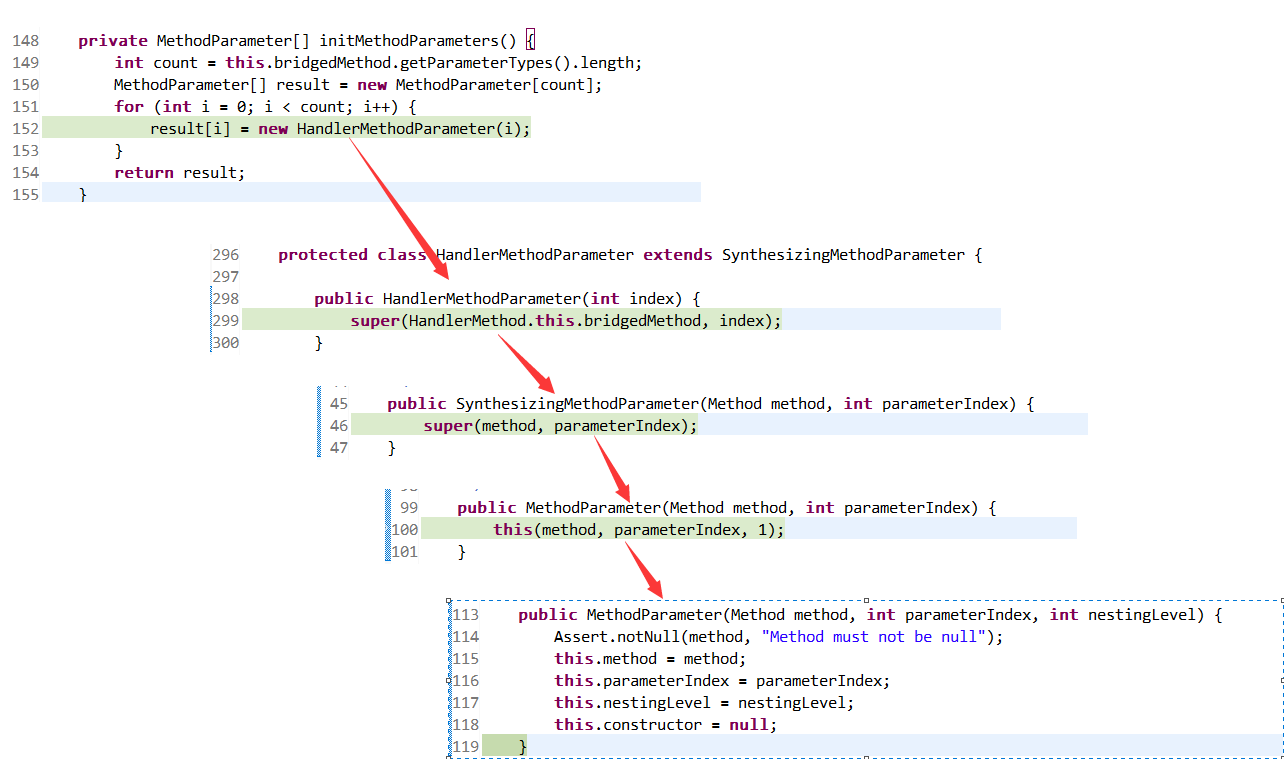
至此,registerHandlerMethod方法分析完毕,detectHandlerMethods方法分析完成,
Spring主要做了哪些工作:将所有请求映射关系保存到上面RequestMappingHandlerMapping的mappingRegistry的相关属性中,详情见上面表格。
分析过SpringMvc的请求流程 SpringMvc流程
篇幅太长,只分析如何找根据请求找到对应的handler? 遍历HandlerMapping对象,调用其getHanlder方法查找controller / handler , RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象的父类AbstractHandlerMapping实现了getHandler方法,方法最开始Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); 那么我们从AbstractHandlerMapping 的 getHandlerInternal开始记录.
1 protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 根据request请求路径以及servlet-mapping得到要请求URL
2 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
3 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
4 logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
5 }
6 this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); //读锁 上锁
7 try {
// 这里就是MVC寻找controller匹配的方法! 下面花大篇幅介绍下
8 HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
9 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
10 if (handlerMethod != null) {
11 logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
12 }
13 else {
14 logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
15 }
16 }
//找到handlerMethod,但bean是controller beanName,用beanFactory getBean替换bean
17 return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); 18 }
19 finally {
20 this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
21 }
22 }
lookupHandlerMethod方法:
逻辑是这样的,先根据请求的URL 从 RequestMappingHandlerMapping的mappingRegistry的urlLookup中尝试寻找RequestMappingInfo;
寻找大致分为两种情况:一种请求URL清楚,不需要通配符比对,那肯定可以直接找到RequestMappingInfo集合,创建Match对象并且添加到集合里面,然后根据规则对Match集合排序选出最优解;
第二种情况URL带有通配符,那需要遍历映射关系再重复第一种情况。
1 protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
2 List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
//return this.urlLookup.get(urlPath);调用mappingRegistry的urlLookup根据URL寻找RequestMappingInfo
3 List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
4 if (directPathMatches != null) {
//遍历找到的RequestMappingInfo集合, 然后寻找匹配的对象并处理添加到matches集合,见 逻辑E 分析
5 addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
6 }
7 if (matches.isEmpty()) { //matches为空,有可能是因为通配符匹配的情况需要再次匹配
8 // No choice but to go through all mappings...
9 addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
10 }
11
12 if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
//返回一个MatchComparator对象
// 持有Comparator属性,并且compare方法是调用了RequestMappingInfo的compareTo
13 Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
//说到底排序还是调用了RequestMappingInfo的compareTo方法, 也存在优先级之分 URL路径>params>headers>comsume>produce>method 排序分析见文章最后
14 Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
15 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
16 logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" +
17 lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
18 }
19 Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); //找到最优匹配
20 if (matches.size() > 1) {
21 if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
22 return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
23 }
24 Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
25 if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { //存在两个匹配且相等 抛出异常
26 Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
27 Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
28 throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
29 request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
30 }
31 }
32 handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); //解析URL变量,完成设置request属性等工作
33 return bestMatch.handlerMethod; //返回最优匹配的HandlerMethod对象
34 }
35 else { //没找到handlerMethod 就返回null
36 return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
37 }
38 }
逻辑E:遍历找到的RequestMappingInfo集合,调用RequestMappingInfo的getMatchCondition进行匹配以获取匹配的RequestMappingInfo对象;寻找到合适的RequestMappingInfo对象之后,创建一个Match对象加入matches集合;
mappingRegistry 的 getMappings方法返回mappingLookup属性,上述表格mappingLookup 存放 RequestMappingInfo--HandlerMethod,根据RequestMappingInfo对象从map中取对象,(逻辑G分析 RequestMappingInfo重写了的hashCode以及equals方法)。 Match对象持有RequestMappingInfo以及HandlerMethod属性;此处方法调用结束matches可能包含多个Match结果;
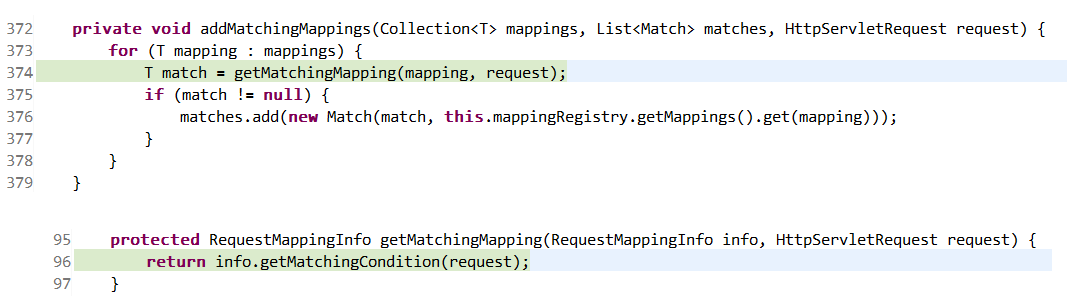
RequestMappingInfo的getMatchingCondition方法
1 public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
//如果RequestMappingInfo没有指定methods属性,返回RequestMappingInfo本身,否则方法匹配
2 RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
//下面几个匹配逻辑是一样的,匹配了返回自身,没匹配返回null,具体参数作用、如何匹配看吧;
3 ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
4 HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
5 ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
6 ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
7 //有一个条件匹配不上就直接返回null
8 if (methods == null || params == null || headers == null || consumes == null || produces == null) {
9 return null;
10 }
11 //其他匹配上了,最重要的匹配请求URL, 路径匹配作为 逻辑F 分析
12 PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
13 if (patterns == null) {
14 return null;
15 }
16
17 RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
18 if (custom == null) {
19 return null;
20 }
21
22 return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, patterns,
//寻找到匹配之后,构造一个新的RequestMappingInfo对象,持有上述匹配之后的结果返回
23 methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition()); 24 }
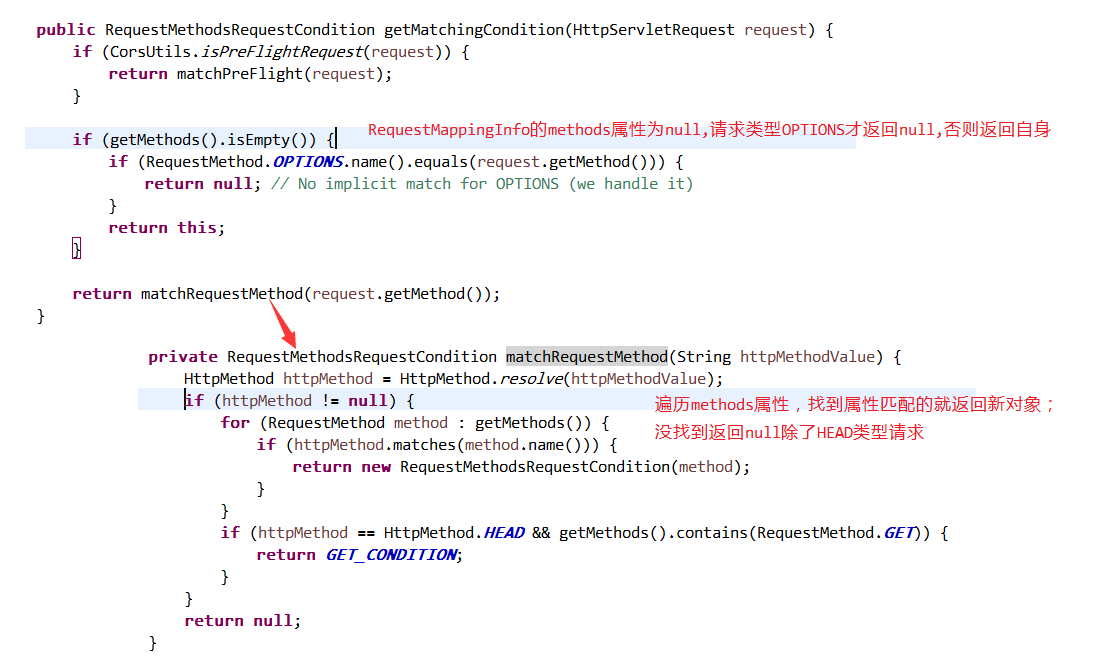
逻辑F:PatternsRequestCondition匹配
调用PatternsRequestCondition 的 getMatchingPattern 方法进行URL匹配;遍历PatternsRequestCondition的 patterns属性,逐个getMatchingPattern进行比较,匹配上将pattern存入集合,并且使用AntPatternComparator进行排序,排序之后集合加入到一个新的PatternsRequestCondition对象中;
//pattern就是patterns属性当前迭代的元素,lookupPath就是servlet-mapping下请求URL
1 private String getMatchingPattern(String pattern, String lookupPath) { 2 if (pattern.equals(lookupPath)) { //两者相等 无疑义直接返回 这种是没有通配符 * ?这种都会很容易匹配到并且返回
3 return pattern;
4 }
5 if (this.useSuffixPatternMatch) { // useSuffixPatternMatch默认为true
6 if (!this.fileExtensions.isEmpty() && lookupPath.indexOf('.') != -1) { // fileExtensions默认为空
7 for (String extension : this.fileExtensions) {
8 if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + extension, lookupPath)) {
9 return pattern + extension;
10 }
11 }
12 }
13 else {
14 boolean hasSuffix = pattern.indexOf('.') != -1; //pattern字符串是否有 .
15 if (!hasSuffix && this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + ".*", lookupPath)) { //没有 . 就用AntPathMatcher的match匹配 pattern.* lookupPath
16 return pattern + ".*";
17 }
18 }
19 }
20 if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern, lookupPath)) {
// 用AntPathMatcher的match匹配 pattern lookupPath,匹配上就返回pattern
21 return pattern;
22 }
23 if (this.useTrailingSlashMatch) {
24 if (!pattern.endsWith("/") && this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + "/", lookupPath)) {
25 return pattern +"/";
26 }
27 }
28 return null;
29 }
逻辑G:先介绍下为什么要看RequestMappingInfo的hashCode以及equals方法?RequestMappingInfo作为key存储在Map中,肯定需要重写HashCode以及equals方法;
RequestMappingInfo的hashCode以及equals方法: 比较的时候会先调用hashCode判断值是否相等,相等再比较equals方法,如果相等则认为是同一个对象;
先来看hashCode方法,将RequestMappingInfo的所有RequestCondition属性按公式求和,这些属性都是AbstractRequestCondition,equals和hashCode方法都调用了getContent方法,而AbstractRequestCondition的各种实现类的getContent方法,比如PatternsRequestCondition实现方式就是返回patterns(URL)集合;比如RequestMethodsRequestCondition实现就是返回methods集合;
RequestMappingInfo
1 public boolean equals(Object other) {
2 if (this == other) {
3 return true;
4 }
5 if (!(other instanceof RequestMappingInfo)) {
6 return false;
7 }
8 RequestMappingInfo otherInfo = (RequestMappingInfo) other;
9 return (this.patternsCondition.equals(otherInfo.patternsCondition) &&
10 this.methodsCondition.equals(otherInfo.methodsCondition) &&
11 this.paramsCondition.equals(otherInfo.paramsCondition) &&
12 this.headersCondition.equals(otherInfo.headersCondition) &&
13 this.consumesCondition.equals(otherInfo.consumesCondition) &&
14 this.producesCondition.equals(otherInfo.producesCondition) &&
15 this.customConditionHolder.equals(otherInfo.customConditionHolder));
16 }
17
18 @Override
19 public int hashCode() {
20 return (this.patternsCondition.hashCode() * 31 + // primary differentiation
21 this.methodsCondition.hashCode() + this.paramsCondition.hashCode() +
22 this.headersCondition.hashCode() + this.consumesCondition.hashCode() +
23 this.producesCondition.hashCode() + this.customConditionHolder.hashCode());
24 }
AbstractRequestCondition
1 public boolean equals(Object obj) {
2 if (this == obj) {
3 return true;
4 }
5 if (obj != null && getClass() == obj.getClass()) {
6 AbstractRequestCondition<?> other = (AbstractRequestCondition<?>) obj;
7 return getContent().equals(other.getContent());
8 }
9 return false;
10 }
11
12 @Override
13 public int hashCode() {
14 return getContent().hashCode();
15 }
分析到上面,getHandlerInternal已经找到了对应的HandlerMethod对象,调用getHandlerExecutionChain封装成HandlerExecutionChain;
1 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
2 HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
3 (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// //构造一个HandlerExecutionChain对象,持有handlerMethod 4
5 String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
6 for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
//adaptedInterceptors在开启<mvc:annotation-drvien/>之后不为空,多了一个MappedInterceptor拦截器
7 if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
8 MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
9 if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
10 chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
//将ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor添加到HandlerExecutionChain的interceptorList属性中
11 }
12 }
13 else {
14 chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
15 }
16 }
17 return chain; //返回HandlerExecutionChain对象
18 }
Tip1:这个RequestMappingHandlerMapping的MappedInterceptor是从哪里注入的呢?
开启了<mvc:annotation-driven />之后 Spring向容器中注入了这样两个bean的定义,MappedInterceptor,该对象持有ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor对象;
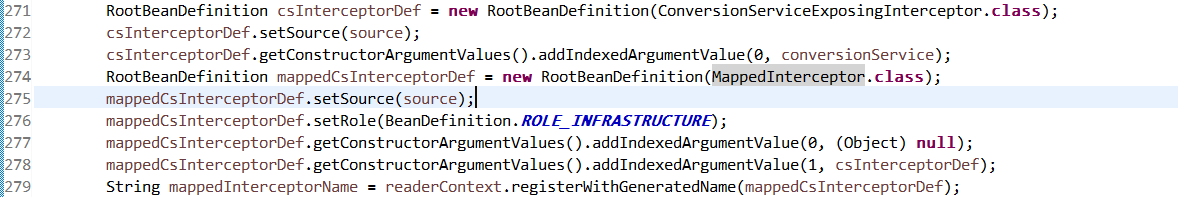
容器中有了MappedInterceptor对象,什么时候给RequestMappingHandlerMapping设置的adaptedInterceptors呢?通过打断点分析到,RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,Spring向其注入ApplicationContext的时候,调用了initApplicationContext方法,不断进入方法最后进入到父类AbstractHandlerMapping的initApplicationContext方法,
1 protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
2 extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
3 detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors); //此处添加了RequestMappingHandlerMapping的adaptedInterceptors
4 initInterceptors();
5 }
6
7 protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List<HandlerInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) {
//这里将容器中的MappedInterceptor添加到了RequestMappingHandlerMapping的adaptedInterceptors
8 mappedInterceptors.addAll(
9 BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
10 getApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
11 }
至此,如何找到HandlerMethod已经分析完毕;
总结
SpringMvc请求寻找规则 : 如果一个请求同时匹配上多个方法,按照如下顺序选择执行哪个方法:
先URL匹配的方法 >>>>> params满足的方法 >>>>> headers 满足的方法 >>>>>>consume满足的方法 >>>> produce 满足的方法 >>>> method满足的方法
如果一个请求匹配上了多个RequestMappingInfo筛选:
之前介绍过排序是调用 RequestMappingInfo的compareTo进行排序
1 public int compareTo(RequestMappingInfo other, HttpServletRequest request) {
2 int result = this.patternsCondition.compareTo(other.getPatternsCondition(), request); //优先URL进行匹配
3 if (result != 0) {
4 return result;
5 }
6 result = this.paramsCondition.compareTo(other.getParamsCondition(), request);
7 if (result != 0) {
8 return result;
9 }
10 result = this.headersCondition.compareTo(other.getHeadersCondition(), request);
11 if (result != 0) {
12 return result;
13 }
14 result = this.consumesCondition.compareTo(other.getConsumesCondition(), request);
15 if (result != 0) {
16 return result;
17 }
18 result = this.producesCondition.compareTo(other.getProducesCondition(), request);
19 if (result != 0) {
20 return result;
21 }
22 result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
23 if (result != 0) {
24 return result;
25 }
26 result = this.customConditionHolder.compareTo(other.customConditionHolder, request);
27 if (result != 0) {
28 return result;
29 }
30 return 0;
31 }
介绍下URL如何排序吧,其他类似; 假设两个URL /get1 可以被匹配 /get* 以及 /get?
1 public int compareTo(PatternsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
2 String lookupPath = this.pathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
3 Comparator<String> patternComparator = this.pathMatcher.getPatternComparator(lookupPath); //获取AntPatternComparator比较器
4 Iterator<String> iterator = this.patterns.iterator();
5 Iterator<String> iteratorOther = other.patterns.iterator();
6 while (iterator.hasNext() && iteratorOther.hasNext()) {
7 int result = patternComparator.compare(iterator.next(), iteratorOther.next()); //URL比较规则在这里
8 if (result != 0) {
9 return result;
10 }
11 }
12 if (iterator.hasNext()) {
13 return -1;
14 }
15 else if (iteratorOther.hasNext()) {
16 return 1;
17 }
18 else {
19 return 0;
20 }
21 }
URL比较规则:按照请求URL通配符按一定权重计算排序顺序,{个数+*个数+ ** 个数 ;所以 get* 比get?排在前面;
1 public int compare(String pattern1, String pattern2) { //例子中pattern1为 /get* pattern2为/get?
2 PatternInfo info1 = new PatternInfo(pattern1); //具体查看下面构造方法
3 PatternInfo info2 = new PatternInfo(pattern2);
4
5 if (info1.isLeastSpecific() && info2.isLeastSpecific()) {
6 return 0;
7 }
8 else if (info1.isLeastSpecific()) {
9 return 1;
10 }
11 else if (info2.isLeastSpecific()) { //上面三种情况是 比较 /**的情况
12 return -1;
13 }
14
15 boolean pattern1EqualsPath = pattern1.equals(path);
16 boolean pattern2EqualsPath = pattern2.equals(path);
17 if (pattern1EqualsPath && pattern2EqualsPath) {
18 return 0;
19 }
20 else if (pattern1EqualsPath) {
21 return -1;
22 }
23 else if (pattern2EqualsPath) { //这三种情况是比较 pattern1 pattern2存在和请求URL完全匹配的情况
24 return 1;
25 }
26
27 if (info1.isPrefixPattern() && info2.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {
28 return 1;
29 }
30 else if (info2.isPrefixPattern() && info1.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) { //哪个pattern的 /**多 哪个排在前面
31 return -1;
32 }
33
34 if (info1.getTotalCount() != info2.getTotalCount()) {
35 return info1.getTotalCount() - info2.getTotalCount(); //按照权重来排序了 {算1 *算1 **算2 哪个大哪个排前面 /get*权重为1排前面
36 }
37
38 if (info1.getLength() != info2.getLength()) {
39 return info2.getLength() - info1.getLength();
40 }
41
42 if (info1.getSingleWildcards() < info2.getSingleWildcards()) {
43 return -1;
44 }
45 else if (info2.getSingleWildcards() < info1.getSingleWildcards()) {
46 return 1;
47 }
48
49 if (info1.getUriVars() < info2.getUriVars()) {
50 return -1;
51 }
52 else if (info2.getUriVars() < info1.getUriVars()) {
53 return 1;
54 }
55
56 return 0;
57 }
58
59 public PatternInfo(String pattern) {
60 this.pattern = pattern;
61 if (this.pattern != null) {
62 initCounters();
63 this.catchAllPattern = this.pattern.equals("/**"); //代表匹配所有就是pattern为 /**
64 this.prefixPattern = !this.catchAllPattern && this.pattern.endsWith("/**");
65 }
66 if (this.uriVars == 0) {
67 this.length = (this.pattern != null ? this.pattern.length() : 0);
68 }
69 }
70
71 protected void initCounters() {
72 int pos = 0;
73 while (pos < this.pattern.length()) {
74 if (this.pattern.charAt(pos) == '{') { //存在变量 则uriVars自增
75 this.uriVars++;
76 pos++;
77 }
78 else if (this.pattern.charAt(pos) == '*') { //解析到*
79 if (pos + 1 < this.pattern.length() && this.pattern.charAt(pos + 1) == '*') {
80 this.doubleWildcards++; // doubleWildcards代表有两个*的
81 pos += 2;
82 }
83 else if (pos > 0 && !this.pattern.substring(pos - 1).equals(".*")) { //最后一位是* 且倒数第二位不是 *
84 this.singleWildcards++; // singleWildcards代表有单个*
85 pos++;
86 }
87 else {
88 pos++;
89 }
90 }
91 else {
92 pos++;
93 }
94 }
95 }