Preface
注:鉴于很多网站随意爬取数据,可能导致内容残缺以及引用失效等问题,影响阅读,请认准原创网址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/lv-anchoret/category/1368696.html
我们这节主要讲把之前的概率密度做混合,以得到更好的效果
我们上一篇以前经常用关于cos函数的pdf,上一节用的是与光源采样相关的pdf,那么,我们把两者结合到一起,协调它们之间的比例,我们就可以得到一个有着两种概率密度模型的pdf,这往往是更贴近生活的,那么我们今天就来学习测试一下。
Ready
这一节就是把前几篇的概率密度做混合,所以,需要的就是熟悉之前的内容。
当然,之前的框架代码也比较丑,基本都是在lerp函数里面做调整,所以,我们顺便把框架搭得更好一点
正文
我们都知道,设计pdf的一个很重要的原则就是使得累积概率密度达到且只达到1,所以,我们先采用一种非常简单的比例协调方式混合两个pdf。
例如我们有如下的混合密度方程
pdf_mixture(direction) = 1/2 * pdf_reflection(direction) + 1/2 * pdf_light(direction)
即,两者各占一半
要实现两者,代码描述也很简单:
if ( rand01() < 0.5 ) pdf_reflection(); ... else pdf_light(); ...
///pdf.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [ time ] 2019.3 // [brief ] In the Monte Carlo system, pdf acts as the // most important element of Important-Sample // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { // the basic class of pdf system class pdf { public: /* @brief: we get the value of pdf function by this interface @param: the direction of location @retur: the value of the pdf function */ virtual rtvar value(const rtvec & direction)const = 0; /* @brief: generate a random number with a Probability model @param: none @retur: the Three-dimensional random vector */ virtual rtvec generate()const = 0; }; }//rt namespace
我们来实现关于它的一些子类
首先我们来实现关于cosine 概率密度的模型
///cosine_pdf.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [ time ] 2019.3 // [brief ] one of the pdf' forms // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class cosine_pdf :public pdf { public: //constructor cosine_pdf(const rtvec& w); /* @brief: we get the value of pdf function by this interface @param: the direction of location @retur: the value of the pdf function */ virtual rtvar value(const rtvec& direction)const; /* @brief: generate a random number with a Probability model @param: none @retur: the Three-dimensional random vector */ virtual rtvec generate()const; private: onb _uvw; }; inline cosine_pdf::cosine_pdf(const rtvec& w) { _uvw.build_from_w(w); } rtvar cosine_pdf::value(const rtvec& direction)const { rtvar cosine = dot(direction.ret_unitization(), _uvw.w()); if (cosine > 0.) return cosine / π; else return 0.; } rtvec cosine_pdf::generate()const { return _uvw.local(random_cosine_direction()); } }
这个模型之前细说过,cosine大于0的时候返回cosine/π,反之,则返回0。因为光线反射之后如果和表面法线的夹角为钝角的时候,违反反射规律,不以反射。生成随机数的那个之前也讲过,在上上一篇
其实这些都不是新东西,就是把之前讲的的那一套整合了一下
得到结果也就是之前的效果
我们把主函数里面的lerp()也改一下
每个像素点采样100次,取均值,即sample 为 100时

这是代码敲错了,意外得到的一张图

现在我们尝试,光源采样,即
///hit_pdf.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [ time ] 2019.3 // [brief ] toward to the hitable // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class hit_pdf :public pdf { public: /* @param: info -> Geometry information origion -> the point of intersection */ hit_pdf(intersect* info, const rtvec& origion) :_intersectp(info) ,_o(origion) { } /* @brief: we get the value of pdf function by this interface @param: the direction of location @retur: the value of the pdf function */ virtual rtvar value(const rtvec& direction)const { return _intersectp->pdf_value(_o, direction); } /* @brief: generate a random number with a Probability model @param: none @retur: the Three-dimensional random vector */ virtual rtvec generate()const { return _intersectp->random(_o); } private: rtvec _o; intersect * _intersectp; }; }// rt namespace
对应的intersect类也要改一下
/// intersect.hpp //https://www.cnblogs.com/lv-anchoret/p/10190092.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [refre ] 2019.3 // [brief ] the intersect-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include "E:OpenGL光线追踪code ay tracing 1-3 ay tracing 1-3 ay.hpp" namespace rt { class material; class aabb; // the infomation of intersection point struct hitInfo { lvgm::precision _t; //ray 中的系数t rtvec _p; //相交点、撞击点 rtvec _n; //_p点的表面法线 material* _materialp; //材质 rtvar _u; //texture-u rtvar _v; //texture-v }; // the statement of intersect class class intersect { public: /* @brief: 撞击函数,求取撞击点相关记录信息 @param: sight->视线 系数t的上下界->筛选撞击点 info->返回撞击点信息 @retur: 是否存在合法撞击点 */ virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const = 0; /* @brief: get the box of Geometry */ virtual aabb getbox()const = 0; /* Get the value of pdf function */ virtual rtvar pdf_value(const rtvec& o, const rtvec& v)const { return 0.; } /* generate the random number */ virtual rtvec random(const rtvec& o)const { return rtvec(1, 0, 0); } }; }// rt namespace
因为我们现在只是拿区域光源做实验,并不是所有的几何体派生类都要继承pdf相关的方法,所以,它们两个以虚函数的形式存在即可。
那么就剩下xz长方形了
rtvar xz_rect::pdf_value(const rtvec& o, const rtvec& v)const { hitInfo rec; if (this->hit(ray(o, v), 1e-3, rt::rtInf(), rec)) { rtvar area = (_x2 - _x1)*(_z2 - _z1); rtvar distance_squared = rec._t * rec._t * v.squar(); rtvar cosine = fabs(dot(v, rec._n) / v.normal()); return distance_squared / (cosine*area); } else return 0.; } rtvec xz_rect::random(const rtvec& o)const { rtvec random_point = rtvec(_x1 + lvgm::rand01() * (_x2 - _x1), _other, _z1 + lvgm::rand01()*(_z2 - _z1)); return random_point - o; }
把上一篇写在lerp函数里面的一大堆东西整合到类里面
那么我们的lerp就统一化了:
我们取sample为10,即可得到很好的效果:

现在我们将写一个关于混合概率密度的类:
///mixture_pdf.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [ time ] 2019.3 // [brief ] mixture pdfs // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class mixture_pdf :public pdf { public: mixture_pdf(pdf * p1, pdf* p2) { _p[0] = p1; _p[1] = p2; } /* @brief: we get the value of pdf function by this interface @param: the direction of location @retur: the value of the pdf function */ virtual rtvar value(const rtvec& direction)const { return 0.5*_p[0]->value(direction) + 0.5*_p[1]->value(direction); } /* @brief: generate a random number with a Probability model @param: none @retur: the Three-dimensional random vector */ virtual rtvec generate()const { if (lvgm::rand01() < 0.5) return _p[0]->generate(); else return _p[1]->generate(); } private: pdf* _p[2]; }; }// rt namespace
我们的lerp函数如下:
我们采样10次得到:
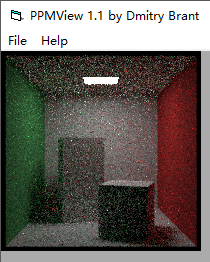
但是觉得效果不是很理想,我们来做一些测试
1. pdf 方程修改为 mixture_pdf = 1/3 * hit_pdf + 2/3 * cosine_pdf

2. pdf 方程修改为 mixture_pdf = 2/3 * hit_pdf + 1/3 * cosine_pdf

3. random修改 2/3 取 hit_pdf产生的随机值, 1/3 取 cosine_pdf 产生的随机值
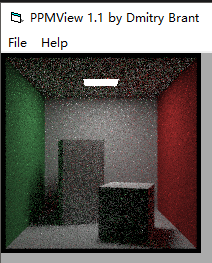
4. random修改 1/3 取 hit_pdf产生的随机值, 2/3 取 cosine_pdf 产生的随机值
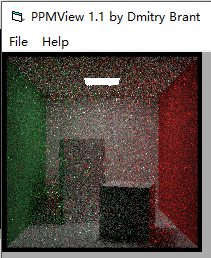
我们去上述方案的3、1,即:

得到图:
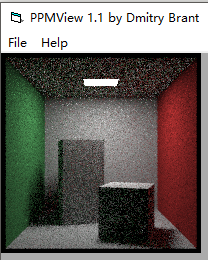
这张图显然比均分的效果要好
这里我们看不出到底是random起作用还是value,我们不妨取2、3组合
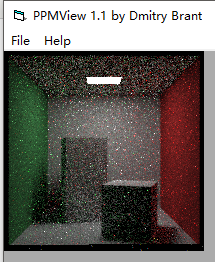
3把2的彩色噪声消除了些,但是这张图和原始的均分图差不多一样
所以结论,random和value的比例交叉比较好
我们采样1000次得到:
渲染中。。。。(就是清晰了点)
/***********************************************************************************/
跑了一晚上爬起来发现除零错误了,又抽空跑完了

/************************************************************************************/
本书第九章(下一章)介绍了一些关于当前渲染器的看法
作者在描述阴影光线和混合密度设计时,作者个人更偏向于混合密度设计,所以并没有在渲染器中采用阴影光线
作者描述了关于lerp函数中内存问题以及编码的不足
作者描述了关于玻璃材质和镜面的一些处理方法
作者还描述了关于HDR的0~1浮点表示以及RGB分组的0~255表示,还说明了这个渲染器是RGB的且基于物理的,还有一种是基于光谱的,以及两者结合的,但做起来很难,所以我们坚持RGB且基于物理的渲染器。


感谢您的阅读,生活愉快~