英文(词频统计)
def getText(): # 编写获得文本函数
txt = open("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\a.txt", mode='tr').read() # 打开文本文件只读
txt = txt.lower() # 将所有的英文字符变成小写
for ch in '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_’{|}`':
txt = txt.replace(ch, " ") # 用空格替换以上的特殊符号
return txt # 返回归一化处理后的文本
hamletTxt = getText() # 读取文件
words = hamletTxt.split() # 由于是以空格分隔,所以采用.split变成一个列表
counts = {} # 定义一个字典,用映射关系可以标记每个单词出现的次数
for word in words: # 在words列表中逐一取出每一个单词
counts[word] = counts.get(word, 0) + 1 # .get()函数用word作为键索引字典,如果在字典就返回已有次数加一,不在则为0+1(相当于往字典新加了一个元素)
items = list(counts.items()) # 将counts变成列表类型
items.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # 对列表按照键值对的2个元素的第二个元素进行由大到小的排序
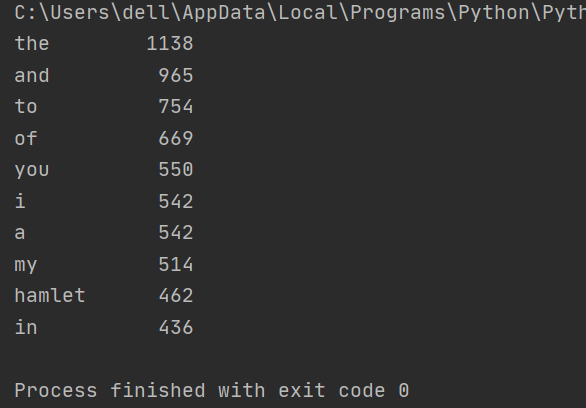
for i in range(10): # 前10名
word, count = items[i] # 将前10名的单词和次数保存在items中
print("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word, count)) # 打印出前10的单词和次数
中文(三国演义 词频统计)
- 不同:中文不存在大小写问题,使用jieba库进行分词,不用考虑标点符号
import jieba
txt = open("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8").read()
words = jieba.lcut(txt)
counts = {}#创建一个字典
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
else:
counts[word] = counts.get(word,0) + 1#计数
items = list(counts.items())#转换成列表
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)
for i in range(15):
word,count = items[i]
print("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word,count))#打印
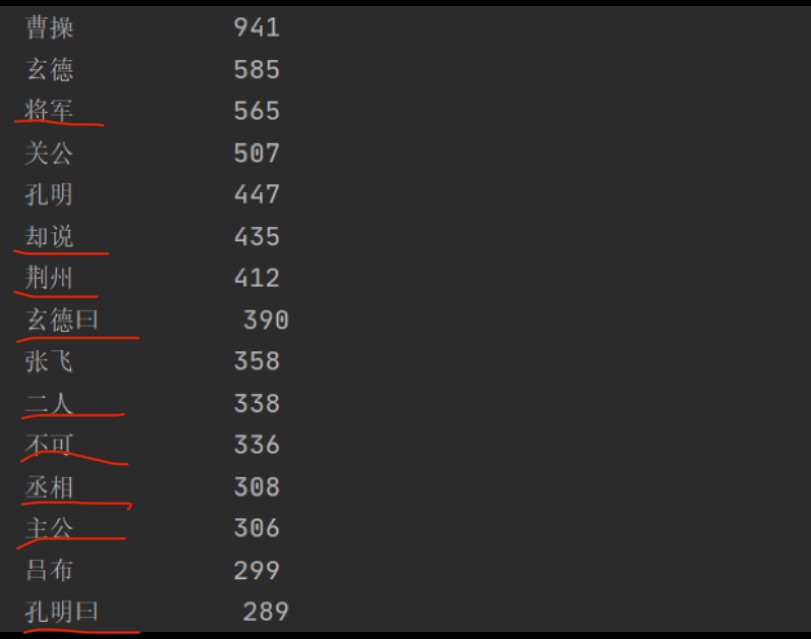
词频统计2.0->三国演义人物出场统计
-
排除上图红笔勾画的与人物无关的词语如将军,却说...
-
整合词意相同的人名,如孔明,诸葛亮,孔明说...
import jieba
txt = open("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8").read()
excludes = {"将军","却说","荆州","二人","不可","不能","如此"}#把不是人名的词加到集合excludes中
words = jieba.lcut(txt)
counts = {}#创建一个字典
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
elif word == "诸葛亮" or word == "孔明曰":
rword = "孔明"
elif word == "关公" or word == "云长":
rword = "关羽"
elif word == "玄德" or word == "玄德曰":
rword = "刘备"#整合操作
elif word == "孟德" or word == "丞相":
rword = "曹操"#整合操作
else:
rword = word
counts[word] = counts.get(word,0) + 1#计数
for word in excludes:
del counts[word] # 排除操作
items = list(counts.items())#转换成列表
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)
for i in range(10):
word,count = items[i]
print("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word,count))#打印
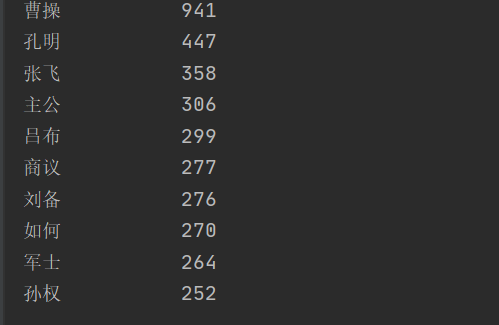
- 结果优化:可以经过不断地调试,把结果中不是人名的词加到encludes集合中,最终可得到期望的结果
词云实现
import jieba
import wordcloud#词云库
f = open("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\a.txt",encoding="utf-8")
t = f.read()
f.close()
ls = jieba.lcut(t)#分词后保存到ls
txt = " ".join(ls) #用空格将列表的每一个元素连接起来
w = wordcloud.WordCloud( font_path = "msyh.ttc",width = 1000,height = 700,background_color = "white")#绘制词云
w.generate(txt)#加载文本
w.to_file("grwordcloud.png")#生成词云文件

更多操作:1)限制字数:在绘制词云代码中加max_words = 10
2)底部更有形:代码第三行添加from imageio import imread第四行加mask = imread(“图片”),绘制词云代码第一个参数后加mask = mask