通过url访问资源有三个步骤:
-
接收请求
-
处理请求
-
响应请求
web服务器:将某个主机上的资源映射为一个URL供外界访问,完成接收和响应请求
servlet容器:存放着servlet对象(由程序员编程提供),处理请求
Servlet接口
Servlet接口定义了5种方法:
- init()
- service()
- destroy()
- getServletConfig()
- getServletInfo()
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Servlet {
//tomcat反射创建servlet之后,调用init方法传入ServletConfig,对于每一个Servlet实例,init()方法只能被调用一次
void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
//该方法返回容器调用init()方法时传递给Servlet对象的ServletConfig对象,ServletConfig对象包含了Servlet的初始化参数。
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
//tomcat解析http请求,封装成对象传入,容器调用service()方法来处理客户端的请求
void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
String getServletInfo();
void destroy();
}
ServletConfig:
封装了servlet的参数信息,从web.xml中获取,init-param标签的参数
<!--注册servlet-->
<servlet>
<!--为Servlet注册一个友好的名字-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!--指明为哪一个Servlet类起个友好的名字,名字要写全限定名-->
<servlet-class>com.yoocar.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
<!--配置参数-->
<init-param>
<param-name>user</param-name>
<param-value>root</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>pwd</param-name>
<param-value>123456</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--标签中间写的值,必须是正整数,数字越小,优先级越高-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
获取ServletConfig
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
//在servlet的整个生命周期内,servlet的init()方法,只会被调用一次,就是在第一次访问的时候
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
super.init();
System.out.println("HttpServlet-------------init");
}
/**
*
* @param request 获得浏览器请求
* @param response 获得服务器响应
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Object count = request.getSession().getAttribute("Count");
System.out.println("count==="+count);
//获取ServletConfig对象
getServletConfig();
try {
String userId = request.getParameter("userId");
System.out.println(userId);
String servletPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
System.out.println(servletPath);
//获取回应,以便向浏览器写数据
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream() ;
//写数据
out.write("hello Servlet".getBytes());
//关闭流
out.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
//获取ServletConfig对象
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
ServletConfig servletConfig = super.getServletConfig();
Enumeration<String> initParameterNames = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
while(initParameterNames.hasMoreElements()){
//获取init-param标签配置的参数param-name
String element = initParameterNames.nextElement();
System.out.println("param-name--------"+element);
String value = servletConfig.getInitParameter(element);
System.out.println("param-value--------"+value);
}
return servletConfig;
}
}
ServletRequest:
http请求到了tomcat后,tomcat通过字符串解析,把各个请求头(header),请求地址(URL),请求参数(queryString)都封装进Request。
ServletResponse:
Response在tomcat传给servlet时还是空的对象,servlet逻辑处理后,最终通过response.write()方法,将结果写入response内部的缓冲区,tomcat会在servlet处理结束后拿到response,获取里面的信息,组装成http响应给客户端
GenericServlet
改良版的servlet,抽象类,将ServletConfig提取出来,提升ServletConfig作用域,由局部变量变成全局变量
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//将ServletConfig提取出来
private transient ServletConfig config;
public GenericServlet() {
}
//并不是销毁servlet的方法,而是销毁servlet前一定会调用的方法。默认空实现,可以借此关闭一些资源
public void destroy() {
}
public String getInitParameter(String name) {
return this.getServletConfig().getInitParameter(name);
}
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
return this.getServletConfig().getInitParameterNames();
}
//初始化时已被赋值
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return this.config;
}
//通过ServletConfig获取ServletContext
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return this.getServletConfig().getServletContext();
}
public String getServletInfo() {
return "";
}
//提升ServletConfig作用域,由局部变量变成全局变量
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
//提供给子类覆盖
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
public void log(String message) {
this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message);
}
public void log(String message, Throwable t) {
this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t);
}
//空实现
public abstract void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
public String getServletName() {
return this.config.getServletName();
}
}
HttpServlet
GenericServlet的升级版,针对http请求所定制,在GenericServlet的基础上增加了service方法的实现,完成请求方法的判断
抽象类,用来被子类继承,得到匹配http请求的处理,子类必须重写以下方法中的一个
doGet,doPost,doPut,doDelete 未重写会报错(400,405)
service方法不应该重写,tomcat会为每一个HttpServlet创建单例
模板模式实现
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
try {
request = (HttpServletRequest)req;//强转成http类型,功能更强大
response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
} catch (ClassCastException var6) {
throw new ServletException(lStrings.getString("http.non_http"));
}
//每次都调,关键代码
this.service(request, response);
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取请求方式
String method = req.getMethod();
long lastModified;
//判断逻辑,调用不同的处理方法
if (method.equals("GET")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1L) {
//本来业务逻辑应该直接写在这里,但是父类无法知道子类具体的业务逻辑,所以抽成方法让子类重写,父类的默认实现输出405,没有意义
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) {
ifModifiedSince = -1L;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified / 1000L * 1000L) {
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(304);
}
}
} else if (method.equals("HEAD")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) {
this.doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("TRACE")) {
this.doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method};
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg);
}
}
一个类被声明为抽象的,一般有两个原因:
- 有抽象方法需要被实现
- 没有抽象方法,但是不希望被实例化
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet
ServletContext
servlet上下文,代表web.xml文件,其实就是一个map,服务器会为每个应用创建一个servletContext对象:
- 创建是在服务器启动时完成
- 销毁是在服务器关闭时完成
javaWeb中的四个域对象:都可以看做是map,都有getAttribute()/setAttribute()方法。
-
ServletContext域(Servlet间共享数据)
-
Session域(一次会话间共享数据,也可以理解为多次请求间共享数据)
-
Request域(同一次请求共享数据)
-
Page域(JSP页面内共享数据)
servletConfig
servletConfig对象持有ServletContext的引用,Session域和Request域也可以得到ServletContext
五种方法获取:
* ServletConfig#getServletContext();
* GenericServlet#getServletContext();
* HttpSession#getServletContext();
* HttpServletRequest#getServletContext();
* ServletContextEvent#getServletContext();//创建ioc容器时的监听
Filter
不仅仅是拦截Request
拦截方式有四种:
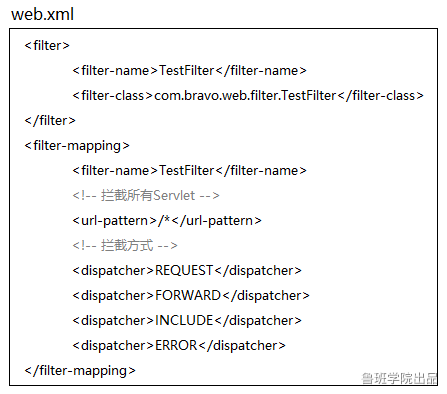
Redirect和REQUEST/FORWARD/INCLUDE/ERROR最大区别在于:
重定向会导致浏览器发送2次请求,FORWARD们是服务器内部的1次请求
因为FORWARD/INCLUDE等请求的分发是服务器内部的流程,不涉及浏览器,REQUEST/FORWARD/INCLUDE/ERROR和Request有关,Redirect通过Response发起
通过配置,Filter可以过滤服务器内部转发的请求
Listener
ServletContextListener
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that the web application initialization
* process is starting.
*
* <p>All ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* initialization before any filters or servlets in the web
* application are initialized.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being initialized
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce);
/**
* Receives notification that the ServletContext is about to be
* shut down.
*
* <p>All servlets and filters will have been destroyed before any
* ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* destruction.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being destroyed
*/
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce);
}
在 Servlet API 中有一个 ServletContextListener 接口,它能够监听 ServletContext 对象的生命周期,实际上就是监听 Web 应用的生命周期。
当Servlet 容器启动或终止Web 应用时,会触发ServletContextEvent 事件,该事件由ServletContextListener 来处理。在 ServletContextListener 接口中定义了处理ServletContextEvent 事件的两个方法。
public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent arg0) {
System.out.println("MyServletContextListener Destoryed");
}
/**
* servletContext初始化
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent arg0) {
System.out.println("MyServletContextListener Init");
ArrayList<String> expressList=new ArrayList<String>();
expressList.add("顺丰速递");
expressList.add("如风达");
expressList.add("宅急送");
expressList.add("EMS");
arg0.getServletContext().setAttribute("expressList", expressList);
}
}
Servlet项目启动执行顺序(重要)
- ServletContainerInitializer.onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx)
- ServletContextListener.contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce)
- Filter-------init(FilterConfig filterConfig)
- HttpServlet-------------init()
- Filter-------doFilter 过滤前
- HttpServlet------------doget/dopost
- Filter-------doFilter 过滤后
ServletContainerInitializer------------onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx)
ServletContextListener contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce)
Filter-------init(FilterConfig filterConfig)
HttpServlet-------------init()
Filter-------doFilter 过滤前
Filter-------doFilter 过滤后
Filter-------doFilter 过滤前
Filter-------doFilter 过滤后
Filter-------doFilter 过滤前
param-name--------pwd
param-value--------123456
param-name--------user
param-value--------root
Filter-------doFilter 过滤后
servlet映射器
每一个url要交给哪个servlet处理,由映射器决定
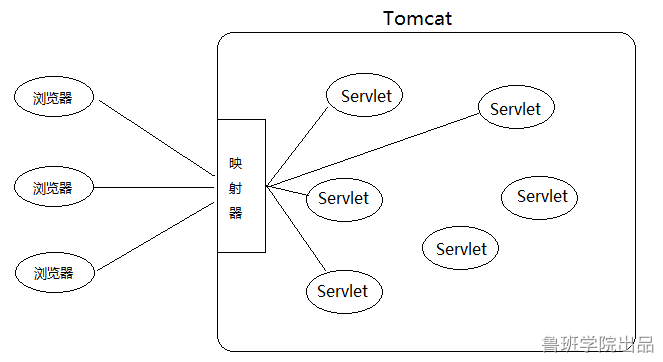
映射器在tomcat中就是Mapper类:
nternalMapWrapper方法定义了七种映射规则
private final void internalMapWrapper(ContextVersion contextVersion,
CharChunk path,
MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {
int pathOffset = path.getOffset();
int pathEnd = path.getEnd();
boolean noServletPath = false;
int length = contextVersion.path.length();
if (length == (pathEnd - pathOffset)) {
noServletPath = true;
}
int servletPath = pathOffset + length;
path.setOffset(servletPath);
// Rule 1 -- 精确匹配
MappedWrapper[] exactWrappers = contextVersion.exactWrappers;
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 2 -- 前缀匹配
boolean checkJspWelcomeFiles = false;
MappedWrapper[] wildcardWrappers = contextVersion.wildcardWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
internalMapWildcardWrapper(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting,
path, mappingData);
if (mappingData.wrapper != null && mappingData.jspWildCard) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
if (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/') {
mappingData.wrapper = null;
checkJspWelcomeFiles = true;
} else {
// See Bugzilla 27704
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars(buf, path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.pathInfo.recycle();
}
}
}
if(mappingData.wrapper == null && noServletPath &&
contextVersion.object.getMapperContextRootRedirectEnabled()) {
// The path is empty, redirect to "/"
path.append('/');
pathEnd = path.getEnd();
mappingData.redirectPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), pathOffset, pathEnd - pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd - 1);
return;
}
// Rule 3 -- 扩展名匹配
MappedWrapper[] extensionWrappers = contextVersion.extensionWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) {
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path, mappingData,
true);
}
...
上面都不匹配,则交给DefaultServlet,就是简单地用IO流读取静态资源并响应给浏览器。如果资源找不到,报404错误
对于静态资源,Tomcat最后会交由一个叫做DefaultServlet的类来处理对于Servlet ,Tomcat最后会交由一个叫做 InvokerServlet的类来处理对于JSP,Tomcat最后会交由一个叫做JspServlet的类来处理
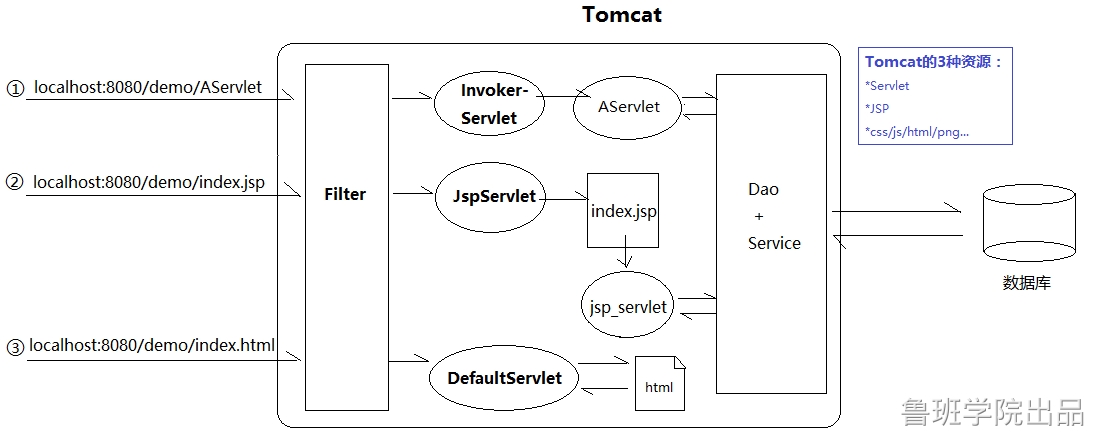
也就是说,servlet,/*这种配置,相当于把DefaultServlet、JspServlet以及我们自己写的其他Servlet都“短路”了,它们都失效了。
这会导致两个问题:
- JSP无法被编译成Servlet输出HTML片段(JspServlet短路)
- HTML/CSS/JS/PNG等资源无法获取(DefaultServlet短路)
DispatcherServlet配置/,会和DefaultServlet产生路径冲突,从而覆盖DefaultServlet。此时,所有对静态资源的请求,映射器都会分发给我们自己写的DispatcherServlet处理。遗憾的是,它只写了业务代码,并不能IO读取并返回静态资源。JspServlet的映射路径没有被覆盖,所以动态资源照常响应。
DispatcherServlet配置/*,虽然JspServlet和DefaultServlet拦截路径还是.jsp和/,没有被覆盖,但无奈的是在到达它们之前,请求已经被DispatcherServlet抢去,所以最终不仅无法处理JSP,也无法处理静态资源。
tomcat中conf/web.xml
相当于每个应用默认都配置了JSPServlet和DefaultServlet处理JSP和静态资源。
servlet SPI机制
要使用Java SPI,需要遵循如下约定:
从servlet3.0开始,web容器启动时为提供给第三方组件机会做一些初始化的工作,例如注册servlet或者filtes等,servlet规范中通过ServletContainerInitializer实现此功能。每个框架要使用ServletContainerInitializer就必须在对应的jar包的META-INF/services 目录创建一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,文件内容指定具体的ServletContainerInitializer实现类,那么,当web容器启动时就会运行这个初始化器做一些组件内的初始化工作。
注意一下,该机制的会调用是实现了ServletContainerInitializer的类/抽象类的onStartup方法,并且把被@HandlesTypes注解的对象,封装成onStartup中的set集合传入
/**
* Interface which allows a library/runtime to be notified of a web
* application's startup phase and perform any required programmatic
* registration of servlets, filters, and listeners in response to it.
*
* <p>Implementations of this interface may be annotated with
* {@link javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes HandlesTypes}, in order to
* receive (at their {@link #onStartup} method) the Set of application
* classes that implement, extend, or have been annotated with the class
* types specified by the annotation.
*
* <p>If an implementation of this interface does not use <tt>HandlesTypes</tt>
* annotation, or none of the application classes match the ones specified
* by the annotation, the container must pass a <tt>null</tt> Set of classes
* to {@link #onStartup}.
*
* <p>When examining the classes of an application to see if they match
* any of the criteria specified by the <tt>HandlesTypes</tt> annontation
* of a <tt>ServletContainerInitializer</tt>, the container may run into
* classloading problems if any of the application's optional JAR
* files are missing. Because the container is not in a position to decide
* whether these types of classloading failures will prevent
* the application from working correctly, it must ignore them,
* while at the same time providing a configuration option that would
* log them.
*
* <p>Implementations of this interface must be declared by a JAR file
* resource located inside the <tt>META-INF/services</tt> directory and
* named for the fully qualified class name of this interface, and will be
* discovered using the runtime's service provider lookup mechanism
* or a container specific mechanism that is semantically equivalent to
* it. In either case, <tt>ServletContainerInitializer</tt> services from web
* fragment JAR files excluded from an absolute ordering must be ignored,
* and the order in which these services are discovered must follow the
* application's classloading delegation model.
*
* @see javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public interface ServletContainerInitializer {
/**
* Notifies this <tt>ServletContainerInitializer</tt> of the startup
* of the application represented by the given <tt>ServletContext</tt>.
*
* <p>If this <tt>ServletContainerInitializer</tt> is bundled in a JAR
* file inside the <tt>WEB-INF/lib</tt> directory of an application,
* its <tt>onStartup</tt> method will be invoked only once during the
* startup of the bundling application. If this
* <tt>ServletContainerInitializer</tt> is bundled inside a JAR file
* outside of any <tt>WEB-INF/lib</tt> directory, but still
* discoverable as described above, its <tt>onStartup</tt> method
* will be invoked every time an application is started.
*
* @param c the Set of application classes that extend, implement, or
* have been annotated with the class types specified by the
* {@link javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes HandlesTypes} annotation,
* or <tt>null</tt> if there are no matches, or this
* <tt>ServletContainerInitializer</tt> has not been annotated with
* <tt>HandlesTypes</tt>
*
* @param ctx the <tt>ServletContext</tt> of the web application that
* is being started and in which the classes contained in <tt>c</tt>
* were found
*
* @throws ServletException if an error has occurred
*/
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx)
throws ServletException;
}
servlet实战
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!-- jsp start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--使用maven tomcat插件时,当前依赖需要注释掉,不然会产生冲突。-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
<version>8.5.31</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<version>8.5.31</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>servlet-demo</finalName>
<pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<!-- see http://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_war_packaging -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
web.xml
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!--<listener>
<listener-class>com.yoocar.listener.HelloListener</listener-class>
</listener>-->
<!--<listener>
<listener-class>com.yoocar.listener.MyListener</listener-class>
</listener>-->
<listener>
<listener-class>com.yoocar.listener.MyServletContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<!--过滤器名称-->
<filter-name>HelloFilter</filter-name>
<!--过滤器类的包路径-->
<filter-class>com.yoocar.filter.HelloFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<!--过滤器映射-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HelloFilter</filter-name>
<!--客户端请求访问任意资源文件时都要经过过滤器过滤,通过则访问文件,否则拦截。-->
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--注册servlet-->
<servlet>
<!--为Servlet注册一个友好的名字-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!--指明为哪一个Servlet类起个友好的名字,名字要写全限定名-->
<servlet-class>com.yoocar.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
<!--配置参数-->
<init-param>
<param-name>user</param-name>
<param-value>root</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>pwd</param-name>
<param-value>123456</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--标签中间写的值,必须是正整数,数字越小,优先级越高-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!--映射关系,下面为地址,即在浏览器中输入的url -->
<servlet-mapping>
<!--指明为哪一个Servlet类配置对外访问路径-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!--指定对外访问的路径-->
<url-pattern>/helloServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--同一个Servlet可以被映射到多个URL上,即多个 <servlet-mapping> 的<servlet-name> 的值,可以是同一个Servlet ;-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>OrderServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.yoocar.servlet.OrderServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>OrderServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/orderServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>OrderServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/orderServlet2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Servlet
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
//在servlet的整个生命周期内,servlet的init()方法,只会被调用一次,就是在第一次访问的时候
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
super.init();
System.out.println("HttpServlet-------------init");
}
//对于servlet的每次访问请求,都会调用一次servlet的service()方法 ;
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.service(req, resp);
System.out.println("HttpServlet-------------service");
}
/**
*
* @param request 获得浏览器请求
* @param response 获得服务器响应
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Object count = request.getSession().getAttribute("Count");
System.out.println("count==="+count);
//获取ServletConfig对象
getServletConfig();
try {
String userId = request.getParameter("userId");
System.out.println(userId);
String servletPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
System.out.println(servletPath);
//获取回应,以便向浏览器写数据
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream() ;
//写数据
out.write("hello Servlet".getBytes());
//关闭流
out.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
//获取ServletConfig对象
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
ServletConfig servletConfig = super.getServletConfig();
Enumeration<String> initParameterNames = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
while(initParameterNames.hasMoreElements()){
//获取init-param标签配置的参数param-name
String element = initParameterNames.nextElement();
System.out.println("param-name--------"+element);
String value = servletConfig.getInitParameter(element);
System.out.println("param-value--------"+value);
}
return servletConfig;
}
}
Filter
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HelloFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println(filterConfig.toString());
System.out.println("Filter-------init");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("Filter-------doFilter 过滤前");
chain.doFilter(request,response);
System.out.println("Filter-------doFilter 过滤后");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("Filter-------destroy");
}
}
ServletContainerInitializer
import javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import java.util.Set;
//spi机制
public class TestServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer{
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c,ServletContext servletContext) {
System.out.println("ServletContainerInitializer------------onStartup");
}
}