本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处.
本文都是springboot的常用和实用功能,话不多说开始吧
定时任务
1.启动类开启注解
@EnableScheduling //开启基于注解的定时任务 @MapperScan("com.pdzx.dao") @SpringBootApplication public class VideoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(VideoApplication.class); } }
2.开启定时任务
@Component public class ScheduledService { //每2秒 执行任务 @Scheduled(cron = "0/2 * * * * ?") public void hello(){ System.out.println("hello....."); } }
看结果
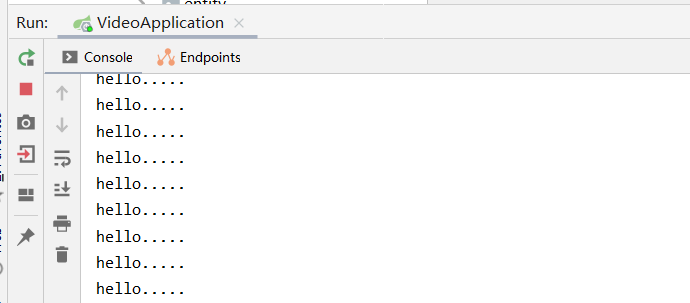
注意cron表达式的用法.
6个参数,分别为:秒 分 时 日 月 周
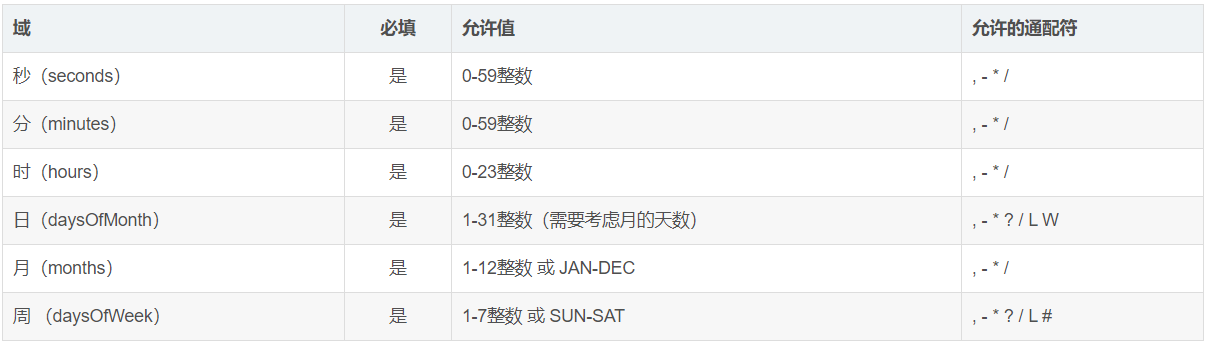
通配符说明:
*:表示匹配该域的任意值。在minutes域使用 * 表示每分钟。在months里表示每个月。在daysOfWeek域表示一周的每一天。
?:只能用在daysofMonth和daysofWeek两个域,表示不指定值,当两个子表达式其中之一被指定了值以后,为了避免冲突,需要将另一个子表达式的值设为 ?。因为daysofMonth和daysofWeek会相互影响。例如想在每月的2号触发调度,不管2号是周几,则只能使用如下写法:0 0 0 2 * ?, 其中最后一位只能用?,而不能使用*,如果使用*表示不管周几都会触发。
-:表示范围。例如在minutes域使用5-20,表示从5分到20分钟每分钟触发一次
/:表示起始时间开始触发,然后每隔固定时间触发一次。例如在minutes域使用5/20,则意味着从当前小时的第5分钟开每20分钟触发一次。
,:表示列出枚举值。例如:在minutes域使用5,20,则意味着在5分和20分时各触发一次。
L:表示最后,是单词“last”的缩写,只能出现在daysofWeek和dayofMonth域。在daysofWeek域使用5L意思是在指定月的最后的一个星期四触发。在dayofMonth域使用5L或者FRIL意思是在指定月的倒数第5天触发。在使用L参数时,不要指定列表或范围。
W:表示有效工作日(周一到周五),只能出现在daysofMonth域,系统将在离指定日期的最近的有效工作日触发事件。例如:在daysofMonth使用5W,如果5号是周六,则将在最近的工作日周五,即4号触发。如果5号是周日,则在6日(周一)触发。如果5日在星期一到星期五中的一天,则就在5日触发。另外,W的最近寻找不会跨过月份 。
LW:这两个字符可以连用,表示指定月的最后一个工作日。
#:用于确定每个月第几个周几,只能出现在daysofMonth域。例如在4#2,表示某月的第二个周三。
常用表达式示例:
例如想在每月的2号触发调度,不管2号是周几,则只能使用如下写法:0 0 0 2 * ?, 其中最后一位只能用?,而不能使用*,如果使用*表示不管周几都会触发
(1)0/2 * * * * ? 表示每2秒 执行任务 (1)0 0/2 * * * ? 表示每2分钟 执行任务 (1)0 0 2 1 * ? 表示在每月的1日的凌晨2点调整任务 (2)0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 表示周一到周五每天上午10:15执行作业 (3)0 15 10 ? 6L 2002-2006 表示2002-2006年的每个月的最后一个星期五上午10:15执行作 (4)0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点 (5)0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时 (6)0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午12点 (7)0 0 12 * * ? 每天中午12点触发 (8)0 15 10 ? * * 每天上午10:15触发 (9)0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发 (10)0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发 (11)0 15 10 * * ? 2005 2005年的每天上午10:15触发 (12)0 * 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发 (13)0 0/5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发 (14)0 0/5 14,18 * * ? 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发 (15)0 0-5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发 (16)0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发 (17)0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 周一至周五的上午10:15触发 (18)0 15 10 15 * ? 每月15日上午10:15触发 (19)0 15 10 L * ? 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发 (20)0 15 10 ? * 6L 每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发 (21)0 15 10 ? * 6L 2002-2005 2002年至2005年的每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发 (22)0 15 10 ? * 6#3 每月的第三个星期五上午10:15触发
异步操作
1.启动类开启注解
@EnableAsync //开启异步注解功能 @EnableScheduling //开启基于注解的定时任务 @MapperScan("com.pdzx.dao") @SpringBootApplication public class VideoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(VideoApplication.class); } }
2.注解标注异步方法
@Component public class AsyncService { //告诉Spring这是一个异步方法,SpringBoot就会自己开一个线程池,进行调用! @Async public void hello(){ try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("业务进行中...."); } }
3.控制层测试
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/async/hello")
public String hello(){
long time1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
asyncService.hello();//调用异步方法
long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Controller :"+(time2-time1));
return "success";
}
}
访问该url,看结果

异步生效了
统一结果返回
封装一个统一的返回类
public class Result<T> { //是否成功 private Boolean success; //状态码 private Integer code; //提示信息 private String msg; //数据 private T data; public Result() { } //自定义返回结果的构造方法 public Result(Boolean success,Integer code, String msg,T data) { this.success = success; this.code = code; this.msg = msg; this.data = data; } //自定义异常返回的结果 public static Result defineError(DefinitionException de){ Result result = new Result(); result.setSuccess(false); result.setCode(de.getErrorCode()); result.setMsg(de.getErrorMsg()); result.setData(null); return result; } //其他异常处理方法返回的结果 public static Result otherError(ErrorEnum errorEnum){ Result result = new Result(); result.setMsg(errorEnum.getErrorMsg()); result.setCode(errorEnum.getErrorCode()); result.setSuccess(false); result.setData(null); return result; } public Boolean getSuccess() { return success; } public void setSuccess(Boolean success) { this.success = success; } public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } public T getData() { return data; } public void setData(T data) { this.data = data; } }
统一异常
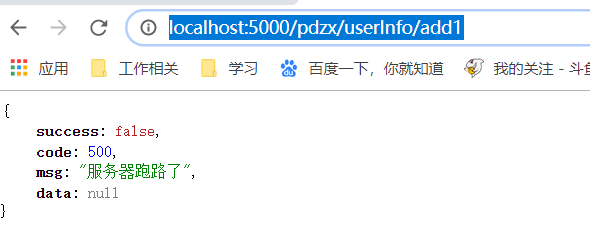
public enum ErrorEnum { // 数据操作错误定义 SUCCESS(200, "nice"), NO_PERMISSION(403,"你没得权限"), NO_AUTH(401,"你能不能先登录一下"), NOT_FOUND(404, "未找到该资源!"), INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500, "服务器跑路了"), ; /** 错误码 */ private Integer errorCode; /** 错误信息 */ private String errorMsg; ErrorEnum(Integer errorCode, String errorMsg) { this.errorCode = errorCode; this.errorMsg = errorMsg; } public Integer getErrorCode() { return errorCode; } public String getErrorMsg() { return errorMsg; } }
全局异常处理
Springboot对于异常的处理也做了不错的支持,
它提供了一个 @ControllerAdvice注解以及 @ExceptionHandler注解,前者是用来开启全局的异常捕获,后者则是说明捕获哪些异常,对那些异常进行处理。如下
1.自定义异常
public class DefinitionException extends RuntimeException { protected Integer errorCode; protected String errorMsg; public DefinitionException(){ } public DefinitionException(Integer errorCode, String errorMsg) { this.errorCode = errorCode; this.errorMsg = errorMsg; } public Integer getErrorCode() { return errorCode; } public void setErrorCode(Integer errorCode) { this.errorCode = errorCode; } public String getErrorMsg() { return errorMsg; } public void setErrorMsg(String errorMsg) { this.errorMsg = errorMsg; } }
2.全局异常处理
@ControllerAdvice public class GlobalExceptionHandler { /** * 处理自定义异常 */ @ExceptionHandler(value = DefinitionException.class) @ResponseBody public Result bizExceptionHandler(DefinitionException e) { return Result.defineError(e); } /** * 处理其他异常 */ @ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class) @ResponseBody public Result exceptionHandler( Exception e) { return Result.otherError(ErrorEnum.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); } }
测试
@RequestMapping("/getDeException")
public Result DeException(){
throw new DefinitionException(400,"我出错了");
}
@RequestMapping("/getException")
public Result Exception(){
Result result = new Result();
int a=1/0;
return result;
}
看结果
首先看自定义异常

看其他异常结果
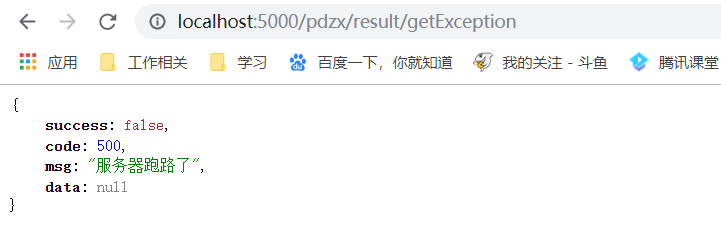
拦截器
拦截器是在servlet执行之前执行的程序(这里就是controller代码执行之前),它主要是用于拦截用户请求并作相应的处理,比如说可以判断用户是否登录,做相关的日志记录,也可以做权限管理。
SpringBoot中的拦截器实现和spring mvc 中是一样的,
它的大致流程是,先自己定义一个拦截器类,并将这个类实现一个HandlerInterceptor类,或者是继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter,都可以实现拦截器的定义。
然后将自己定义的拦截器注入到适配器中,也有两种方式,一种是实现WebMvcConfigurer接口,一种是继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter。下面我们来看看如何完成。
1.自定义拦截器
/**
*
* 自定义的拦截器可以实现HandlerInterceptor接口,也可以继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter类。
重写三个方法,当然也可以只实现一个最重要的preHandle方法。
preHandle方法:此方法会在进入controller之前执行,返回Boolean值决定是否执行后续操作。
postHandle方法:此方法将在controller执行之后执行,但是视图还没有解析,可向ModelAndView中添加数据(前后端不分离的)。
afterCompletion方法:该方法会在整个请求结束(请求结束,但是并未返回结果给客户端)之后执行, 可获取响应数据及异常信息。
*/
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) {
System.out.println("进入拦截器了");
//中间写逻辑代码,比如判断是否登录成功,失败则返回false
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) {
//
System.out.println("controller 执行完了");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
System.out.println("我获取到了一个返回的结果:"+response);
System.out.println("请求结束了");
}
}
2.拦截器注入适配器
@Configuration public class InterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor()) .addPathPatterns("/**")//拦截所有的路径 .excludePathPatterns("/LoginController/*")//配置不需要拦截的路径。 .excludePathPatterns("/hello/login");//配置多个路径。 } }
3.先创建一个登陆的测试,这个接口是不会拦截的。
@RestController @RequestMapping("LoginController") public class Login { @RequestMapping("/login") public String login(){ System.out.println("controller开始执行"); return "login success"; } }
浏览器测试
http://localhost:5000/pdzx/LoginController/login
看结果
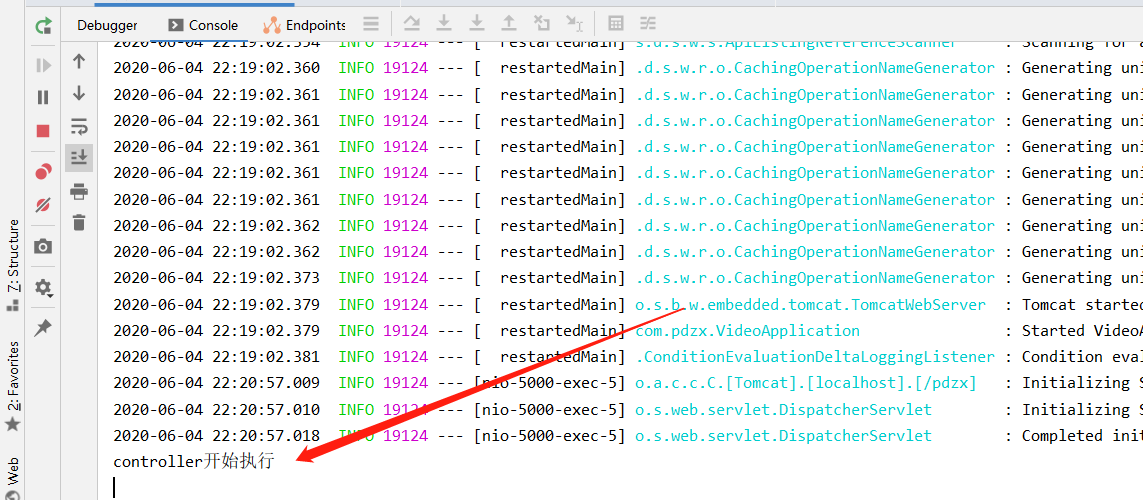
控制台只输出了未拦截接口内的代码,说明这个接口是未拦截的。浏览器的显示就不管了。其实一般是拦截登录接口,这里就将它放开了,以供测试。
4..创建一个拦截的controller
@RestController @RequestMapping("/hello") public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ System.out.println("经过拦截的controller代码执行完毕"); return "hello"; } @RequestMapping("/login") public String login(){ System.out.println("不拦截的controller代码执行完毕"); return "hello login"; } }
测试
http://localhost:5000/pdzx/hello/hello
看结果
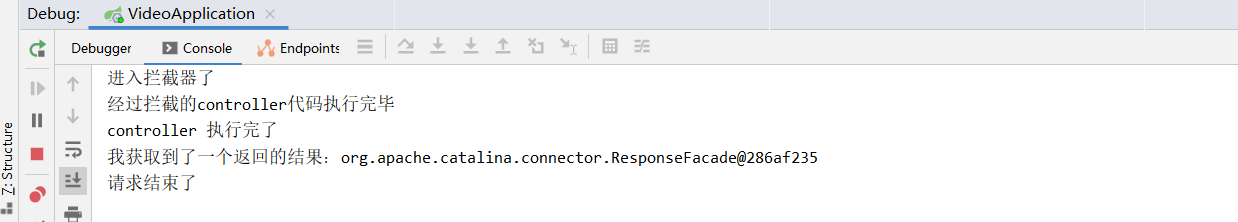
可以看到,首先是进入了拦截器,
通过拦截器之后,进入了controller中的方法,执行完controller的代码之后就进入了自定义拦截器中的postHandle方法,最后进入afterCompletion方法,并获取到了一个response对象。
事务处理
1.开启事务支持
@EnableTransactionManagement//开启事务支持 @EnableAsync //开启异步注解功能 @EnableScheduling //开启基于注解的定时任务 @MapperScan("com.pdzx.dao") @SpringBootApplication public class VideoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(VideoApplication.class); } }
2.@Transactional来修饰一个方法
@Service public class UserInfoServiceImpl { @Autowired private UserInfoMapper userInfoMapper; public int insertSelective(UserInfo record) { return userInfoMapper.insertSelective(record); } public int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(UserInfo record) { return userInfoMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(record); } @Transactional public void add1(UserInfo record){ userInfoMapper.insertSelective(record); int i=1/0; } }
3.controller
@RequestMapping("userInfo")
@RestController
public class UserInfoController {
@Autowired
private UserInfoServiceImpl userInfoService;
@RequestMapping("/add1")
public void add1(){
UserInfo userInfo=new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("张三");
userInfoService.add1(userInfo);
}
}
请求该路径之前,看一下数据库
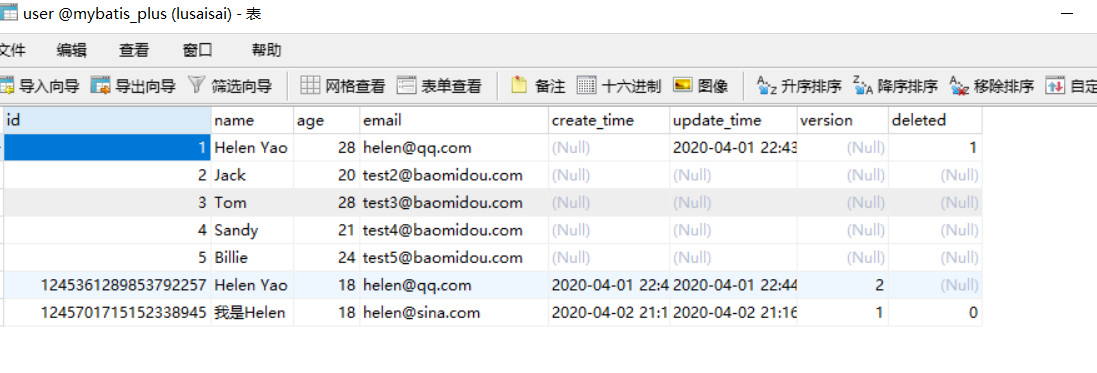
请求该接口
http://localhost:5000/pdzx/userInfo/add1
看结果
看控制台和数据库
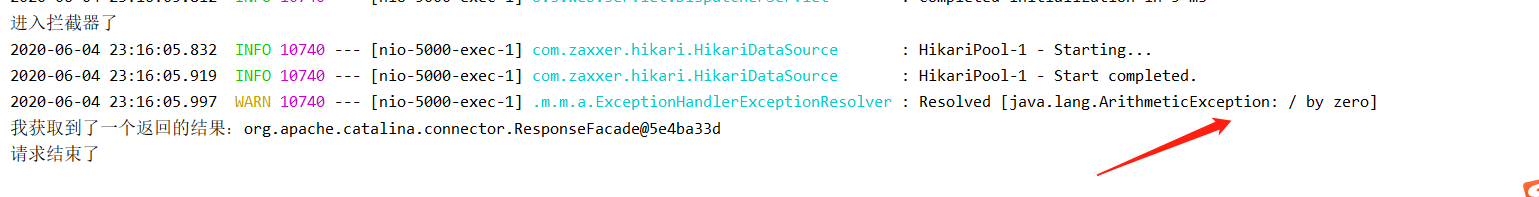
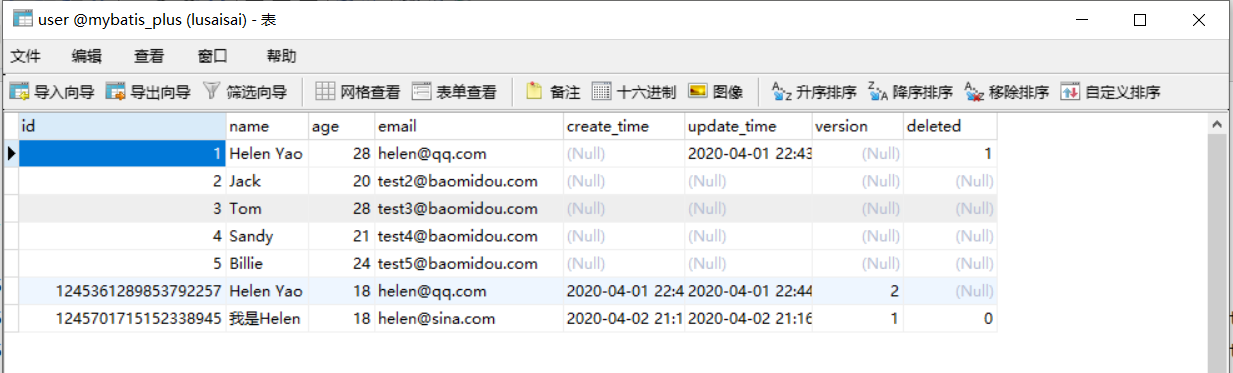
数据没进入数据库
我们把那行错误注释掉
@Transactional public void add1(UserInfo record){ userInfoMapper.insertSelective(record); //int i=1/0; }
再试一下,看结果
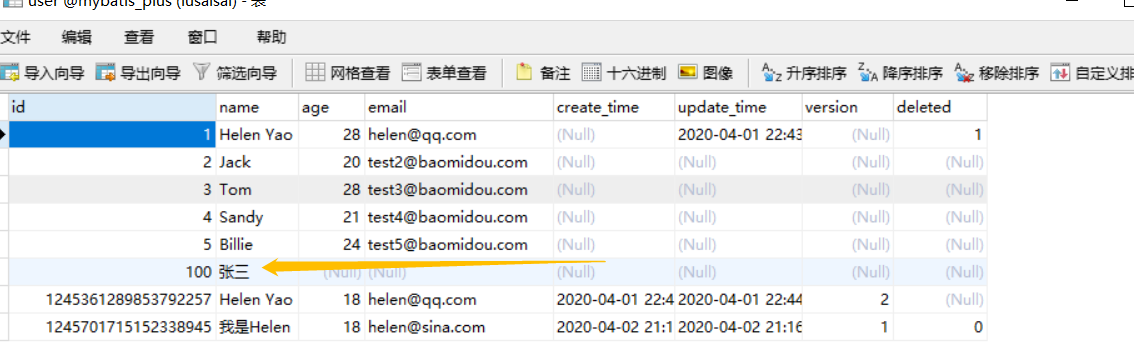
结果了,可以看出,事务处理生效了.
我们再看一个情况:
不带事务的方法调用该类中带事务的方法,不会回滚。
因为spring的回滚是用过代理模式生成的,如果是一个不带事务的方法调用该类的带事务的方法,直接通过this.xxx()调用,而不生成代理事务,所以事务不起作用
看代码,add2,调用带事务处理的updateByPrimaryKeySelective
@Transactional public int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(UserInfo userInfo) { int i=1/0; userInfo=new UserInfo(); userInfo.setId((long)100); userInfo.setName("李四"); return userInfoMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(userInfo); } public void add2(UserInfo record){ userInfoMapper.insertSelective(record); updateByPrimaryKeySelective(record); }
controller层
@RequestMapping("/add2")
public void add2(){
UserInfo userInfo=new UserInfo();
userInfo.setId((long) 150);
userInfo.setName("张三");
userInfoService.add2(userInfo);
}
测试
http://localhost:5000/pdzx/userInfo/add2
看控制台和数据库

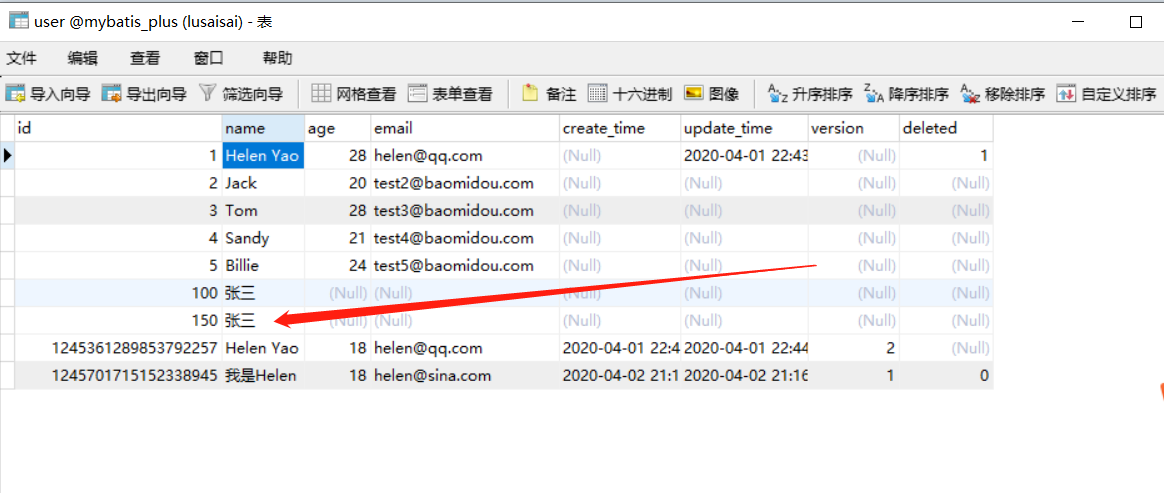
可以看到数据存到数据库了,事物没有生效,这个情况还需注意