1.隐式链接
新建一个工程,选择Win32 Dynamic-Link Library,取名Dll1,选择一个空的动态链接库工程,然后新建一个文件名为Dll1的C++源文件,编辑:
_declspec(dllexport) int add(int a,int b) //加法
{
return a+b;
}
_declspec(dllexport) int subtract(int a,int b) //减法
{
return a-b;
}
编译,生成动态链接库文件:Dll1.dll
2.查看dll文件的导出信息
打开cmd,进入到:D:\>cd D:\c programs\C_WORKSPACE\Dll1\Debug
然后:D:\c programs\C_WORKSPACE\Dll1\Debug>dumpbin /exports Dll1.dll
输出如下信息:
File Type: DLL
Section contains the following exports for Dll1.dll
0 characteristics
4DBBFCA6 time date stamp Sat Apr 30 20:12:22 2011
0.00 version
1 ordinal base
2 number of functions
2 number of names
ordinal hint RVA name
1 0 0000100A ?add@@YAHHH@Z
2 1 00001005 ?subtract@@YAHHH@Z
Summary
7000 .data
1000 .idata
3000 .rdata
2000 .reloc
2A000 .text
3.调用动态链接库
新建一个基于对话框的MFC应用程序,取名DllTest,并在对话框资源中添加两个按钮(id: IDC_BTN_ADD,标题:add)和(id: IDC_BTN_SUBTRACT,标题:subtract),并双击分别添加消息响应函数,编辑:
#pragma comment (lib,"Dll1.lib") //加载库引用文件
extern int add(int a,int b);//声明一下,表明这函数是在外部定义的
extern int subtract(int a,int b);
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnAdd()
{
CString str;
str.Format("5+3=%d",add(5,3));
MessageBox(str);
}
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnSubtract()
{
CString str;
str.Format("5-3=%d",subtract(5,3));
MessageBox(str);
}
将上一步生成的Dll1.lib文件拷贝到这个工程目录下,并在DllTestDlg.cpp中声明:
#pragma comment (lib,"Dll1.lib") //加载库引用文件
运行。OK!
4.查看可执行文件(或dll)的输入信息
方式一
Cmd中输入:D:\c programs\C_WORKSPACE\DllTest\Debug>dumpbin /imports DllTest.exe
方式二
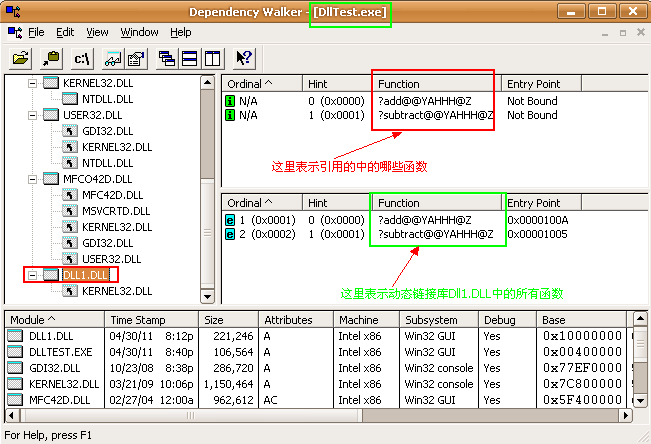
利用microsoft visual studio 6.0的工具depends可以查看可执行文件、动态连接库等二进制文件的输入输出信息。如下图:
5.用_declspec(dllimport)表明从dll中引入函数
修改DllTestDlg.cpp中的:
#pragma comment (lib,"Dll1.lib") //加载库引用文件
//extern int add(int a,int b);//声明一下,表明这函数是在外部定义的
//extern int subtract(int a,int b);
_declspec(dllimport) int add(int a,int b);//指示导入动态链接库中的函数
_declspec(dllimport) int subtract(int a,int b); //告诉编译器这两函数是从Dll1.lib中引入的
6.在动态链接库工程中增加头文件
打开Dll1动态链接库工程,在工程中新建一个C/C++ Head Files,取名叫:Dll1 ,编辑:
_declspec(dllimport) int add(int a,int b);//指示导入动态链接库中的函数
_declspec(dllimport) int subtract(int a,int b);//告诉编译器这两函数是从Dll1.lib中引
并在DllTestDlg.cpp当中包含头文件:#include "..\Dll1\Dll1.h " //包含动态链接库的头文件
7.使dll既可以被自身引用也可以被外部引用
//Dll1.h
#ifdef DLL1_API
#else
#define DLL1_API _declspec(dllimport)
#endif
DLL1_API int add(int a,int b);//指示导入动态链接库中的函数
DLL1_API int subtract(int a,int b);//告诉编译器这两函数是从Dll1.
//dll1.cpp
#define DLL1_API _declspec(dllexport)
#include "Dll1.h"
_declspec(dllexport) int add(int a,int b) //加法
{
return a+b;
}
_declspec(dllexport) int subtract(int a,int b) //减法
{
return a-b;
}
8.在dll中导出类
在Dll1.h中添加:
class DLL1_API Point //Dll1_API是宏定义,用于导出类
{
public:
void output(int x,int y);
};
在dll1.cpp中编辑:
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
.........
.........
void Point::output(int x,int y)
{
HWND hwnd=GetForegroundWindow();//得到调用者进程当前正在使用的窗口句柄
HDC hdc=GetDC(hwnd);
char buf[20];
memset(buf,0,20);
sprintf(buf,"x=%d,y=%d",x,y);//将要输出的字符串打印到buf中
TextOut(hdc,0,0,buf,strlen(buf));
ReleaseDC(hwnd,hdc);
}
编译,并将生成的dll与lib文件复制到DllTest工程目录下。
并在测试程序中的对话框资源上添加一个按钮(id:IDC_BTN_OUTPUT,Caption:output),并添加消息响应函数,编辑:
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnOutput()
{
Point pt;
pt.output(5,3);//输出
}
运行,ok!
导出类中的指定的成员函数
在Dll1.h中编辑:
class /*DLL1_API*/ Point //Dll1_API是宏定义,用于导出类
{
public:
DLL1_API void output(int x,int y);//导出
void test();
};
在Dll1.cpp中编辑:
void Point::test() //实现
{
}
9.修改dll的兼容性
对于其它的C++编译器生成的dll访问客户端,要使用用VC++生成的dll。
在Dll1.h中编辑:
#ifdef DLL1_API
#else
#define DLL1_API extern "C" _declspec(dllimport)
#endif
注释掉:
//class /*DLL1_API*/ Point //Dll1_API是宏定义,用于导出类
/*{
public:
DLL1_API void output(int x,int y);//导出
void test();
};
*/
在dll1.cpp中编辑:
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define DLL1_API extern "C" _declspec(dllexport)
#include "Dll1.h"
注释掉:
/*
void Point::output(int x,int y)
{
HWND hwnd=GetForegroundWindow();//得到调用者进程当前正在使用的窗口句柄
HDC hdc=GetDC(hwnd);
char buf[20];
memset(buf,0,20);
sprintf(buf,"x=%d,y=%d",x,y);//将要输出的字符串打印到buf中
TextOut(hdc,0,0,buf,strlen(buf));
ReleaseDC(hwnd,hdc);
}
void Point::test()
{
}
*/
注意:extern "C",就不能在导出类中的成员函数,同样在类外边的函数,如果用_stdcall调用约定,那么导出的函数名仍然会发生变化,因为_stdcall的调用约定不同于C的调用约定,所以即使用了extern "C"指明了调用约定,在加了_stdcall的函数上,编译时仍然会改变函数的名字。示例,如可以这样修改:
在Dll1.h中,
DLL1_API int _stdcall add(int a,int b);//指示导入动态链接库中的函数
DLL1_API int _stdcall subtract(int a,int b);//告诉编译器这两函数是从Dll1.lib中引
在DLL1_API中
DLL1_API int _stdcall add(int a,int b) //加法
{
return a+b;
}
DLL1_API int _stdcall subtract(int a,int b) //减法
{
return a-b;
}
编译生成dll后,用dumpbin /exports Dll1.dll测试可以发现Dll1.dll中的两个函数的名字被改成了,如下:
_add@8 和 _substract@8 ,其中8表示这个中的参数所占用的字节数。
10.利用模块定义文件(def)解决函数名字改变的问题
新建一个工程,选择Win32 Dynamic-Link Library,取名Dll2,选择一个空的动态链接库工程,然后新建一个文件名为Dll2的C++源文件,编辑:
int add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
int subtract(int a,int b)
{
return a-b;
}
然后在这个工程目录下,新建一个文本文件,并将其名字改成Dll2.def,接着在Dll2工程中选择Project->add to project->files… ,将Dll2.def文件添加到工程,编辑:
LIBRARY Dll2
#表示在动态链接库在要导出的函数
EXPORTS
add
subtract
即使这样改变也没关系,如下:
int _stdcall add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
int _stdcall subtract(int a,int b)
{
return a-b;
}
编译,用dumpbin /exports Dll2.dll测试,可以看到函数名是 add 和 subtract,可见编译后导出的函数名也没有改变。但要注意,相应的测试程中也要改成 _stdcall方式访问。
11.动态加载一个名字不变的动态链接库
在在DllTest.cpp中首先注释掉://#include "..\Dll1\Dll1.h" //包含动态链接库的头文件
再编辑:
//#pragma comment (lib,"Dll1.lib") //加载库引用文件
//extern int add(int a,int b);//声明一下,表明这函数是在外部定义的
//extern int subtract(int a,int b);
//_declspec(dllimport) int add(int a,int b);//指示导入动态链接库中的函数
//_declspec(dllimport) int subtract(int a,int b);//告诉编译器这两函数是从Dll1.lib中引入的
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnAdd()
{
HINSTANCE hInst;
hInst=LoadLibrary("Dll2.dll");//动态加载动态链接库
typedef int (/*_stdcall*/*ADDPROC)(int a,int b);//定义一个表示有两个参数的函数指针类型
ADDPROC Add=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,"add");//用来接收由GetProcAddress返回的dll导出函数的地址
//获得动态链接库导出函数的地址
if(!Add)
{
MessageBox("获取add函数地址失败");
return;
}
CString str;
str.Format("5-3=%d",Add(5,3));
MessageBox(str);
}
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnSubtract()
{
HINSTANCE hInst;
hInst=LoadLibrary("Dll2.dll");//动态加载动态链接库
typedef int (/*_stdcall*/*ADDPROC)(int a,int b);//定义一个表示有两个参数的函数指针类型
ADDPROC Subtract=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,"subtract");//用来接收由GetProcAddress返回的dll导出函数的地址
//获得动态链接库导出函数的地址
if(!Subtract)
{
MessageBox("获取subtract函数地址失败");
return;
}
CString str;
str.Format("5-3=%d",Subtract(5,3));
MessageBox(str);
}
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnOutput()
{
}
并将Dll2.dll拷贝到DllTest工程目录下,编译运行,OK!
12.动态加载名字改变的dll
新建一个工程,选择Win32 Dynamic-Link Library,取名Dll3,选择一个空的动态链接库工程,然后新建一个文件名为Dll3的C++源文件,编辑:
_declspec(dllexport) int add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
_declspec(dllexport) int subtract(int a,int b)
{
return a-b;
}
编译后,将Dll3.dll文件拷贝与DllTest工程目录下,然后对DllTest修改,如下:
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnAdd()
{
HINSTANCE hInst;
//hInst=LoadLibrary("Dll2.dll");//动态加载动态链接库
hInst=LoadLibrary("Dll3.dll");
typedef int (/*_stdcall*/ *ADDPROC)(int a,int b);//定义一个表示有两个参数的函数指针类型
//ADDPROC Add=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,"add");//用来接收由GetProcAddress返回的dll导出函数的地址
//获得动态链接库导出函数的地址
//ADDPROC Add=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,"?add@@YAHHH@Z");
ADDPROC Add=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,MAKEINTRESOURCE(1));
if(!Add)
{
MessageBox("获取add函数地址失败");
return;
}
CString str;
str.Format("5-3=%d",Add(5,3));
MessageBox(str);
FreeLibrary(hInst);//释放动态链接库
}
void CDllTestDlg::OnBtnSubtract()
{
HINSTANCE hInst;
//hInst=LoadLibrary("Dll2.dll");//动态加载动态链接库
hInst=LoadLibrary("Dll3.dll");
typedef int (/*_stdcall*/ *ADDPROC)(int a,int b);//定义一个表示有两个参数的函数指针类型
//ADDPROC Subtract=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,"subtract");//用来接收由GetProcAddress返回的dll导出函数的地址
//获得动态链接库导出函数的地址
//ADDPROC Subtract=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,"?subtract@@YAHHH@Z");
ADDPROC Subtract=(ADDPROC)GetProcAddress(hInst,MAKEINTRESOURCE(2));
if(!Subtract)
{
MessageBox("获取subtract函数地址失败");
return;
}
CString str;
str.Format("5-3=%d",Subtract(5,3));
MessageBox(str);
FreeLibrary(hInst);//释放动态链接库
}
编译运行,OK!!
13.DllMain函数
DllMain函数指动态链接库的入口函数
DllMain
The DllMain function is an optional entry point into a dynamic-link library (DLL). If the function is used, it is called by the system when processes and threads are initialized and terminated, or upon calls to the LoadLibrary and FreeLibrary functions.
DllMain is a placeholder for the library-defined function name. Earlier versions of the SDK documentation used DllEntryPoint as the entry-point function name. You must specify the actual name you use when you build your DLL. For more information, see the documentation included with your development tools.
BOOL WINAPI DllMain(
HINSTANCE hinstDLL, // handle to the DLL module
DWORD fdwReason, // reason for calling function
LPVOID lpvReserved // reserved
);
Parameters
hinstDLL
[in] Handle to the DLL module. The value is the base address of the DLL. The HINSTANCE of a DLL is the same as the HMODULE of the DLL, so hinstDLL can be used in calls to functions that require a module handle.
fdwReason
[in] Specifies a flag indicating why the DLL entry-point function is being called. This parameter can be one of the following values.
|
Value |
Meaning |
|
DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH |
Indicates that the DLL is being loaded into the virtual address space of the current process as a result of the process starting up or as a result of a call to LoadLibrary. DLLs can use this opportunity to initialize any instance data or to use the TlsAlloc function to allocate a thread local storage (TLS) index. |
|
DLL_THREAD_ATTACH |
Indicates that the current process is creating a new thread. When this occurs, the system calls the entry-point function of all DLLs currently attached to the process. The call is made in the context of the new thread. DLLs can use this opportunity to initialize a TLS slot for the thread. A thread calling the DLL entry-point function with DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH does not call the DLL entry-point function with DLL_THREAD_ATTACH. Note that a DLL's entry-point function is called with this value only by threads created after the DLL is loaded by the process. When a DLL is loaded using LoadLibrary, existing threads do not call the entry-point function of the newly loaded DLL. |
|
DLL_THREAD_DETACH |
Indicates that a thread is exiting cleanly. If the DLL has stored a pointer to allocated memory in a TLS slot, it uses this opportunity to free the memory. The system calls the entry-point function of all currently loaded DLLs with this value. The call is made in the context of the exiting thread. |
|
DLL_PROCESS_DETACH |
Indicates that the DLL is being unloaded from the virtual address space of the calling process as a result of unsuccessfully loading the DLL, termination of the process, or a call to FreeLibrary. The DLL can use this opportunity to call the TlsFree function to free any TLS indices allocated by using TlsAlloc and to free any thread local data. Note that the thread that receives the DLL_PROCESS_DETACH notification is not necessarily the same thread that received the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH notification. |
lpvReserved
[in] Specifies further aspects of DLL initialization and cleanup.
If fdwReason is DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, lpvReserved is NULL for dynamic loads and non-NULL for static loads.
If fdwReason is DLL_PROCESS_DETACH, lpvReserved is NULL if DllMain has been called by using FreeLibrary and non-NULL if DllMain has been called during process termination.
Return Values
When the system calls the DllMain function with the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH value, the function returns TRUE if it succeeds or FALSE if initialization fails. If the return value is FALSE when DllMain is called because the process uses the LoadLibrary function, LoadLibrary returns NULL. (The system immediately calls your entry-point function with DLL_PROCESS_DETACH and unloads the DLL.) If the return value is FALSE when DllMain is called during process initialization, the process terminates with an error. To get extended error information, call GetLastError.
When the system calls the DllMain function with any value other than DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, the return value is ignored.
Remarks
During initial process startup or after a call to LoadLibrary, the system scans the list of loaded DLLs for the process. For each DLL that has not already been called with the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH value, the system calls the DLL's entry-point function. This call is made in the context of the thread that caused the process address space to change, such as the primary thread of the process or the thread that called LoadLibrary. Access to the entry point is serialized by the system on a process-wide basis.
There are cases in which the entry-point function is called for a terminating thread even if the DLL never attached to the thread — for example, the entry-point function was never called with the DLL_THREAD_ATTACH value in the context of the thread in either of these two situations:
- The thread was the initial thread in the process, so the system called the entry-point function with the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH value.
- The thread was already running when a call to the LoadLibrary function was made, so the system never called the entry-point function for it.
When a DLL is unloaded from a process as a result of an unsuccessful load of the DLL, termination of the process, or a call to FreeLibrary, the system does not call the DLL's entry-point function with the DLL_THREAD_DETACH value for the individual threads of the process. The DLL is only sent a DLL_PROCESS_DETACH notification. DLLs can take this opportunity to clean up all resources for all threads known to the DLL.
Warning On attach, the body of your DLL entry-point function should perform only simple initialization tasks, such as setting up thread local storage (TLS), creating objects, and opening files. You must not call LoadLibrary in the entry-point function, because you may create dependency loops in the DLL load order. This can result in a DLL being used before the system has executed its initialization code. Similarly, you must not call the FreeLibrary function in the entry-point function on detach, because this can result in a DLL being used after the system has executed its termination code.
Calling functions other than TLS, object-creation, and file functions may result in problems that are difficult to diagnose. For example, calling User, Shell, COM, RPC, and Windows Sockets functions (or any functions that call these functions) can cause access violation errors, because their DLLs call LoadLibrary to load other system components. While it is acceptable to create synchronization objects in DllMain, you should not perform synchronization in DllMain (or a function called by DllMain) because all calls to DllMain are serialized. Waiting on synchronization objects in DllMain can cause a deadlock.
To provide more complex initialization, create an initialization routine for the DLL. You can require applications to call the initialization routine before calling any other routines in the DLL. Otherwise, you can have the initialization routine create a named mutex, and have each routine in the DLL call the initialization routine if the mutex does not exist.