Part A
exercise 1:
为kern/trap.c中的每个时钟中断添加对time_tick的调用。实现sys_time_msec并将其添加到kern/syscall.c中的syscall中,以便用户空间能够访问时间。
在kern/trap.c中添加分支
注意不要傻fufu的重新添加一个分支,在lab4中我们已经添加了时钟中断,此处只要修改一下即可
else if(tf->tf_trapno == IRQ_OFFSET + IRQ_TIMER){ lapic_eoi(); time_tick(); sched_yield(); return; }
在kern/syscall.c中给syscall添加分支:
case(SYS_time_msec): return sys_time_msec();
实现sys_time_msec
在此之前,首先看一下kern/time.c中的几个函数:
static unsigned int ticks; void time_init(void) { ticks = 0; } // This should be called once per timer interrupt. A timer interrupt // fires every 10 ms. void time_tick(void) { ticks++; if (ticks * 10 < ticks) panic("time_tick: time overflowed"); } unsigned int time_msec(void) { return ticks * 10; }
ticks在time.c进行了定义。
所以不能在sys_time_msec中直接 ticks * 10,而是要调用time_msec(),否则会报错ticks未定义。
// Return the current time. static int sys_time_msec(void) { // LAB 6: Your code here. return time_msec(); //panic("sys_time_msec not implemented"); }
键入make INIT_CFLAGS=-DTEST_NO_NS run-testtime
来测试你的代码. 你应当看到进程在1秒内从5开始倒数,“-DTEST_NO_NS”会禁用启动网络服务器进程,因为它会引起panic。

exercise 2:
阅读文档
exercise 3:
首先看看kern/pci.c中的几个函数:
// pci_attach_class matches the class and subclass of a PCI device struct pci_driver pci_attach_class[] = { { PCI_CLASS_BRIDGE, PCI_SUBCLASS_BRIDGE_PCI, &pci_bridge_attach }, { 0, 0, 0 }, }; // pci_attach_vendor matches the vendor ID and device ID of a PCI device. key1 // and key2 should be the vendor ID and device ID respectively
//第一参数应该是venderID,第二个参数是deviseID
struct pci_driver pci_attach_vendor[] = { { PCI_E1000_VENDOR, PCI_E1000_DEVICE, &pci_e1000_attach }, { 0, 0, 0 }, };
pci_attach_class和pci_attach_vendor2个数组就是设备数组
对于pci设备而言
PCI是外围设备互连(Peripheral Component Interconnect)的简称,是在目前计算机系统中得到广泛应用的通用总线接口标准:
--- 在一个PCI系统中,最多可以有256根PCI总线,一般主机上只会用到其中很少的几条。
--- 在一根PCI总线上可以连接多个物理设备,可以是一个网卡、显卡或者声卡等,最多不超过32个。
--- 一个PCI物理设备可以有多个功能,比如同时提供视频解析和声音解析,最多可提供8个功能。
--- 每个功能对应1个256字节的PCI配置空间。
//负责设置需要读写的具体设备
static void pci_conf1_set_addr(uint32_t bus, uint32_t dev, uint32_t func, uint32_t offset) { assert(bus < 256); //8位 最多可以有256根PCI总线,一般主机上只会用到其中很少的几根 assert(dev < 32); //5位 一根PCI总线可以连接多个物理设备,可以是一个网卡、显卡或声卡等,最多不超过32个 assert(func < 8); //3位 一个PCI物理设备可以有多个功能,比如同时提供视频解析和声音解析,最多可提供8个功能。 assert(offset < 256); //8位 每个功能对应1个256字节的PCI配置空间。 assert((offset & 0x3) == 0);//最后两位必须为00? uint32_t v = (1 << 31) | // config-space (bus << 16) | (dev << 11) | (func << 8) | (offset); outl(pci_conf1_addr_ioport, v); }
//读取PCI配置空间中特定位置的配置值
static uint32_t pci_conf_read(struct pci_func *f, uint32_t off) { pci_conf1_set_addr(f->bus->busno, f->dev, f->func, off); return inl(pci_conf1_data_ioport); } //设置PCI配置空间中特定位置的配置值 static void pci_conf_write(struct pci_func *f, uint32_t off, uint32_t v) { pci_conf1_set_addr(f->bus->busno, f->dev, f->func, off); outl(pci_conf1_data_ioport, v); }
初始化PCI的大致流程:
在pci_init函数中,root_bus被全部清0,然后交给pci_scan_bus函数来扫描这条总线上的所有设备,说明在JOS中E1000网卡是连接在0号总线上的。pci_scan_bus函数来顺次查找0号总线上的32个设备,如果发现其存在,那么顺次扫描它们每个功能对应的配置地址空间,将一些关键的控制参数读入到pci_func中进行保存。得到pci_func函数后,被传入pci_attach函数去查找是否为已存在的设备,并用相应的初始化函数来初始化设备。
在手册的5.2节中可以找到venderID和deviceID:
82540EM-A 8086h 100E Desktop(台式机)
在kern/ PCI.c中的pci_attach_vendor数组中添加一个条目,以便在找到匹配的PCI设备时触发函数(请确保将它放在表示 末尾的{0,0,0}条目之前)
struct pci_driver pci_attach_vendor[] = { { PCI_VENDOR_ID, PCI_DEVICE_ID, &e1000_init }, { 0, 0, 0 }, };
前两个参数PCI_VENDOR_ID, PCI_DEVICE_ID的定义放在kern/pcireg.h文件中,这个文件是用来存放PCI的配置信息的
#define PCI_VENDOR_ID 0x8086 #define PCI_DEVICE_ID 0x100E
第三个参数应该是他初始化的时候应该调用的函数,可以定义在kern/e1000.c中
int e1000_init(struct pci_func *pcif) { pci_func_enable(pcif); return 1; }
然后在kern/e1000.h中声明这个函数,让pic.c进行调用
#include <kern/pci.h> int e1000_init(struct pci_func *pcif);

exercise 4 :
在kern/e1000.c中的函数添加:
int e1000_init(struct pci_func *pcif) { pci_func_enable(pcif); pci_e1000 = mmio_map_region(pcif->reg_base[0], pcif->reg_size[0]); return 1; }
我们使用变量pci_e1000来记录映射的位置,以便稍后访问刚才映射的寄存器。
如果要尝试打印设备状态寄存器
在 QEMU's e1000_hw.h 中有关于状态寄存器的定义。
#define E1000_STATUS 0x00008 /* Device Status - RO */
在kern/e1000.h中添加
#define E1000_STATUS 0x00008 /* Device Status - RO */ #define e1000_print_status(offset) cprintf("the E1000 status register: [%08x] ", *(pci_e1000+(offset>>2))); // 由于pci_e1000是uint32_t的,如果直接加offset,就相当于加了offset*sizeof(uint32_t) // 例如the E1000:[ef804000] offset:[00000008] sum:[ef804020]
// 并且定义 pci_e1000
uint32_t *pci_e1000;
修改
int e1000_init(struct pci_func *pcif) { pci_func_enable(pcif); pci_e1000 = mmio_map_region(pcif->reg_base[0], pcif->reg_size[0]); e1000_print_status(E1000_STATUS); return 1; }
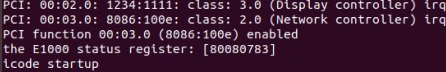
exercise5:
在kern/e1000.c中:
void e1000_transmit_init(){ memset(tx_list, 0, sizeof(struct tx_desc) * TX_MAX); memset(tx_buf, 0, sizeof(struct packets) * TX_MAX); //每一个传输描述符都对应着一个packet for (int i = 0; i < TX_MAX; i++) { tx_list[i].addr = PADDR(tx_buf[i].buffer); //不太懂为什么可以用PADDR //24=4(16进制相对于2进制)*6 tx_list[i].cmd = (E1000_TXD_CMD_RS >> 24) | (E1000_TXD_CMD_EOP >> 24); //因为RSV除了82544GC/EI之外,所有以太网控制器都应该保留这个位,并将其编程为0b。 //而LC,EC在全双工没有意义, tx_list[i].status = E1000_TXD_STAT_DD; } //(TDBAL/TDBAH)指向传输描述符队列的base和high //将pci_e1000视为数组的话,他存放的元素应该是32位的, //以太网控制器中的寄存器都是32位的, pci_e1000[E1000_TDBAL >> 2] = PADDR(tx_list); pci_e1000[E1000_TDBAH >> 2] = 0; pci_e1000[E1000_TDLEN >> 2] = TX_MAX * sizeof(struct tx_desc); pci_e1000[E1000_TDH >> 2] = 0; pci_e1000[E1000_TDT >> 2] = 0; pci_e1000[E1000_TCTL >> 2] |= (E1000_TCTL_EN | E1000_TCTL_PSP | (E1000_TCTL_CT & (0x10 << 4)) | (E1000_TCTL_COLD & (0x40 << 12))); pci_e1000[E1000_TIPG >> 2] |= (10) | (4 << 10) | (6 << 20); }
int e1000_init(struct pci_func* pcif) { pci_func_enable(pcif); //pci_e1000 是1个指针,指向映射地址, uint32_t* pci_e1000; //他创建了一个虚拟内存映射 pci_e1000 = mmio_map_region(pcif->reg_base[0], pcif->reg_size[0]); e1000_print_status(E1000_STATUS); e1000_transmit_init();return 1; }
在kern/e1000.h中加入:
#include <inc/string.h> //以下定义来自 QEMU's e1000_hw.h #define E1000_TCTL 0x00400 /* TX Control - RW */ #define E1000_TDBAL 0x03800 /* TX Descriptor Base Address Low - RW */ #define E1000_TDBAH 0x03804 /* TX Descriptor Base Address High - RW */ #define E1000_TDLEN 0x03808 /* TX Descriptor Length - RW */ #define E1000_TDH 0x03810 /* TX Descriptor Head - RW */ #define E1000_TDT 0x03818 /* TX Descripotr Tail - RW */ #define E1000_TIPG 0x00410 /* TX Inter-packet gap -RW */ #define E1000_TCTL_EN 0x00000002 /* enable tx */ #define E1000_TCTL_BCE 0x00000004 /* busy check enable */ #define E1000_TCTL_PSP 0x00000008 /* pad short packets */ #define E1000_TCTL_CT 0x00000ff0 /* collision threshold */ #define E1000_TCTL_COLD 0x003ff000 /* collision distance */ #define E1000_TXD_CMD_RS 0x08000000 /* Report Status */ #define E1000_TXD_CMD_EOP 0x01000000 /* End of Packet */ #define E1000_TXD_STAT_DD 0x00000001 /* Descriptor Done */ #define TX_MAX 64 //legacy transmit descriptor format struct tx_desc { uint64_t addr; //Address of the transmit descriptor in the host memory uint16_t length; //The Checksum offset field indicates where to insert a TCP checksum if this mode is enabled. uint8_t cso; uint8_t cmd; uint8_t status; uint8_t css; //The Checksum start field (TDESC.CSS) indicates where to begin computing the checksum. uint16_t special; }__attribute__((packed));//告诉编译器取消结构在编译过程中的优化对齐,按照实际占用字节数进行对齐, //传输描述符数组 struct tx_desc tx_list[TX_MAX]; //以太网数据包的最大大小为1518字节,将其限制在2048方便对齐 struct packets { char buffer[2048]; }__attribute__((packed)); //缓冲区数组 struct packets tx_buf[TX_MAX];
void e1000_transmit_init();
运行make E1000_DEBUG=TXERR,TX qemu
在设置TDT register时,应该会看到一条“e1000: tx disabled”消息(因为这是在设置TCTL.EN之前发生的),并且不再有“e1000”消息

exercise 6:
在kern/e1000.c中加入
int e1000_transmit(void* addr, int length) { //TDT是传输描述符数组的索引 int tail = pci_e1000[E1000_TDT >> 2]; //得到下一个描述符 struct tx_desc* tx_next = &tx_list[tail]; //如果包长度超出了,就直接截住 if (length > sizeof(struct packets)) length = sizeof(struct packets); //如果DD位被设置了,就说明这个传输描述符安全回收,可以传输下一个包,也就是队列还没有满 if ((tx_next->status & E1000_TXD_STAT_DD) == E1000_TXD_STAT_DD) { //没有满,把包复制到缓冲区里面去 memmove(KADDR(tx_next->addr), addr, length); tx_next->status &= !E1000_TXD_STAT_DD; //表示现在该描述符还没被处理 tx_next->length = (uint16_t)length; //更新TDT,注意是循环队列 pci_e1000[E1000_TDT >> 2] = (tail + 1) % TX_MAX; cprintf("my message:%s, %d, %02x ", tx_buf[tail].buffer, tx_list[tail].length, tx_list[tail].status); return 0; } //DD位没有被设置,传输队列满了 return -1; }
在kern/e1000.h中声明这个函数
在kern/monitor.c中添加kern/e1000.h头文件
然后:
void monitor(struct Trapframe *tf) { char *buf; cprintf("Welcome to the JOS kernel monitor! "); cprintf("Type 'help' for a list of commands. "); e1000_transmit("I'm here", 10); if (tf != NULL) print_trapframe(tf); while (1) { buf = readline("K> "); if (buf != NULL) if (runcmd(buf, tf) < 0) break; } }
在qemu中测试:
make E1000_DEBUG=TXERR,TX qemu
能得到以下结果:
e1000: index 0: 0x2b02c0 : 900000a 0 my message:I'm here, 10, 00
在qemu中测试:
tcpdump -XXnr qemu.pcap
得到以下结果:
reading from file qemu.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet) 16:09:40.990305 [|ether] 0x0000: 4927 6d20 6865 7265 004b I'm.here.K
exercise 7:
在kern/syscall.c中添加系统调用函数
//network packet send static int sys_packet_try_send(void *addr, size_t len){ user_mem_assert(curenv, addr, len, PTE_U); //考虑没这么周全 return e1000_transmit(addr, len); }
在diapstach中添加分支:
case (SYS_packet_try_send): return sys_packet_try_send((void *)a1,a2);
添加声明和定义:
//在kern/syscall.c中 #include<kern/e1000.h> //lib/syscall.c中 int sys_packet_try_send(void* buf, size_t len) { return syscall(SYS_packet_try_send, 0,(uint32_t)buf, len, 0,0,0); } //inc/syscall.h中要声明 SYS_packet_try_send, //inc/lib.h中
int sys_packet_try_send(void *data_va,size_t len);
exercise 8:
# include <inc/lib.h>
void
output(envid_t ns_envid)
{
binaryname = "ns_output";
int r;
int perm;
// LAB 6: Your code here:
// - read a packet from the network server
// - send the packet to the device driver
envid_t from_env;
while(1){
if( ipc_recv(&from_env, &nsipcbuf, &perm) != NSREQ_OUTPUT)
continue;
while((r = sys_packet_try_send(nsipcbuf.pkt.jp_data, nsipcbuf.pkt.jp_len)<0))
sys_yield();
}
}
运行 make grade 可以看到part a的测试全部通过