凸包:能围住所有给出的点的面积最小的多边形(个人理解)
Graham:选取y值最小的点,将其它点极角排序,依次把1~n号点加入栈中,判断当前点、栈顶、栈顶下面那个点三者的关系(嘻嘻),一直这样做就好了
判断用叉积,也就是如下图的要判掉(top--)
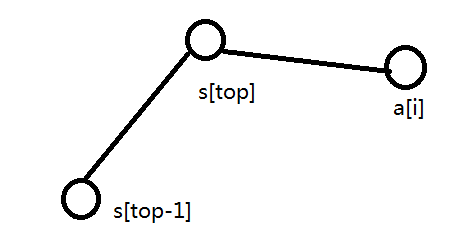
其实上图是不对的哦,你有没有反应过来呢~按极角排序后不会有这种情况哦,肯定是先连a[i],再连s[top]的

具体实现看代码吧~

#include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm> #define sqr(x) (x)*(x) #define rep(i,x,y) for (int i=(x);i<=(y);i++) #define per(i,x,y) for (int i=(x);i>=(y);i--) typedef double DBD; using namespace std; const int N=100010; struct point{int x,y;}a[N],s[N],b[N]; int n,top; int read() {int d=0,f=1; char c=getchar(); while (c<'0'||c>'9') {if (c=='-') f=-1; c=getchar();} while (c>='0'&&c<='9') d=(d<<3)+(d<<1)+c-48,c=getchar(); return d*f;} DBD dis(int x,int xx,int y,int yy){return sqrt(sqr(x-xx)+sqr(y-yy));} bool cross(point x,point y,point z){return (x.x-z.x)*(y.y-z.y)-(y.x-z.x)*(x.y-z.y)>=0;} bool cmp(point A,point B){return (A.x-a[1].x)*(B.y-a[1].y)-(B.x-a[1].x)*(A.y-a[1].y)>=0;} int main() { //judge(); n=read(); int p=0; a[0].y=1e9; rep(i,1,n) { a[i].x=read(); a[i].y=read(); if (a[i].y<a[p].y||a[i].y==a[p].y&&a[i].x<a[p].x) p=i; } swap(a[1],a[p]); sort(a+2,a+1+n,cmp); s[1]=a[1]; s[2]=a[2]; top=2; rep(i,3,n) { while (top>=2&&cross(a[i],s[top],s[top-1])) top--; s[++top]=a[i]; } DBD ans=0; for (int i=1;i<top;i++) ans+=dis(s[i].x,s[i+1].x,s[i].y,s[i+1].y); ans+=dis(s[1].x,s[top].x,s[1].y,s[top].y); printf("%.1lf",ans); return 0; }
Andrew:
据说比Graham更快更稳定,但我不是很懂。。。
具体过程(哪里具体了。。。):将所有点以x为第一关键字,y为第二关键字排序,分别求出上下凸壳,求的时候一样的判法,就好了

#include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm> #define sqr(x) (x)*(x) #define rep(i,x,y) for (int i=(x);i<=(y);i++) #define per(i,x,y) for (int i=(x);i>=(y);i--) typedef double DBD; using namespace std; const int N=100010; struct point{int x,y;}a[N],s[N]; int n,top; int read() {int d=0,f=1; char c=getchar(); while (c<'0'||c>'9') {if (c=='-') f=-1; c=getchar();} while (c>='0'&&c<='9') d=(d<<3)+(d<<1)+c-48,c=getchar(); return d*f;} DBD dis(int x,int xx,int y,int yy){return sqrt(sqr(x-xx)+sqr(y-yy));} DBD cross(point x,point y,point z){return (x.x-z.x)*(y.y-z.y)-(y.x-z.x)*(x.y-z.y);} bool cmp(point a,point b){return a.x<b.x||a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y;} int main() { n=read(); rep(i,1,n) a[i].x=read(),a[i].y=read(); sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp); rep(i,1,n) { while (top>1&&cross(a[i],s[top],s[top-1])>=0) top--; s[++top]=a[i]; } int k=top; per(i,n-1,1) { while (top>k&&cross(a[i],s[top],s[top-1])>=0) top--; s[++top]=a[i]; } DBD ans=0; rep(i,1,top-1) ans+=dis(s[i].x,s[i+1].x,s[i].y,s[i+1].y); ans+=dis(s[1].x,s[top].x,s[1].y,s[top].y); printf("%.1lf",ans); return 0; }
可能你会疑问:为什么第n个点一定在凸包上呢?当然了,因为它的x最大,即使有和它x一样的,它的y更大,yy一下就脑补出来了
