1. 什么是RPC调用(远程过程调用)remote procedure call

半双工和全双工通信(实现难度和成本)
二进制协议
. 更小的数据包体积
. 更快的编解码速率
2. Buffer 编解码二进制数据包 (node 的二进制Buffer模块)
#buffer创建 // 具体用法参见文档 1. Buffer.from() 2. Buffer.alloc() var buffer = Buffer.from('guiqing'); // <Buffer 67 75 69 71 69 6e 67> var buffer = Buffer.from('股'); //<Buffer e8 82 a1> 对于默认的utf-8编码;英文占用一个字节,中文占用三个字节,为16进制 #buffer的写入 buffer.writeInt8 buffer.writeInt16BE buffer.writeInt16LE 为啥writeInt8没有大小端,是因为一个字节为8位,刚好不需要两位,没有顺序之分
原生动态将多个string转为二进制的话,可能还需要获取写入的string对应的字节长度,以便管理下一次写入的offset;
可以通过Buffer.byteLength()来获取
(Protocol Buffers)用来编码二进制数据
protocol-buffers(npm包,用于方便实现编码二进制数据)
var obj = { a: 1 } var buffer = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(obj)) console.log(buffer.toString())// 可以将json数据直接这样转为二进制数据
3. net 搭建多路复用的RPC通道

对应的https://github.com/geektime-geekbang/geek-nodejs/tree/master/chapter2/rpc
4. HTTP 服务性能测试
压力测试工具(ab、webbench)
通常用ab (https://www.jianshu.com/p/43d04d8baaf7)
找到性能瓶颈
. top (cpu、内存)
. iostat (硬盘)
5. Node.js性能分析工具
1⃣️ 自带的 profile 启动命令的时候带上--prof (eg. node --prof app.js)
这时会生成一个*.log 文件
可以通过命令: node --prof-process *.log > profile.txt (生成文件, 然后主要看这里,看主要的耗时)

2⃣️ Chrome devtool (eg. node --inspect-brk app.js)
chrome://inspect 进入

3⃣️ Clinic.js
4⃣️ 内存分析,可以点击Memory
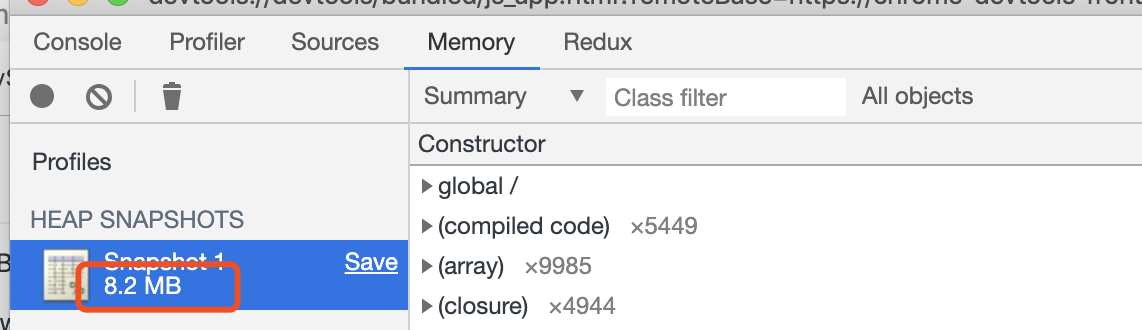
这个就是你所占有的内存总量
6. 石头剪刀布游戏
1⃣️ process.argv
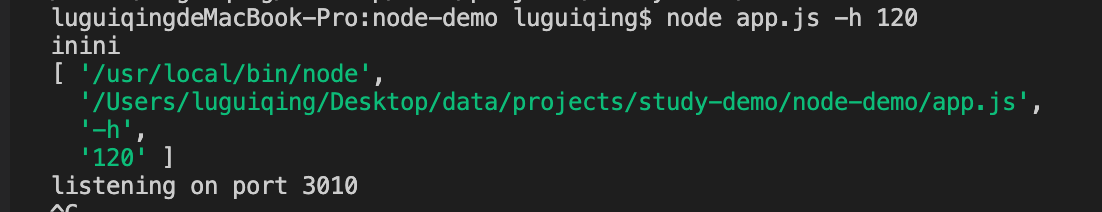
可以获取到用户输入的指令参数
2⃣️ module.exports 和 exports的区别
#lib.js exports.a = 'hello world'; module.exports = function (){ console.log('exports被重新赋值了,上面定义的属性获取不到') } setTimeout(function(){ console.log(exports); // {a: 'hello world'} }, 2000) #index.js const lib = require('./lib.js'); // lib 是引用类型 console.log(lib); //[Function] lib.b = '我修改了对象'
3⃣️ process.stdin
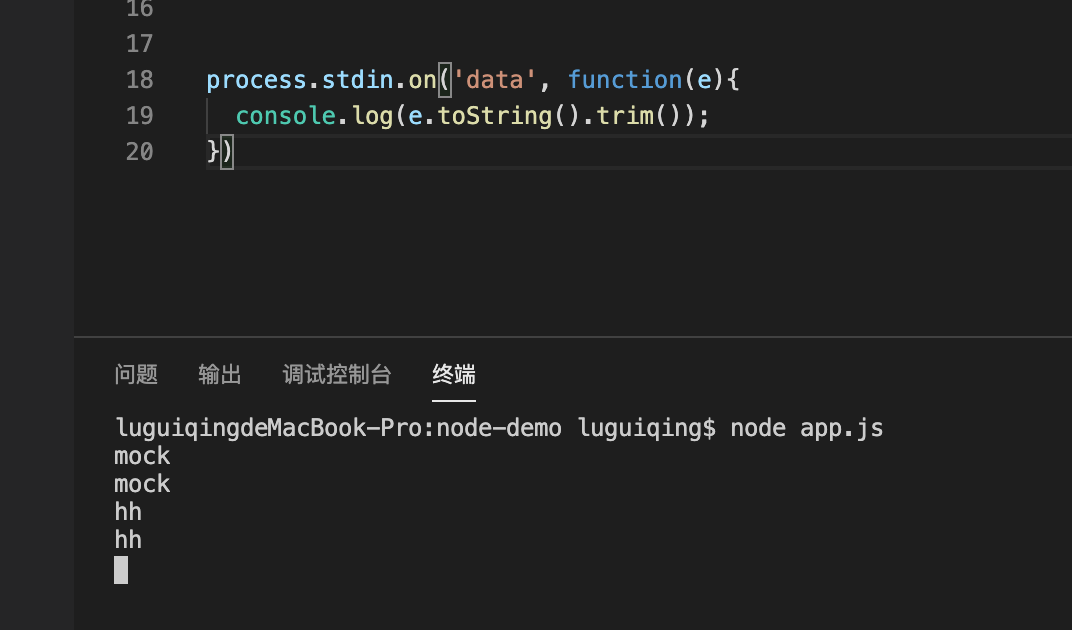
7. callback 为啥采用error-first 模式
/** * try catch只能抓到一个调用堆栈内,即一个事件循环里的错误 */ // try { interview(function (err, res) { if (err) { console.log('cry') return; } console.log('smile') }) // } catch (e) { // console.log('cry') // } function interview(callback) { setTimeout(() => { if (Math.random() > 0.2) { callback(null, 'success') } else { // throw new Error('fail'); callback(new Error('fail')) } }, 500) }
8. promise 的状态是和最后一个then或者catch相关,或者是then中的其他promise状态相关
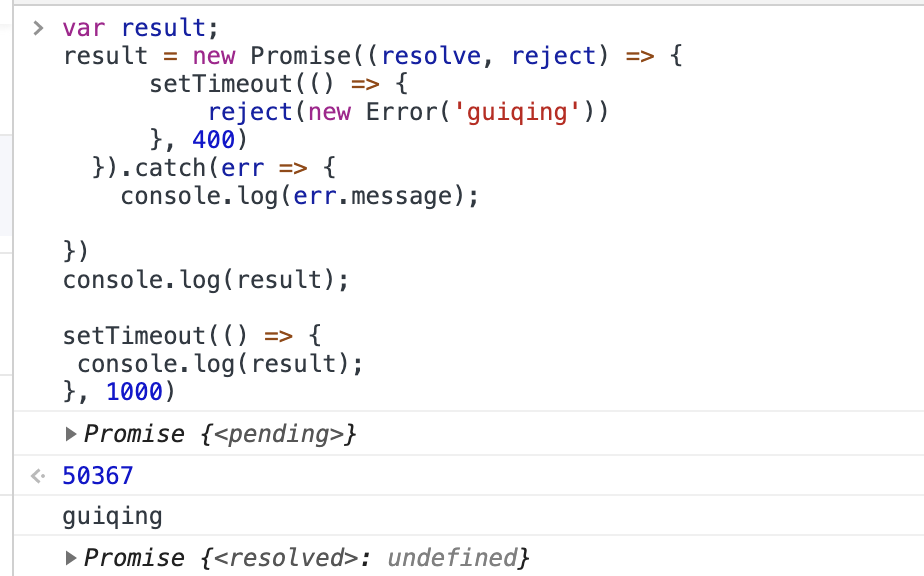
9. koa的优势
1⃣️. 不绑定中间间,更简洁
2⃣️. 使用async/await实现中间件,有暂停的能力(await next());在异步的情况下也符合洋葱模型
10. 使用es6模版和vm作为渲染引擎
// template.js
const fs = require('fs'); const vm = require('vm'); const templateCache = {}; const templateContext = vm.createContext({ include: function (name, data) { const template = templateCache[name] || createTemplate(name) return template(data); } }); function createTemplate(templatePath) { templateCache[templatePath] = vm.runInContext( `(function (data) { with (data) { return \`${fs.readFileSync(templatePath, 'utf-8')}\` } })`, templateContext ); return templateCache[templatePath] } module.exports = createTemplate
// 使用 index.js
const template = require('./template');
const detailTemplate = template(__dirname + '/template/index.html');
app.use(async (ctx) => {
ctx.status = 200;
ctx.body = detailTemplate(result);
})
渲染引擎模版要提供
1⃣️ include 子模版
2⃣️ 具备防止xss攻击,helper函数
11. graphQL: Facebook开发的实现API服务的库
比Restful的优势在于能够让前端有“自定义查询”数据的能力
koa-graphql(npm包)
12. 前后端同构
场景:服务端渲染,同时前端可以进行无刷新排序和分类等操作
难点:由于我们使用redux或者vuex; 所以数据方面比较难同构, react 可以用 next.js 进行服务端渲染
axios支持运行在浏览器和node.js
13. 子进程(child_process)和 工作线程(worker_threads)和集群(cluster)
# child_process.fork() 方法是 child_process.spawn(), 能和父进程进行通信 # index.js const cp = require('child_process'); const child_process_demo = cp.fork(__dirname + '/child.js'); child_process_demo.send('hello'); #child.js process.on('messaage', function(str) { console.log(str); process.send('world'); // process是全局变量, 且为当前子进程全局变量,所以只会接收到child_process_demo的消息 })
const cluster = require('cluster');
const os = require('os');
if (cluster.isMaster) {
for(let i = 0; i < os.cpus().length / 2; i++) {
cluster.fork();
};
} else {
require('./app.js');
};
//子进程启动的时候也会执行这个文件,并且isMaster是false
// cluster 启动多个子进程,但是能监听同个端口是进行了处理的。
// 处理成类似server.listen({fd: 7});这里不太清楚没细究
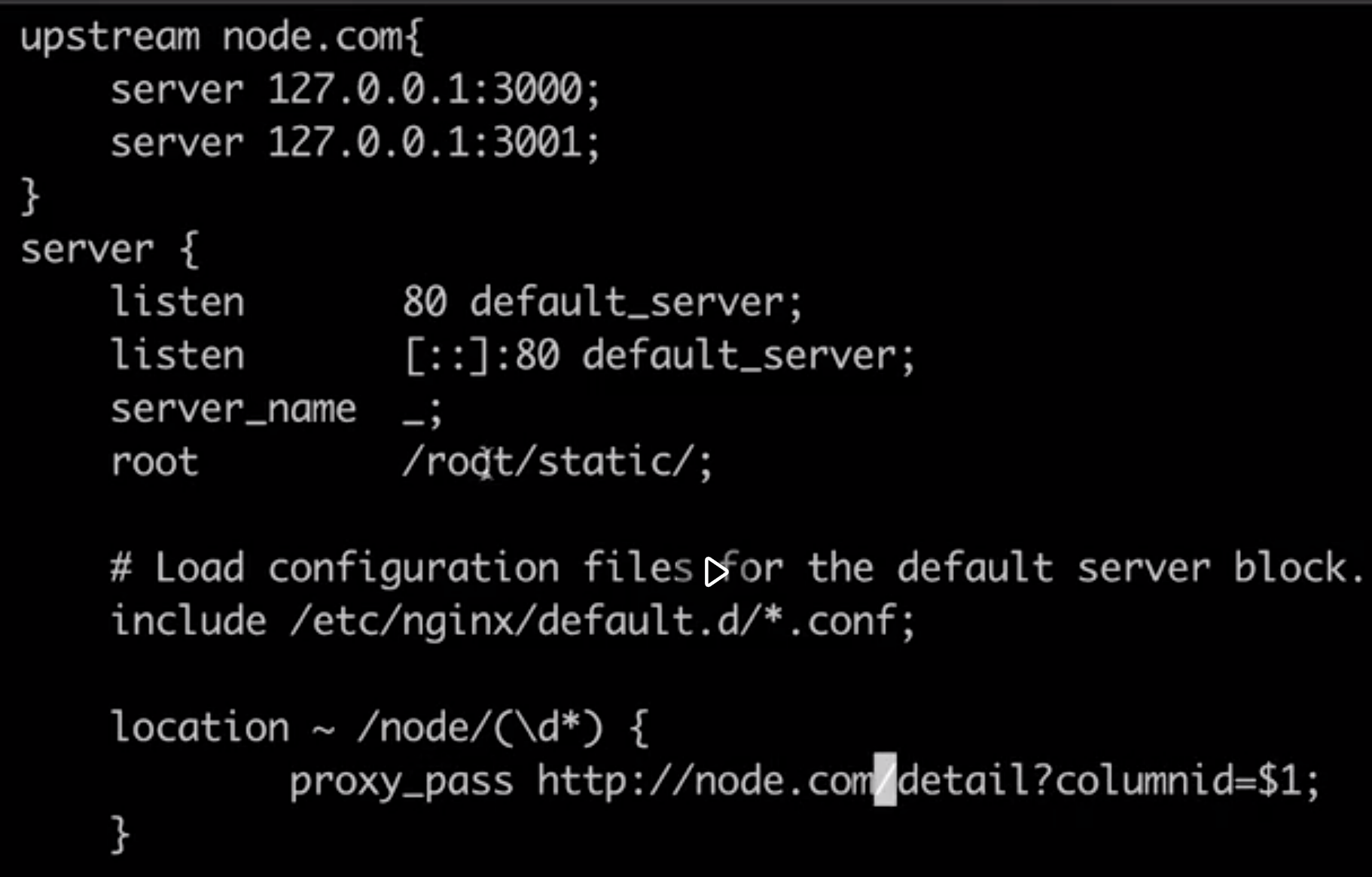
14. 反向代理和缓存服务 (nginx)
15. serverless (渐进式)
云函数(自行百度理解)
const fs = require('fs');
const mkdirp = require('mkdirp');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const mfs = new (require('memory-fs'));
module.exports = function (
businessName,
dataJSPath,
templatePath
) {
mkdirp.sync(__dirname + '/../business/' + businessName);
fs
.createReadStream(templatePath)
.pipe(fs.createWriteStream(__dirname + '/../business/' + businessName + '/template.tpl'));
const compileTask = webpack({
mode: 'development',
devtool: false,
target: 'node',
entry: dataJSPath,
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /.proto$/, use: 'text-loader' }
]
},
output: {
path: "/whatever",
filename: "data.js"
}
});
compileTask.outputFileSystem = mfs; // 这里可以借鉴,将webpack打包出来的文件先存在内存
compileTask.run(function(err) {
if (err) { return }
const content = mfs.readFileSync('/whatever/data.js')
fs.writeFileSync(__dirname + '/../business/' + businessName + '/data.js', content);
})
}