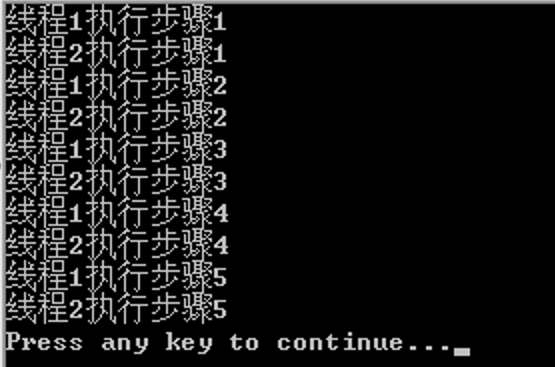
SimpleThread.java
public class SimpleThread extends Thread { public SimpleThread(String name) { // 参数为线程名称 setName(name); } public void run() { // 覆盖run()方法 int i = 0; while (i++ < 5) { // 循环5次 try { System.out.println(getName() + "执行步骤" + i); Thread.sleep(1000); // 休眠1秒 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleThread thread1 = new SimpleThread("线程1"); // 创建线程1 SimpleThread thread2 = new SimpleThread("线程2"); // 创建线程2 thread1.start(); // 启动线程1 thread2.start(); // 启动线程2 } }
SimpleRunnable.java
public class SimpleRunnable implements Runnable { public void run() { // 覆盖run()方法 int i = 15; while (i-- >= 1) { // 循环15次 try { System.out.print("*"); Thread.sleep(500); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(new SimpleRunnable(),"线程1"); // 创建线程1 thread1.start(); // 启动线程1 } }
![]()
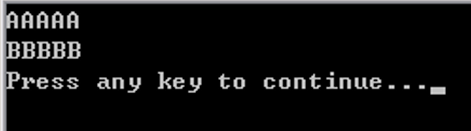
SyncThread.java
public class SyncThread extends Thread { private char cha; public SyncThread(char cha) { // 构造函数 this.cha = cha; } public void run() { PrintClass.printch(cha); // 调用同步方法 System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SyncThread t1 = new SyncThread('A'); // 创建线程A SyncThread t2 = new SyncThread('B'); // 创建线程B t1.start(); // 启动线程A t2.start(); // 启动线程B } } class PrintClass { public static synchronized void printch(char cha) { // 同步方法 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); // 打印一个字符休息1秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.print(cha); } } }
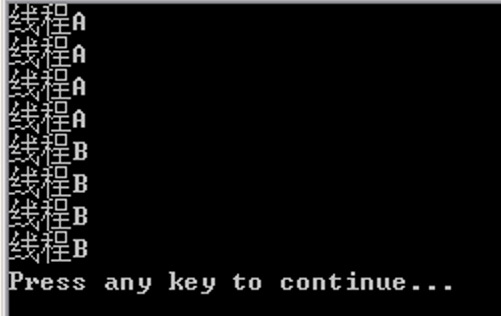
SyncThread2.java
public class SyncThread extends Thread { private String cha; public SyncThread(String cha) { // 构造函数 this.cha = cha; } public void run() { PrintClass.printch(cha); // 调用同步方法 } public static void main(String[] args) { SyncThread t1 = new SyncThread("线程A"); // 创建线程A SyncThread t2 = new SyncThread("线程B"); // 创建线程B t1.start(); // 启动线程A t2.start(); // 启动线程B } } class PrintClass { static Object printer = new Object(); // 实例化Object对象 public static void printch(String cha) { // 同步方法 synchronized (printer) { // 同步块 for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println(cha + " "); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
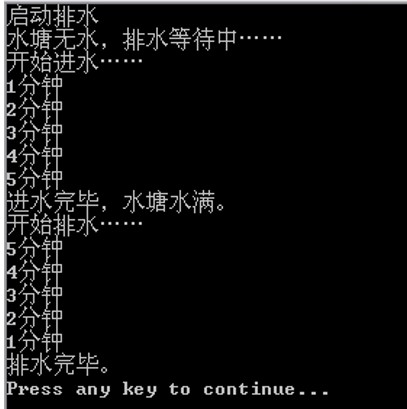
ThreadA.java
public class ThreadA extends Thread { Water water; public ThreadA(Water waterArg) { water = waterArg; } public void run() { System.out.println("开始进水....."); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { // 循环5次 try { Thread.sleep(1000); // 休眠1秒,模拟1分钟的时间 System.out.println(i + "分钟"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } water.setWater(true); // 设置水塘有水状态 System.out.println("进水完毕,水塘水满。"); synchronized (water) { water.notify(); // 线程调用notify()方法 } } }
ThreadB.java
public class ThreadB extends Thread { Water water; public ThreadB(Water waterArg) { water = waterArg; } public void run() { System.out.println("启动排水"); if (water.isEmpty()) { // 如果水塘无水 synchronized (water) { // 同步代码块 try { System.out.println("水塘无水,排水等待中....."); water.wait(); // 使线程处于等待状态 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } System.out.println("开始排水....."); for (int i = 5; i >= 1; i--) { // 循环5侧 try { Thread.sleep(1000); // 休眠1秒,模拟1分钟 System.out.println(i + "分钟"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } water.setWater(false); // 设置水塘无水状态 System.out.println("排水完毕。"); } }
Water.java
public class Water { boolean water = false; // 反应水塘状态的变量 public boolean isEmpty() { // 判断水塘是否无水的方法 return water ? false : true; } public void setWater(boolean haveWater) { // 更改水塘状态的方法 this.water = haveWater; } public static void main(String[] args) { Water water=new Water(); // 创建水塘对象 ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(water); // 创建进水线程 ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(water); // 创建排水线程 threadB.start(); // 启动排水线程 threadA.start(); // 启动进水线程 } }