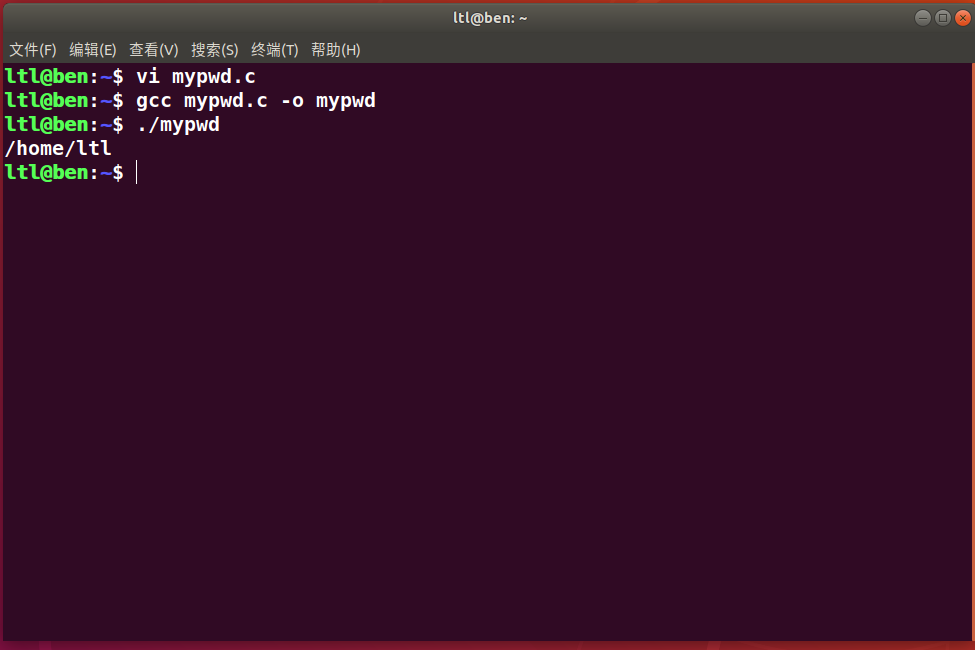
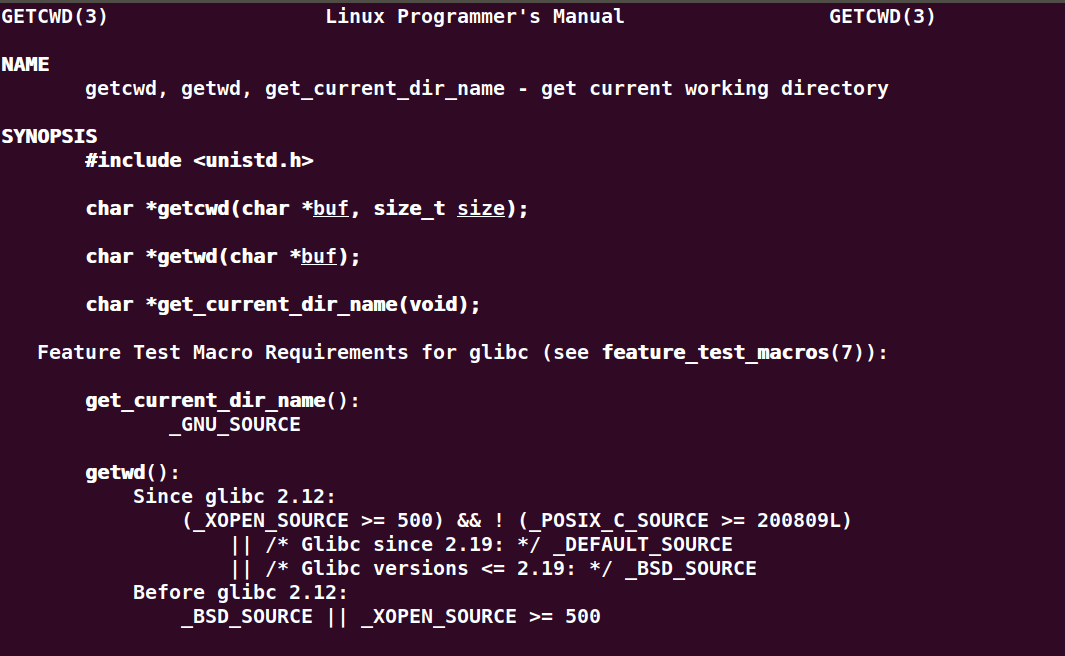
学习pwd命令
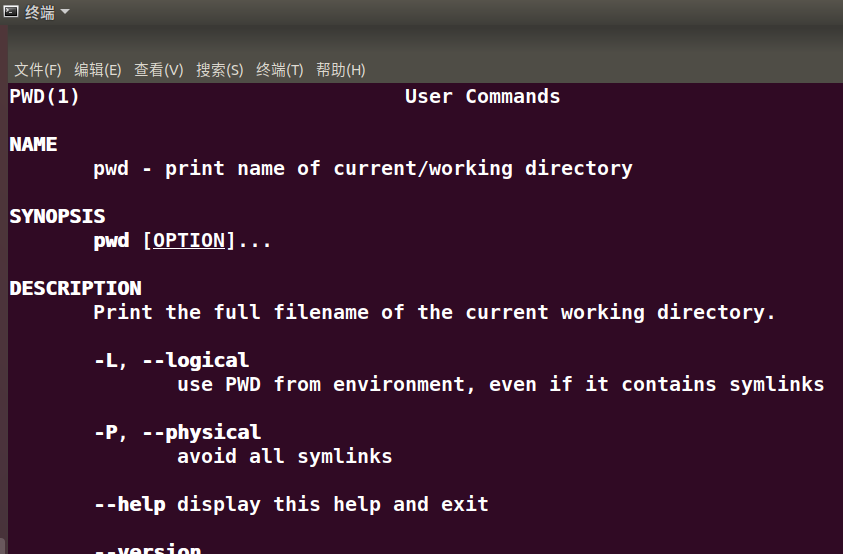
研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
man -k pwd
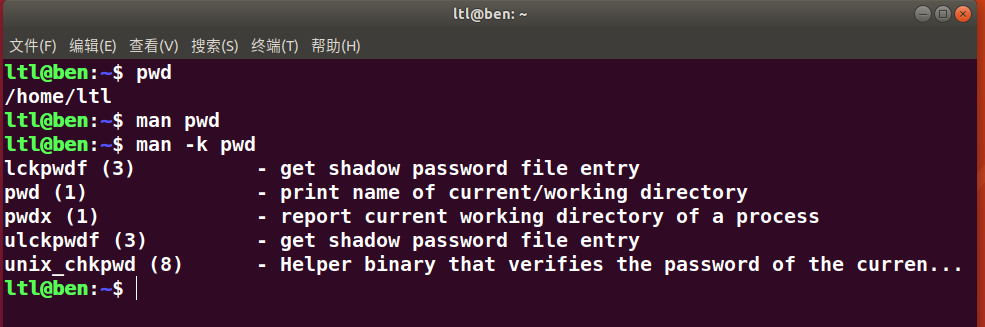
man -k current directory | grep 2
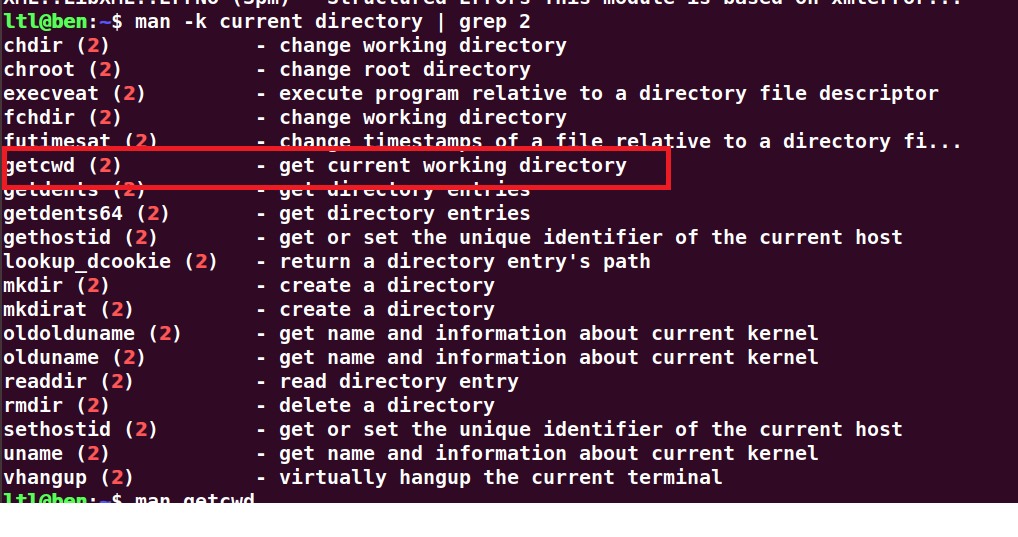
man getcwd
伪代码
void get_file_name(*filepath){
获取当前i-Node;
通过i-Node获取当前路径名称filepath(%s);
cd ..;
获取当前i-Node;
通过i-Node获取当前路径名filepath称(%s);
get_file_name(*filepath);
if(..i-Node == . i-Node){
return;
}
printf('/'+filename);
return;
}
实现mypwd
编写mypwd
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <pwd.h>
ino_t get_inode(char *);
void printpathto(ino_t);
void inum_to_name(ino_t, char *, int);
int main() {
printpathto(get_inode(".")); /* print path to here */
putchar('
'); /* then add newline */
return 0;
}
/*
* prints path leading down to an object with this inode
* kind of recursive
*/
void printpathto(ino_t this_inode) {
ino_t my_inode;
char its_name[BUFSIZ];
if (get_inode("..") != this_inode) {
chdir(".."); /* up one dir */
inum_to_name(this_inode, its_name, BUFSIZ);/* get its name*/
my_inode = get_inode("."); /* print head */
printpathto(my_inode); /* recursively */
printf("/%s", its_name); /* now print name of this */
}
}
void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find, char *namebuf, int buflen) {
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *direntp;
dir = opendir(".");
while ((direntp = readdir(dir)) != NULL)
if (direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find) {
strncpy(namebuf, direntp->d_name, buflen);
namebuf[buflen - 1] = '�';
closedir(dir);
return;
}
exit(1);
}
ino_t get_inode(char *filename) { //返回文件的i-Node值
struct stat file;
if (stat(filename, &info) == -1) {
perror(fname);
return 1;
}
return file.st_ino;
}
测试mypwd