1. 什么是hive
1.1. hive基本思想
Hive是基于Hadoop的一个数据仓库工具(离线),可以将结构化的数据文件映射为一张数据库表,并提供类SQL查询功能。
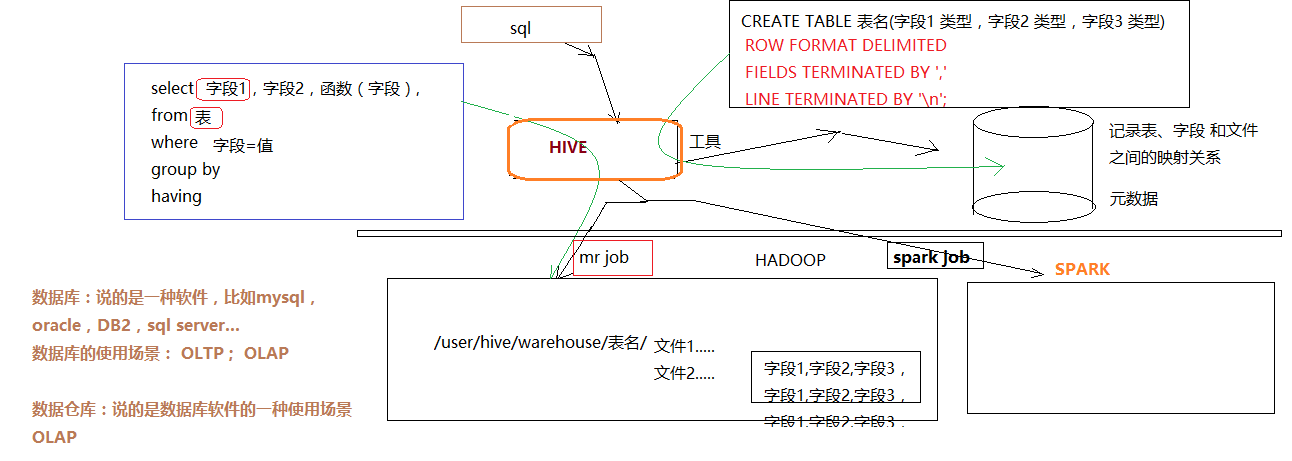
1.2. 为什么使用Hive
直接使用hadoop所面临的问题
人员学习成本太高
项目周期要求太短
MapReduce实现复杂查询逻辑开发难度太大
为什么要使用Hive?
操作接口采用类SQL语法,提供快速开发的能力。
避免了去写MapReduce,减少开发人员的学习成本。
功能扩展很方便。
1.3. Hive的特点
可扩展
Hive可以自由的扩展集群的规模,一般情况下不需要重启服务。
延展性
Hive支持用户自定义函数,用户可以根据自己的需求来实现自己的函数。
容错
良好的容错性,节点出现问题SQL仍可完成执行。
2. hive的基本架构

Jobtracker是hadoop1.x中的组件,它的功能相当于:
Resourcemanager+MRAppMaster
TaskTracker 相当于:
Nodemanager + yarnchild
3. hive安装
3.1. 最简安装:用内嵌derby作为元数据库
准备工作:安装hive的机器上应该有HADOOP环境(安装目录,HADOOP_HOME环境变量)
安装:直接解压一个hive安装包即可
此时,安装的这个hive实例使用其内嵌的derby数据库作为记录元数据的数据库
此模式不便于让团队成员之间共享协作
3.2. 标准安装:将mysql作为元数据库
3.2.1. mysql安装
① 上传mysql安装包
② 解压:
[root@mylove ~]# tar -xvf MySQL-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm-bundle.tar
③ 安装mysql的server包
[root@mylove ~]# rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
依赖报错:
缺perl
yum install perl
安装完perl后 ,继续重新安装mysql-server
(可以配置一个本地yum源进行安装:
1、先在vmware中给这台虚拟机连接一个光盘镜像
2、挂在光驱到一个指定目录:mount -t iso9660 -o loop /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
3、将yum的配置文件中baseURL指向/mnt/cdrom
)
[root@mylove ~]# rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
又出错:包冲突conflict with
移除老版本的冲突包:mysql-libs-5.1.73-3.el6_5.x86_64
[root@mylove ~]# rpm -e mysql-libs-5.1.73-3.el6_5.x86_64 --nodeps
继续重新安装mysql-server
[root@mylove ~]# rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
成功后,注意提示:里面有初始密码及如何改密码的信息
初始密码:/root/.mysql_secret
改密码脚本:/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
④ 安装mysql的客户端包:
[root@mylove ~]# rpm -ivh MySQL-client-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
⑤ 启动mysql的服务端:
[root@mylove ~]# service mysql start
Starting MySQL. SUCCESS!
⑥ 修改root的初始密码:
[root@mylove ~]# /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation 按提示
⑦ 测试:
用mysql命令行客户端登陆mysql服务器看能否成功
[root@mylove ~]# mysql -uroot -proot
mysql> show databases;
⑧ 给root用户授予从任何机器上登陆mysql服务器的权限:
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '你的密码' with grant option;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
注意点:要让mysql可以远程登录访问
最直接测试方法:从windows上用Navicat去连接,能连,则可以,不能连,则要去mysql的机器上用命令行客户端进行授权:
在mysql的机器上,启动命令行客户端:
mysql -uroot -proot
mysql>grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by 'root的密码' with grant option;
mysql>flush privileges;
3.2.2. hive的元数据库配置
vi conf/hive-site.xml
|
<configuration> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name> <value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true</value> <description>JDBC connect string for a JDBC metastore</description> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name> <value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value> <description>Driver class name for a JDBC metastore</description> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name> <value>root</value> <description>username to use against metastore database</description> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name> <value>root</value> <description>password to use against metastore database</description> </property> </configuration> |
2、上传一个mysql的驱动jar包到hive的安装目录的lib中
3、配置HADOOP_HOME 和HIVE_HOME到系统环境变量中:/etc/profile
4、source /etc/profile
5、hive启动测试
然后用命令启动hive交互界面:
[root@hdp20-04 ~]# hive
4. hive使用方式
4.1. 最基本使用方式
启动一个hive交互shell
bin/hive
hive>
设置一些基本参数,让hive使用起来更便捷,比如:
1、让提示符显示当前库:
hive>set hive.cli.print.current.db=true;
2、显示查询结果时显示字段名称:
hive>set hive.cli.print.header=true;
但是这样设置只对当前会话有效,重启hive会话后就失效,解决办法:
在linux的当前用户目录中,编辑一个.hiverc文件,将参数写入其中:
vi .hiverc
|
set hive.cli.print.header=true; set hive.cli.print.current.db=true; |
4.2. 启动hive服务使用
启动hive的服务:
[root@hdp20-04 hive-1.2.1]# bin/hiveserver2 -hiveconf hive.root.logger=DEBUG,console
上述启动,会将这个服务启动在前台,如果要启动在后台,则命令如下:
nohup bin/hiveserver2 1>/dev/null 2>&1 &
启动成功后,可以在别的节点上用beeline去连接
v 方式(1)
[root@hdp20-04 hive-1.2.1]# bin/beeline 回车,进入beeline的命令界面
输入命令连接hiveserver2
beeline> !connect jdbc:hive2://hadoop01:10000
(hadoop01是hiveserver2所启动的那台主机名,端口默认是10000)
v 方式(2)
启动时直接连接:
bin/beeline -u jdbc:hive2://hadoop01:10000 -n root
接下来就可以做正常sql查询了
4.3. 脚本化运行
大量的hive查询任务,如果用交互式shell来进行输入的话,显然效率及其低下,因此,生产中更多的是使用脚本化运行机制:
该机制的核心点是:hive可以用一次性命令的方式来执行给定的hql语句
[root@hdp20-04 ~]# hive -e "insert into table t_dest select * from t_src;"
然后,进一步,可以将上述命令写入shell脚本中,以便于脚本化运行hive任务,并控制、调度众多hive任务,示例如下:
vi t_order_etl.sh
|
#!/bin/bash hive -e "select * from db_order.t_order" hive -e "select * from default.t_user" hql="create table default.t_bash as select * from db_order.t_order" hive -e "$hql" |
如果要执行的hql语句特别复杂,那么,可以把hql语句写入一个文件:
vi x.hql
|
select * from db_order.t_order; select count(1) from db_order.t_user; |
然后,用hive -f /root/x.hql 来执行
5. hive建库建表与数据导入
5.1. 建库
hive中有一个默认的库:
库名: default
库目录:hdfs://hdp20-01:9000/user/hive/warehouse
新建库:
create database db_order;
库建好后,在hdfs中会生成一个库目录:
hdfs://hdp20-01:9000/user/hive/warehouse/db_order.db
5.2. 建表
5.2.1. 基本建表语句
use db_order;
create table t_order(id string,create_time string,amount float,uid string);
表建好后,会在所属的库目录中生成一个表目录
/user/hive/warehouse/db_order.db/t_order
只是,这样建表的话,hive会认为表数据文件中的字段分隔符为 ^A(�01)
正确的建表语句为:
create table t_order(id string,create_time string,amount float,uid string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';
这样就指定了,我们的表数据文件中的字段分隔符为 ","
5.2.2. 删除表
drop table t_order;
删除表的效果是:
hive会从元数据库中清除关于这个表的信息;
hive还会从hdfs中删除这个表的表目录;
5.2.3. 内部表与外部表
内部表(MANAGED_TABLE):表目录按照hive的规范来部署,位于hive的仓库目录/user/hive/warehouse中
外部表(EXTERNAL_TABLE):表目录由建表用户自己指定
create external table t_access(ip string,url string,access_time string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
location '/access/log';
外部表和内部表的特性差别:
1、内部表的目录在hive的仓库目录中 VS 外部表的目录由用户指定
2、drop一个内部表时:hive会清除相关元数据,并删除表数据目录
3、drop一个外部表时:hive只会清除相关元数据;
一个hive的数据仓库,最底层的表,一定是来自于外部系统,为了不影响外部系统的工作逻辑,在hive中可建external表来映射这些外部系统产生的数据目录;
然后,后续的etl操作,产生的各种中间表建议用managed_table(内部表)
5.2.4. 分区表
分区表的实质是:在表目录中为数据文件创建分区子目录,以便于在查询时,MR程序可以针对分区子目录中的数据进行处理,缩减读取数据的范围。
比如,网站每天产生的浏览记录,浏览记录应该建一个表来存放,但是,有时候,我们可能只需要对某一天的浏览记录进行分析
这时,就可以将这个表建为分区表,每天的数据导入其中的一个分区;
当然,每日的分区目录,应该有一个目录名(分区字段)
5.2.4.1. 一个分区字段的实例:
示例如下:
1、创建带分区的表
|
create table t_access(ip string,url string,access_time string) partitioned by(dt string) row format delimited fields terminated by ','; |
注意:分区字段不能是表定义中的已存在字段
2、向分区中导入数据
load data local inpath '/root/access.log.2017-08-04.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170804');
load data local inpath '/root/access.log.2017-08-05.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170805');
3、针对分区数据进行查询
a、统计8月4号的总PV:
select count(*) from t_access where dt='20170804';
实质:就是将分区字段当成表字段来用,就可以使用where子句指定分区了
b、统计表中所有数据总的PV:
select count(*) from t_access;
实质:不指定分区条件即可
5.2.4.2. 多个分区字段示例
建表:
create table t_partition(id int,name string,age int)
partitioned by(department string,sex string,howold int)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
导数据:
load data local inpath '/root/p1.dat' into table t_partition partition(department='xiangsheng',sex='male',howold=20);
5.2.5. CTAS建表语法
可以通过已存在表来建表:
1、create table t_user_2 like t_user;
新建的t_user_2表结构定义与源表t_user一致,但是没有数据
2、在建表的同时插入数据
|
create table t_access_user as select ip,url from t_access; |
t_access_user会根据select查询的字段来建表,同时将查询的结果插入新表中
5.3. 数据导入导出
5.3.1. 将数据文件导入hive的表
方式1:导入数据的一种方式:
手动用hdfs命令,将文件放入表目录;
方式2:在hive的交互式shell中用hive命令来导入本地数据到表目录
hive>load data local inpath '/root/order.data.2' into table t_order;
方式3:用hive命令导入hdfs中的数据文件到表目录
hive>load data inpath '/access.log.2017-08-06.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170806');
注意:导本地文件和导HDFS文件的区别:
本地文件导入表:复制
hdfs文件导入表:移动
5.3.2. 将hive表中的数据导出到指定路径的文件
1、将hive表中的数据导入HDFS的文件
insert overwrite directory '/root/access-data'
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
select * from t_access;
2、将hive表中的数据导入本地磁盘文件
insert overwrite local directory '/root/access-data'
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
select * from t_access limit 100000;
5.3.3. hive文件格式
HIVE支持很多种文件格式: SEQUENCE FILE | TEXT FILE | PARQUET FILE | RC FILE
create table t_pq(movie string,rate int) stored as textfile;
create table t_pq(movie string,rate int) stored as sequencefile;
create table t_pq(movie string,rate int) stored as parquetfile;
演示:
1、先建一个存储文本文件的表
create table t_access_text(ip string,url string,access_time string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
stored as textfile;
导入文本数据到表中:
load data local inpath '/root/access-data/000000_0' into table t_access_text;
2、建一个存储sequence file文件的表:
create table t_access_seq(ip string,url string,access_time string)
stored as sequencefile;
从文本表中查询数据插入sequencefile表中,生成数据文件就是sequencefile格式的了:
insert into t_access_seq
select * from t_access_text;
3、建一个存储parquet file文件的表:
create table t_access_parq(ip string,url string,access_time string)
stored as parquetfile;
5.4. 数据类型
5.4.1. 数字类型
TINYINT (1字节整数)
SMALLINT (2字节整数)
INT/INTEGER (4字节整数)
BIGINT (8字节整数)
FLOAT (4字节浮点数)
DOUBLE (8字节双精度浮点数)
示例:
create table t_test(a string ,b int,c bigint,d float,e double,f tinyint,g smallint)
5.4.2. 时间类型
TIMESTAMP (时间戳) (包含年月日时分秒的一种封装)
DATE (日期)(只包含年月日)
示例,假如有以下数据文件:
|
1,zhangsan,1985-06-30 2,lisi,1986-07-10 3,wangwu,1985-08-09 |
那么,就可以建一个表来对数据进行映射
create table t_customer(id int,name string,birthday date)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
然后导入数据
load data local inpath '/root/customer.dat' into table t_customer;
然后,就可以正确查询
5.4.3. 字符串类型
STRING
VARCHAR (字符串1-65355长度,超长截断)
CHAR (字符串,最大长度255)
5.4.4. 其他类型
BOOLEAN(布尔类型):true false
BINARY (二进制):
5.4.5. 复合类型
5.4.5.1. array数组类型
arrays: ARRAY<data_type> )
示例:array类型的应用
假如有如下数据需要用hive的表去映射:
|
战狼2,吴京:吴刚:龙母,2017-08-16 三生三世十里桃花,刘亦菲:杨洋,2017-08-20 |
设想:如果主演信息用一个数组来映射比较方便
建表:
create table t_movie(moive_name string,actors array<string>,first_show date)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':';
导入数据:
load data local inpath '/root/movie.dat' into table t_movie;
查询:
select * from t_movie;
select moive_name,actors[0] from t_movie;
select moive_name,actors from t_movie where array_contains(actors,'吴刚');
select moive_name,size(actors) from t_movie;
5.4.5.2. map类型
maps: MAP<primitive_type, data_type>
1) 假如有以下数据:
|
1,zhangsan,father:xiaoming#mother:xiaohuang#brother:xiaoxu,28 2,lisi,father:mayun#mother:huangyi#brother:guanyu,22 3,wangwu,father:wangjianlin#mother:ruhua#sister:jingtian,29 4,mayun,father:mayongzhen#mother:angelababy,26 |
可以用一个map类型来对上述数据中的家庭成员进行描述
2) 建表语句:
create table t_person(id int,name string,family_members map<string,string>,age int)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by '#'
map keys terminated by ':';
3) 查询
select * from t_person;
## 取map字段的指定key的值
select id,name,family_members['father'] as father from t_person;
## 取map字段的所有key
select id,name,map_keys(family_members) as relation from t_person;
## 取map字段的所有value
select id,name,map_values(family_members) from t_person;
select id,name,map_values(family_members)[0] from t_person;
## 综合:查询有brother的用户信息
|
select id,name,father from (select id,name,family_members['brother'] as father from t_person) tmp where father is not null; |
5.4.5.3. struct类型
structs: STRUCT<col_name : data_type, ...>
1) 假如有如下数据:
|
1,zhangsan,18:male:beijing 2,lisi,28:female:shanghai |
其中的用户信息包含:年龄:整数,性别:字符串,地址:字符串
设想用一个字段来描述整个用户信息,可以采用struct
2) 建表:
create table t_person_struct(id int,name string,info struct<age:int,sex:string,addr:string>)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':';
3) 查询
select * from t_person_struct;
select id,name,info.age from t_person_struct;
5.5. 修改表定义
仅修改Hive元数据,不会触动表中的数据,用户需要确定实际的数据布局符合元数据的定义。
修改表名:
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name
示例:alter table t_1 rename to t_x;
修改分区名:
alter table t_partition partition(department='xiangsheng',sex='male',howold=20) rename to partition(department='1',sex='1',howold=20);
添加分区:
alter table t_partition add partition (department='2',sex='0',howold=40);
删除分区:
alter table t_partition drop partition (department='2',sex='2',howold=24);
修改表的文件格式定义:
ALTER TABLE table_name [PARTITION partitionSpec] SET FILEFORMAT file_format
alter table t_partition partition(department='2',sex='0',howold=40 ) set fileformat sequencefile;
修改列名定义:
ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE [COLUMN] col_old_name col_new_name column_type [COMMENTcol_comment] [FIRST|(AFTER column_name)]
alter table t_user change price jiage float first;
增加/替换列:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD|REPLACE COLUMNS (col_name data_type[COMMENT col_comment], ...)
alter table t_user add columns (sex string,addr string);
alter table t_user replace columns (id string,age int,price float);
6. hive查询语法
sql是一门面向集合的编程语言;
select 1;
提示:在做小数据量查询测试时,可以让hive将mrjob提交给本地运行器运行,可以在hive会话中设置如下参数:
hive> set hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true;
6.1. 基本查询示例
select * from t_access;
select count(*) from t_access;
select max(ip) from t_access;
6.2. 条件查询
select * from t_access where access_time<'2017-08-06 15:30:20'
select * from t_access where access_time<'2017-08-06 16:30:20' and ip>'192.168.33.3';
6.3. join关联查询示例
假如有a.txt文件
|
a,1 b,2 c,3 d,4 |
假如有b.txt文件
|
a,xx b,yy d,zz e,pp |
进行各种join查询:
1、inner join(join)
|
select a.name as aname, a.numb as anumb, b.name as bname, b.nick as bnick from t_a a join t_b b on a.name=b.name |
结果:
|
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--+ | aname | anumb | bname | bnick | +--------+--------+--------+--------+--+ | a | 1 | a | xx | | b | 2 | b | yy | | d | 4 | d | zz | +--------+--------+--------+--------+--+ |
2、left outer join(left join)
|
select a.name as aname, a.numb as anumb, b.name as bname, b.nick as bnick from t_a a left outer join t_b b on a.name=b.name |
结果:
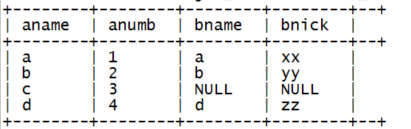
3、right outer join(right join)
|
select a.name as aname, a.numb as anumb, b.name as bname, b.nick as bnick from t_a a right outer join t_b b on a.name=b.name |
结果:

4、full outer join(full join)
|
select a.name as aname, a.numb as anumb, b.name as bname, b.nick as bnick from t_a a full join t_b b on a.name=b.name; |
结果:
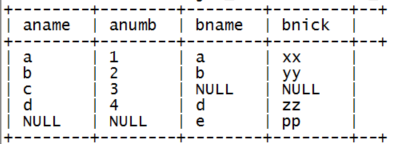
6.4. left semi join
Left semi join :相当于join连接两个表后产生的数据中的左半部分
hive中不支持exist/IN子查询,可以用left semi join来实现同样的效果:
|
select a.name as aname, a.numb as anumb from t_a a left semi join t_b b on a.name=b.name; |
结果:

注意: left semi join的 select子句中,不能有右表的字段
6.5. group by分组聚合
|
20170804,192.168.33.66,http://www.edu360.cn/job 20180804,192.168.33.40,http://www.edu360.cn/study 20180805,192.168.20.18,http://www.edu36.cn/job 20180805,192.168.20.28,http://www.edu36.cn/login 20180806,192.168.20.38,http://www.edu36.cn/job 20180806,192.168.20.38,http://www.edu36.cn/study 20180807,192.168.33.40,http://www.edu36.cn/login 20180807,192.168.20.88,http://www.edu36.cn/job |
select dt,count(*),max(ip) as cnt from t_access group by dt;
select dt,count(*),max(ip) as cnt from t_access group by dt having dt>'20170804';
select
dt,count(*),max(ip) as cnt
from t_access
where url='http://www.edu360.cn/job'
group by dt having dt>'20170804';
注意: 一旦有group by子句,那么,在select子句中就不能有 (分组字段,聚合函数) 以外的字段
## 为什么where必须写在group by的前面,为什么group by后面的条件只能用having
因为,where是用于在真正执行查询逻辑之前过滤数据用的
having是对group by聚合之后的结果进行再过滤;
上述语句的执行逻辑:
1、where过滤不满足条件的数据
2、用聚合函数和group by进行数据运算聚合,得到聚合结果
3、用having条件过滤掉聚合结果中不满足条件的数据
6.6. 子查询
|
1,zhangsan,father:xiaoming#mother:xiaohuang#brother:xiaoxu,28 2,lisi,father:mayun#mother:huangyi#brother:guanyu,22 3,wangwu,father:wangjianlin#mother:ruhua#sister:jingtian,29 4,mayun,father:mayongzhen#mother:angelababy,26 |
-- 查询有兄弟的人
select id,name,brother
from
(select id,name,family_members['brother'] as brother from t_person) tmp
where brother is not null;
另一种写法:
select id,name,family_members[‘brother’]
from t_person where array_contains(map_keys(family_members),”brother”);
7. hive函数使用
小技巧:测试函数的用法,可以专门准备一个专门的dual表
create table dual(x string);
insert into table dual values('');
其实:直接用常量来测试函数即可
select substr("abcdefg",1,3);
hive的所有函数手册:
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+UDF#LanguageManualUDF-Built-inTable-GeneratingFunctions(UDTF)
7.1. 常用内置函数
7.1.1. 类型转换函数
select cast("5" as int) ;
select cast("2017-08-03" as date) ;
select cast(current_timestamp as date);
示例:
|
1 |
1995-05-05 13:30:59 |
1200.3 |
|
2 |
1994-04-05 13:30:59 |
2200 |
|
3 |
1996-06-01 12:20:30 |
80000.5 |
create table t_fun(id string,birthday string,salary string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
select id,cast(birthday as date) as bir,cast(salary as float) from t_fun;
7.1.2. 数学运算函数
select round(5.4); ## 5 四舍五入
select round(5.1345,3) ; ##5.135
select ceil(5.4) ; // select ceiling(5.4) from dual; ## 6 向上取整
select floor(5.4); ## 5 向下取整
select abs(-5.4) ; ## 5.4 绝对值
select greatest(3,5,6) ; ## 6
select least(3,5,6) from dual; ##求多个输入参数中的最小值
示例:
有表如下:
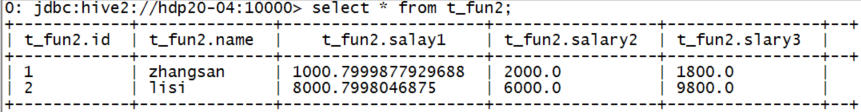
select greatest(cast(s1 as double),cast(s2 as double),cast(s3 as double)) from t_fun2;
结果:
+---------+--+
| _c0 |
+---------+--+
| 2000.0 |
| 9800.0 |
+---------+--+
select max(age) from t_person; 聚合函数
select min(age) from t_person; 聚合函数
7.1.3. 字符串函数
substr(string str, int start) ## 截取子串
substring(string str, int start)
示例:select substr("abcdefg",2) from dual;
substr(string, int start, int len)
substring(string, int start, int len)
示例:select substr("abcdefg",2,3) from dual;
concat(string A, string B...) ## 拼接字符串
concat_ws(string SEP, string A, string B...)
示例:select concat("ab","xy") from dual; ## abxy
select concat_ws(".","192","168","33","44") from dual; ## 192.168.33.44
length(string A)
示例:select length("192.168.33.44") from dual; ## 13
split(string str, string pat)
示例:select split("192.168.33.44",".") from dual; 错误的,因为.号是正则语法中的特定字符
select split("192.168.33.44","\.") from dual;
upper(string str) ##转大写
lower(string str)
7.1.4. 时间函数
select current_timestamp; ## 获取当前的时间戳(详细时间信息)
select current_date; ## 获取当前的日期
## 取当前时间的秒数时间戳--(距离格林威治时间1970-1-1 0:0:0秒的差距)
select unix_timestamp();
## unix时间戳转字符串
from_unixtime(bigint unixtime[, string format])
示例:select from_unixtime(unix_timestamp());
select from_unixtime(unix_timestamp(),"yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
## 字符串转unix时间戳
unix_timestamp(string date, string pattern)
示例: select unix_timestamp("2017-08-10 17:50:30");
select unix_timestamp("2017-08-10 17:50:30","yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
## 将字符串转成日期date
select to_date("2017-09-17 16:58:32");
7.1.5. 条件控制函数
7.1.5.1. case when
语法:
CASE [ expression ]
WHEN condition1 THEN result1
WHEN condition2 THEN result2
...
WHEN conditionn THEN resultn
ELSE result
END
示例:
select id,name,
case
when age<28 then 'youngth'
when age>27 and age<40 then 'zhongnian'
else 'old'
end
from t_user;
7.1.5.2. IF
select id,if(age>25,'working','worked') from t_user;
select moive_name,if(array_contains(actors,'吴刚'),'好电影',’烂片儿’)
from t_movie;
7.1.6. 集合函数
array_contains(Array<T>, value) 返回boolean值
示例:
select moive_name,array_contains(actors,'吴刚') from t_movie;
select array_contains(array('a','b','c'),'c') from dual;
sort_array(Array<T>) 返回排序后的数组
示例:
select sort_array(array('c','b','a')) from dual;
select 'haha',sort_array(array('c','b','a')) as xx from (select 0) tmp;
size(Array<T>) 返回一个集合的长度,int值
示例:
select moive_name,size(actors) as actor_number from t_movie;
size(Map<K.V>) 返回一个int值
map_keys(Map<K.V>) 返回一个map字段的所有key,结果类型为:数组
map_values(Map<K.V>) 返回一个map字段的所有value,结果类型为:数组
7.1.7. 常见聚合函数
sum
avg
max
min
count
7.1.8. 表生成函数
7.1.8.1. 行转列函数:explode()
假如有以下数据:
|
1,zhangsan,化学:物理:数学:语文 2,lisi,化学:数学:生物:生理:卫生 3,wangwu,化学:语文:英语:体育:生物 |
映射成一张表:
create table t_stu_subject(id int,name string,subjects array<string>)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':';
使用explode()对数组字段“炸裂”
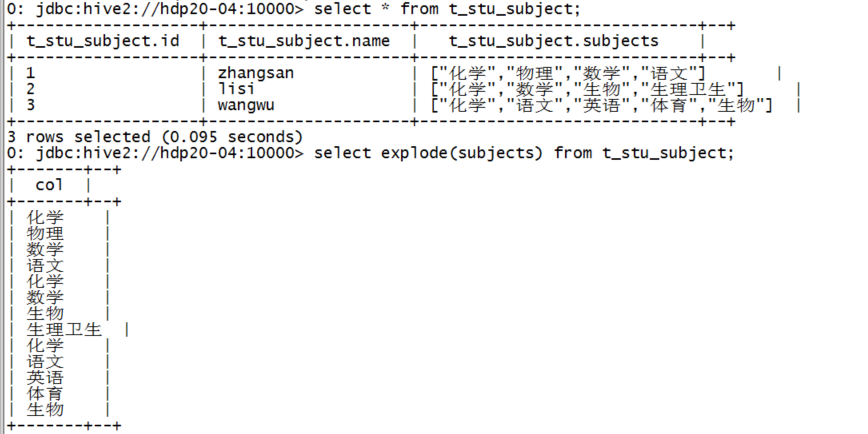
然后,我们利用这个explode的结果,来求去重的课程:
|
select distinct tmp.sub from (select explode(subjects) as sub from t_stu_subject) tmp; |
7.1.8.2. 表生成函数lateral view
select id,name,tmp.sub
from t_stu_subject lateral view explode(subjects) tmp as sub;
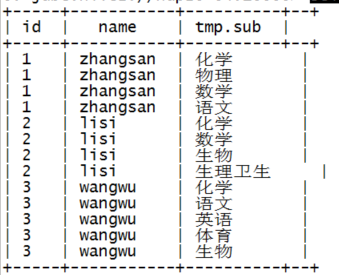
理解: lateral view 相当于两个表在join
左表:是原表
右表:是explode(某个集合字段)之后产生的表
而且:这个join只在同一行的数据间进行
那样,可以方便做更多的查询:
比如,查询选修了生物课的同学
select a.id,a.name,a.sub from
(select id,name,tmp.sub as sub from t_stu_subject lateral view explode(subjects) tmp as sub) a
where sub='生物';
7.1.9. json解析函数:表生成函数
需求:有如下json格式的电影评分数据:
|
{"movie":"1193","rate":"5","timeStamp":"978300760","uid":"1"} {"movie":"661","rate":"3","timeStamp":"978302109","uid":"1"} {"movie":"914","rate":"3","timeStamp":"978301968","uid":"1"} {"movie":"3408","rate":"4","timeStamp":"978300275","uid":"1"} {"movie":"2355","rate":"5","timeStamp":"978824291","uid":"1"} {"movie":"1197","rate":"3","timeStamp":"978302268","uid":"1"} |
需要做各种统计分析。
发现,直接对json做sql查询不方便,需要将json数据解析成普通的结构化数据表。可以采用hive中内置的json_tuple()函数
实现步骤:
1、创建一个原始表用来对应原始的json数据
create table t_json(json string);
load data local inpath ‘/root/rating.json’ into table t_json;
2、利用json_tuple进行json数据解析
测试,示例:
select json_tuple(json,'movie','rate','timeStamp','uid') as(movie,rate,ts,uid) from t_json limit 10;
产生结果:
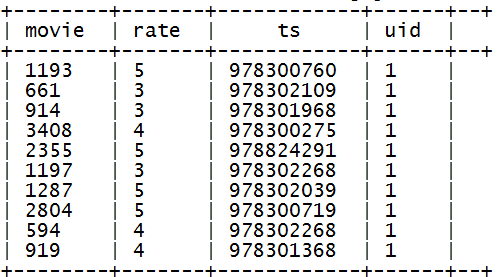
真正解析整张json表,将解析结果数据插入一张新表
create table t_movie_rate
as
select json_tuple(json,'movie','rate','timeStamp','uid') as(movie,rate,ts,uid) from t_json;
利用json_tuple从原始json数据表中,etl出一个详细信息表:
|
create table t_rate as select uid, movie, rate, year(from_unixtime(cast(ts as bigint))) as year, month(from_unixtime(cast(ts as bigint))) as month, day(from_unixtime(cast(ts as bigint))) as day, hour(from_unixtime(cast(ts as bigint))) as hour, minute(from_unixtime(cast(ts as bigint))) as minute, from_unixtime(cast(ts as bigint)) as ts from (select json_tuple(rateinfo,'movie','rate','timeStamp','uid') as(movie,rate,ts,uid) from t_json) tmp ; |
7.1.10. 分析函数:row_number() over()——分组TOPN
7.1.10.1. 需求
有如下数据:
|
1,18,a,male 2,19,b,male 3,22,c,female 4,16,d,female 5,30,e,male 6,26,f,female |
需要查询出每种性别中年龄最大的2条数据
create table t_rn(id int,age int,name string,sex string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘,’;
7.1.10.2. 实现:
使用row_number函数,对表中的数据按照性别分组,按照年龄倒序排序并进行标记
hql代码:
select id,age,name,sex,
row_number() over(partition by sex order by age desc) as rank
from t_rownumber
产生结果:
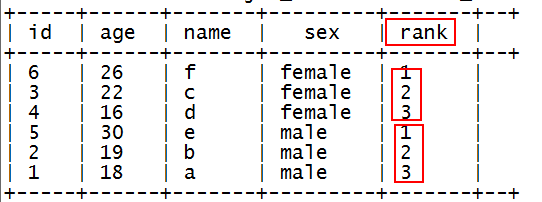
然后,利用上面的结果,查询出rank<=2的即为最终需求
select id,age,name,sex
from
(select id,age,name,sex,
row_number() over(partition by sex order by age desc) as rank
from t_rownumber) tmp
where rank<=2;