当前为vue3的基础知识点,为总结b站某视频的知识文章,在刚开始学习时自我保存在语雀,现在分享到博客。
目前找不到原视频文章地址了!!!要有兄弟看到原文地址:欢迎在下面评论!
Vue3新的特性
- Composition API(组合API)
- setup配置
- ref与reactive
- watch与watchEffect
- provide与inject
- 新的内置组件
- Fragment
- Teleport
- Suspense
- 其他改变
- 新的生命周期钩子
- data 选项应始终被声明为一个函数
- 移除keyCode支持作为 v-on 的修饰符
创建Vue3.0工程
1.使用 vue-cli 创建
官方文档:https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/guide/creating-a-project.html#vue-create
## 查看@vue/cli版本,确保@vue/cli版本在4.5.0以上 vue --version ## 安装或者升级你的@vue/cli npm install -g @vue/cli ## 创建 vue create vue_test ## 启动 cd vue_test npm run serve
常用 Composition API
官方文档: https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/composition-api-introduction.html
1.拉开序幕的setup
- 理解:Vue3.0中一个新的配置项,值为一个函数。
- setup是所有Composition API(组合API)“ 表演的舞台 ”。
- 组件中所用到的:数据、方法等等,均要配置在setup中。
- setup函数的两种返回值:
- 若返回一个对象,则对象中的属性、方法, 在模板中均可以直接使用。(重点关注!)
- 若返回一个渲染函数:则可以自定义渲染内容。(了解)

<template>
<h1>测试setup,拿数据</h1>
<h3>姓名:{{ name }}</h3>
<h3>年龄:{{ age }}</h3>
<button @click="sayHello">打招呼</button>
</template>
<script>
// 渲染函数 要导入这个
import { h } from '@vue/runtime-core';
export default {
name: "TestSetup",
//此处只是测试setup, 不考虑响应式的问题
setup() {
//数据
let name = "张三",
age = 15;
//方法
function sayHello() {
alert(`我叫${name},我${age}岁了,你好!`);
}
//返回一个对象 (常用)
return {
name,
age,
sayHello,
};
//返回一个函数(渲染函数--了解)
// return ()=> h('h1','返回一个函数(渲染函数)')
},
};
</script>
<style>
</style>
5.注意点:
- 尽量不要与Vue2.x配置混用
- Vue2.x配置(data、methos、computed...)中可以访问到setup中的属性、方法。
- 但在setup中不能访问到Vue2.x配置(data、methos、computed...)。
- 如果有重名, setup优先。
- setup不能是一个async函数,因为返回值不再是return的对象, 而是promise, 模板看不到return对象中的属性。(后期也可以返回一个Promise实例,但需要Suspense和异步组件的配合)
2.ref函数
- 作用: 定义一个响应式的数据
- 语法:
const xxx = ref(initValue)- 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用对象(reference对象,简称ref对象)。
- JS中操作数据:
xxx.value - 模板中读取数据: 不需要.value,直接:
<div>{{xxx}}</div>
- 备注:
- 接收的数据可以是:基本类型、也可以是对象类型。
- 基本类型的数据:响应式依然是靠
Object.defineProperty()的get与set完成的。 - 对象类型的数据:内部 “ 求助 ” 了Vue3.0中的一个新函数——
reactive函数。

<template>
<h1>学习ref</h1>
<h3>姓名:{{ name }}</h3>
<h3>年龄:{{ age }}</h3>
<button @click="alterName">修改姓名</button>
</template>
<script>
// 响应式 ref
import { ref } from '@vue/reactivity';
export default {
name: "testRef",
setup() {
//数据
let name = ref("张三"),
age = 15,
obj = ref({
type:'前端工程师',
salary:'5K'
});
//方法
function alterName() {
//成功
name.value = "修改姓名"
//对象
obj.value.type = "修改工作"
obj.value.salary = "60k"
//修改失败
age ="修改年龄"
}
//返回一个对象 (常用)
return {
name,
age,
alterName,
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
</style>
3.reactive函数
- 作用: 定义一个对象类型的响应式数据(基本类型不要用它,要用
ref函数) - 语法:
const 代理对象= reactive(源对象)接收一个对象(或数组),返回一个代理对象(Proxy的实例对象,简称proxy对象) - reactive定义的响应式数据是“深层次的”。
- 内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据进行操作。

<template>
<h1>学习reactive</h1>
<h3>工作:{{ obj.type }}</h3>
<h3>薪水:{{ obj.salary }}</h3>
<h3>爱好:{{ list }}</h3>
<button @click="alterName">修改姓名</button>
</template>
<script>
/*
响应式
reactive 对象类型
*/
import { reactive } from "@vue/reactivity";
export default {
name: "testRef",
setup() {
//数据
let obj = reactive({
type: "前端工程师",
salary: "5K",
}),
list = reactive(['吃饭','睡觉','打豆豆']);
//方法
function alterName() {
//对象
obj.type = "修改工作";
obj.salary = "60k";
//数组
list[0] = '出去玩'
}
//返回一个对象 (常用)
return {
obj,
list,
alterName,
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
</style>
4.reactive对比ref
- 从定义数据角度对比:
- ref用来定义:基本类型数据。
- reactive用来定义:对象(或数组)类型数据。
- 备注:ref也可以用来定义对象(或数组)类型数据, 它内部会自动通过
reactive转为代理对象。
- 从原理角度对比:
- ref通过
Object.defineProperty()的get与set来实现响应式(数据劫持)。 - reactive通过使用Proxy来实现响应式(数据劫持), 并通过Reflect操作源对象内部的数据。
- ref通过
- 从使用角度对比:
- ref定义的数据:操作数据需要
.value,读取数据时模板中直接读取不需要.value。 - reactive定义的数据:操作数据与读取数据:均不需要
.value。
5.setup的两个注意点
- setup执行的时机
- 在beforeCreate之前执行一次,this是undefined。
- setup的参数
- props:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,且组件内部声明接收了的属性。
- context:上下文对象
- attrs: 值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,但没有在props配置中声明的属性, 相当于
this.$attrs。 - slots: 收到的插槽内容, 相当于
this.$slots。 - emit: 分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于
this.$emit。
6.组件传值,插槽,自定义事件
代码实例

//父页面 <template> <Demo @hello="showHelloMsg" msg="你好啊" school="尚硅谷"> <template v-slot:qwe> <span>尚硅谷</span> </template> <template v-slot:asd> <span>尚硅谷</span> </template> </Demo> </template> <script> import Demo from './components/Demo' export default { name: 'App', components:{Demo}, setup(){ function showHelloMsg(value){ alert(`你好啊,你触发了hello事件,我收到的参数是:${value}!`) } return { showHelloMsg } } } </script> //组件 <template> <h1>一个人的信息</h1> <h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2> <h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2> <button @click="test">测试触发一下Demo组件的Hello事件</button> </template> <script> import {reactive} from 'vue' export default { name: 'Demo', //接收参数 props:['msg','school'], //声明接收 自定义事件 emits:['hello'], //setup 的参数 setup(props,context){ // console.log('---setup---',props) //接收参数 // console.log('---setup---',context) //上下文 // console.log('---setup---',context.attrs) //相当与Vue2中的$attrs // console.log('---setup---',context.emit) //触发自定义事件的。 console.log('---setup---',context.slots) //插槽 //数据 let person = reactive({ name:'张三', age:18 }) //方法 function test(){ context.emit('hello',666) } //返回一个对象(常用) return { person, test } } } </script>
7.计算属性与监视
computed函数
- 与Vue2.x中computed配置功能一致
- 写法

<template>
<h1>一个人的信息</h1>
姓:<input type="text" v-model="person.firstName">
<br>
名:<input type="text" v-model="person.lastName">
<br>
<span>全名:{{person.fullName}}</span>
<br>
全名:<input type="text" v-model="person.fullName">
</template>
<script>
//导入 computed 计算属性
import {reactive,computed} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Demo',
setup(){
//数据
let person = reactive({
firstName:'张',
lastName:'三'
})
//计算属性——简写(没有考虑计算属性被修改的情况)
/* person.fullName = computed(()=>{
return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName
}) */
//计算属性——完整写法(考虑读和写)
person.fullName = computed({
get(){
return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName
},
set(value){
const nameArr = value.split('-')
person.firstName = nameArr[0]
person.lastName = nameArr[1]
}
})
//返回一个对象(常用)
return {
person
}
}
}
</script>
watch函数
- 与Vue2.x中watch配置功能一致
- 两个小“坑”:
- 监视reactive定义的响应式数据时:oldValue无法正确获取、强制开启了深度监视(deep配置失效)。
- 监视reactive定义的响应式数据中某个属性时:deep配置有效。

<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
<hr>
<h2>当前的信息为:{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="msg+='!'">修改信息</button>
<hr>
<h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{person.job.j1.salary}}K</h2>
<button @click="person.name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="person.age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,reactive,watch} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Demo',
setup(){
//数据
let sum = ref(0)
let msg = ref('你好啊')
let person = reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
//情况一:监视ref所定义的一个响应式数据
/* watch(sum,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('sum变了',newValue,oldValue)
},{immediate:true}) */
//情况二:监视ref所定义的多个响应式数据
/* watch([sum,msg],(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('sum或msg变了',newValue,oldValue)
},{immediate:true}) */
/*
情况三:监视reactive所定义的一个响应式数据的全部属性
1.注意:此处无法正确的获取oldValue
2.注意:强制开启了深度监视(deep配置无效)
*/
/* watch(person,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person变化了',newValue,oldValue)
},{deep:false}) //此处的deep配置无效 */
//情况四:监视reactive所定义的一个响应式数据中的某个属性
/* watch(()=>person.name,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的name变化了',newValue,oldValue)
}) */
//情况五:监视reactive所定义的一个响应式数据中的某些属性
/* watch([()=>person.name,()=>person.age],(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的name或age变化了',newValue,oldValue)
}) */
//特殊情况
/* watch(()=>person.job,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的job变化了',newValue,oldValue)
},{deep:true}) //此处由于监视的是reactive素定义的对象中的某个属性,所以deep配置有效 */
//返回一个对象(常用)
return {
sum,
msg,
person
}
}
}
</script>
watch监视ref数据的说明

<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
<hr>
<h2>当前的信息为:{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="msg+='!'">修改信息</button>
<hr>
<h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{person.job.j1.salary}}K</h2>
<button @click="person.name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="person.age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,reactive,watch} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Demo',
setup(){
//数据
let sum = ref(0)
let msg = ref('你好啊')
let person = ref({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
console.log(person)
watch(sum,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('sum的值变化了',newValue,oldValue)
})
/*
person 为 reactive 函数的对象
deep:true 需要开启深度监视
person.value 直接监视 reactive 函数的对象
可以参考上面 情况三
*/
watch(person,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的值变化了',newValue,oldValue)
},{deep:true})
//返回一个对象(常用)
return {
sum,
msg,
person
}
}
}
</script>
watchEffect函数
- watch的套路是:既要指明监视的属性,也要指明监视的回调。
- watchEffect的套路是:不用指明监视哪个属性,监视的回调中用到哪个属性,那就监视哪个属性。
- watchEffect有点像computed:
- 但computed注重的计算出来的值(回调函数的返回值),所以必须要写返回值。
- 而watchEffect更注重的是过程(回调函数的函数体),所以不用写返回值。

<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
<hr>
<h2>当前的信息为:{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="msg+='!'">修改信息</button>
<hr>
<h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{person.job.j1.salary}}K</h2>
<button @click="person.name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="person.age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,reactive,watch,watchEffect} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Demo',
setup(){
//数据
let sum = ref(0)
let msg = ref('你好啊')
let person = reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
//监视watch('监视属性','回调','配置')
/* watch(sum,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('sum的值变化了',newValue,oldValue)
},{immediate:true}) */
//不用指明监视哪个属性,监视的回调中用到哪个属性,那就监视哪个属性
watchEffect(()=>{
const x1 = sum.value
const x2 = person.job.j1.salary
console.log('watchEffect所指定的回调执行了')
})
//返回一个对象(常用)
return {
sum,
msg,
person
}
}
}
</script>
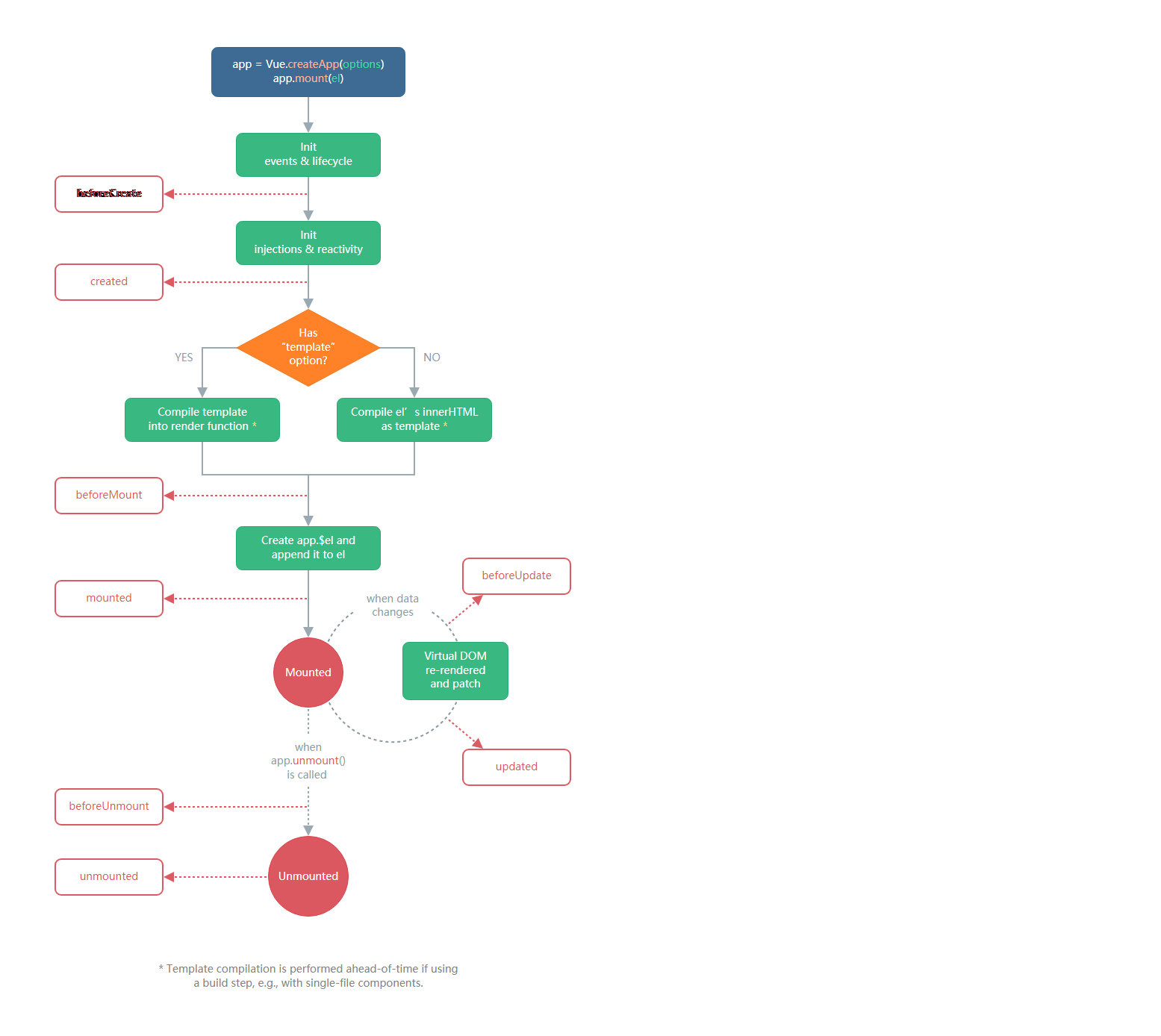
8.生命周期
2.0与3.0对比
| vue2 | vue3 |
|
|
setup()
|
|
|
setup()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
代码实例

<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
</template>
<script>
//导入生命周期
import {ref,onBeforeMount,onMounted,
onBeforeUpdate,onUpdated,
onBeforeUnmount,onUnmounted} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Demo',
setup(){
console.log('---setup---')
//数据
let sum = ref(0)
//通过组合式API的形式去使用生命周期钩子
//先执行组合式 之后 配置项的形式 生命周期
onBeforeMount(()=>{
console.log('---onBeforeMount---')
})
onMounted(()=>{
console.log('---onMounted---')
})
onBeforeUpdate(()=>{
console.log('---onBeforeUpdate---')
})
onUpdated(()=>{
console.log('---onUpdated---')
})
onBeforeUnmount(()=>{
console.log('---onBeforeUnmount---')
})
onUnmounted(()=>{
console.log('---onUnmounted---')
})
//返回一个对象(常用)
return {sum}
},
//通过配置项的形式使用生命周期钩子
//先执行组合式 之后 配置项的形式 生命周期
//#region
beforeCreate() {
console.log('---beforeCreate---')
},
created() {
console.log('---created---')
},
beforeMount() {
console.log('---beforeMount---')
},
mounted() {
console.log('---mounted---')
},
beforeUpdate(){
console.log('---beforeUpdate---')
},
updated() {
console.log('---updated---')
},
beforeUnmount() {
console.log('---beforeUnmount---')
},
unmounted() {
console.log('---unmounted---')
},
//#endregion
}
</script>