链表1
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
找出两个单链表相交的起始节点
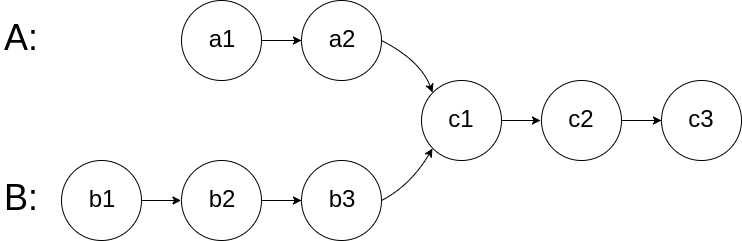
/**
* 思路:
* 去除长链表左边长的部分,将两个链表变成相等长度的链表,一起前进,找出是否有相等的位置
*/
class Solution1 {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode1(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode a = headA;
int lena = 0;
ListNode b = headB;
int lenb = 0;
while (a != null) {
a = a.next;
lena++;
}
while (b != null) {
b = b.next;
lenb++;
}
if (lena > lenb) {
int len = lena - lenb;
while (len-- > 0) {
headA = headA.next;
}
while (headA != headB && headA != null) {
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
if (headA == headB) return headA;
}
if (lena < lenb) {
int len = lenb - lena;
while (len-- > 0) {
headB = headB.next;
}
while (headA != headB && headA != null) {
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
if (headA == headB) return headA;
}
if (lena == lenb) {
while (headA != headB && headA != null) {
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
if (headA == headB) return headA;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 大神解法
*/
public ListNode getIntersectionNode2(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
判断链表是否有环
/**
* 1. HashSet:
* 时间复杂度:O(n),对于含有 nn 个元素的链表,我们访问每个元素最多一次。
* 添加一个结点到哈希表中只需要花费 O(1) 的时间。
* 空间复杂度:O(n),空间取决于添加到哈希表中的元素数目,最多可以添加 n 个元素。
*
* 2. 双指针:
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
class Solution2 {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode low = head;
ListNode fast = head;
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
while (fast.next != null && low.next != null) {
low = low.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
if (low == fast) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。如果链表无环,则返回 null
/**
* 1. HashSet
*
* 2. 快慢指针:指针从 相遇点 出发和从 链表的头 出发,最后会遍历相同数目的节点后在环的入口处相遇。
*/
class Solution3 {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null) {
if (set.contains(head)) return head;
set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return null;
}
}
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
/**
* 示例:
* 输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
* 输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
*/
/**
* 方法1:
* 递归:进去保存链表,回去返回
*
* 时间复杂度:O(n + m)。
* 空间复杂度:O(n + m)。
*/
class Solution5 {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
/**
* 方法2:
* 迭代
*
* 时间复杂度:O(n + m)。
* 空间复杂度:O(1)。
*/
class Solution6 {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode listNode = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = listNode;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
cur = cur.next;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
cur = cur.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return listNode.next;
}
}
合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表
/**
* 1. 暴力法:放数组里排序
* 时间复杂度:O(NlogN)
* 空间复杂度:O(N)
*
* 2. 分治
* 时间复杂度:O(Nlogk) ,其中 k 是链表的数目。
* 空间复杂度:O(1)。
*
* 3. 优先队列
* 先添加k个链表的头,然后根据优先队列取出最小的。
* 然后把最小的节点的下一个添加到优先队列,再取最小的。
* 如果null则不添加到优先队列中。
* 直到优先队列为空。
*
* 时间复杂度:O(Nlogk)
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution7 {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) return null;
return recursion(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
private ListNode recursion(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) return lists[left];
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
ListNode l1 = recursion(lists, left, mid);
ListNode l2 = recursion(lists, mid + 1, right);
return merger(l1, l2);
}
private ListNode merger(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = merger(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = merger(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表
/**
* 示例:
* 给定 1->2->3->4, 你应该返回 2->1->4->3.
*/
/**
* 递归
*/
class Solution8 {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(next.next);
next.next = head;
return next;
}
}
/**
* 非递归
*/
class Solution9 {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode fakeHead = new ListNode(0);
fakeHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = fakeHead; //前一个遍历的节点
ListNode ptr = pre.next; //当前节点
while (ptr != null && ptr.next != null) {
ListNode temp = ptr.next; //要与ptr交换位置的节点
ListNode next = temp.next; //下一个要遍历的节点,先存储起来
pre.next = temp; //因为pre是上一个的节点,所以需要连接下一个被交换后的节点
temp.next = ptr; //交换节点
pre = ptr; //前一个遍历的节点
ptr = next; //当前节点
}
pre.next = ptr; //!!很重要,最后的连接整理
return fakeHead.next;
}
}
链表2
class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node random;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val, Node _next, Node _random) {
val = _val;
next = _next;
random = _random;
}
}
返回链表的深拷贝
/**
* 给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
*
* 要求返回这个链表的深拷贝。
*
* 思路:递归,入栈时复制node,出栈时将node相连
*
* 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是链表中节点的数目。
* 空间复杂度:O(N) 。我们需要维护一个回溯的栈,同时也需要记录已经被深拷贝过的节点,也就是维护一个已访问字典。
*/
class Solution4 {
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
//当前节点已经存在,则无需创建,直接返回节点
if (map.containsKey(head)) {
return map.get(head);
}
//创建节点,并保存再map中
Node node = new Node(head.val, null, null);
map.put(head, node);
//回溯,将节点相连
node.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
node.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
return node;
}
}
