AIO(Asynchronous Input and Output)
异步IO则采用“订阅-通知”模式:
即应用程序向操作系统注册IO监听,然后继续做自己的事情。
当操作系统发生IO事件,并且准备好数据后,在主动通知应用程序,触发相应的函数
NIO在网络操作中,提供了非阻塞的方法,但是NIO的IO行为还是同步的。
NIO的业务线程是在IO操作准备好时,得到通知,接着就由这个线程自行进行IO操作(IO操作本身是同步的)
AIO不是在IO操作准备好时再通知线程,而是在IO操作已经完成后,再给线程发出通知。
因此AIO是不会阻塞的,此时我们的业务逻辑将变成一个回调函数,等待IO操作完成后,由系统自动触发。
基本操作
与NIO不同,当进行读写操作时,AIO只须直接调用API的read或write方法即可。
两种方法均为异步的:
对于读操作而言,当有流可读取时,操作系统会将可读的流传入read方法的缓冲区,并通知应用程序;
对于写操作而言,当操作系统将write方法传递的流写入完毕时,操作系统主动通知应用程序。
即可以理解为,read/write方法都是异步的,完成后会主动调用回调函数。
在JDK1.7中,这部分内容被称作NIO2,主要在Java.nio.channels包下增加了下面四个异步通道:
AsynchronousSocketChannel
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
AsynchronousFileChannel
AsynchronousDatagramChannel
在AIO socket编程中,服务端通道是AsynchronousServerSocketChannel:
open()静态工厂:
public static AsynchronousServerSocketChannel open(AsynchronousChannelGroup group)
public static AsynchronousServerSocketChannel open()
如果参数是null,则由系统默认提供程序创建resulting channel,并且绑定到默认组
bind()方法用于绑定服务端IP地址(还有端口号)。
accept()用于接收用户连接请求。
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel server = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT);
public abstract <A> void accept(A attachment,CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel,? super A> handler);
public abstract Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> accept();
在客户端使用的通道是AsynchronousSocketChannel:
这个通道处理提供open静态工厂方法外,还提供了read和write方法。
public abstract Future<Void> connect(SocketAddress remote);
Future对象的get()方法会阻塞该线程,所以这种方式是阻塞式的异步IO
public abstract <A> void connect(SocketAddress remote,
A attachment,
CompletionHandler<Void,? super A> handler);
在AIO编程中,发出一个事件(accept read write等)之后要指定事件处理类(回调函数),AIO中的事件处理类是
CompletionHandler<V,A>,接口定义了如下两个方法,分别在异步操作成功和失败时被回调:
void completed(V result, A attachment); //第一个参数代表IO操作返回的对象,第二个参数代表发起IO操作时传入的附加参数
void failed(Throwable exc, A attachment); //第一个参数代表IO操作失败引发的异常或错误
异步channel API提供了两种方式监控/控制异步操作(connect,accept, read,write等):
第一种方式是返回java.util.concurrent.Future对象,
检查Future的状态可以得到操作是否完成还是失败,还是进行中(future.get()阻塞当前进程以判断IO操作完成)
第二种方式为操作提供一个回调参数java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler
这个回调类包含completed,failed两个方法。
Future方式(异步阻塞)
Future是在JDK1.5中加入Java并发包的,该接口提供get()方法用于获取任务完成之后的处理结果。
在AIO中,可以接受一个I/O连接请求,返回一个Future对象。
然后可以基于该返回对象进行后续的操作,包括使其阻塞、查看是否完成、超时异常。
使用异步Channel时,accept()、connect()、read()、write()等方法都不会阻塞,
也就是说如果使用返回Future的这些方法,程序并不能直到什么时候成功IO,
必须要使用get方法,等get方法的阻塞结束后才能确保IO完成,继续执行下面的操作。
FutureClient
public class ClientOnFuture {
static final int PORT = 10000;
static final String IP = "localhost";
static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//尝试创建AsynchronousSocketChannel
try (AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open()) {
//获取连接
Future<Void> connect = socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(IP, PORT));
//返回连接状态
Void aVoid = connect.get();
//返回null表示连接成功
if (aVoid == null) {
/**
* 向服务端发送数据
*/
Future<Integer> write = socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("客户端说:我连接成功了!".getBytes()));
Integer integer = write.get();
System.out.println("服务端接收的字节长度:" + integer);
/**
* 接收服务端数据
*/
while (socketChannel.read(buffer).get() != -1) {
buffer.flip();
CharBuffer decode = Charset.defaultCharset().decode(buffer);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
buffer.compact();
} else {
buffer.clear();
}
int r = new Random().nextInt(10);
if (r == 5) {
System.out.println("客户端关闭!");
break;
} else {
/**
* 如果在频繁调用write()的时候,在上一个操作没有写完的情况下,
* 调用write会触发WritePendingException异常
*
* 应此此处最好在调用write()之后调用get()阻塞以便确认io操作完成
*/
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(("客户端发送的数据:" + r).getBytes())).get();
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("无法建立连接!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出错了!");
}
}
}
FutureServer
public class ServerOnFuture {
static final int PORT = 10000;
static final String IP = "localhost";
static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()) {
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP, PORT));
while (true) {
Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> channelFuture = serverSocketChannel.accept();
try (AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = channelFuture.get()) {
while (socketChannel.read(buffer).get() != -1) {
buffer.flip();
/**
* 此处要注意:千万不能直接操作buffer(因为write要用到buffer),否则客户端会阻塞并报错
* “java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.io.IOException: 指定的网络名不再可用。”
*
* 缓冲区的复制有分两种:
* 1、完全复制:调用duplicate()函数或者asReadOnlyBuffer()函数
* 2、部分复制:调用slice函数
*
* duplicate()函数创建了一个与原始缓冲区相似的新缓冲区。
* 每个缓冲区有自己的位置信息,但对缓冲区的修改都会映射到同一个底层数组上。
*/
//复制一个缓冲区会创建一个新的 Buffer 对象,但并不复制数据。原始缓冲区和副本都会操作同样的数据元素。
ByteBuffer duplicate = buffer.duplicate();
CharBuffer decode = Charset.defaultCharset().decode(duplicate);
System.out.println("收到客户端数据:" + decode);
/**
* 写回数据(get()会阻塞以等待io操作完成)
*/
socketChannel.write(buffer).get();
/**
* 清理buffer,准备下一次read
*/
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
/**
* 如果未写完,表示buffer还有数据,则只清理写过的数据
* compact()方法只会清除已经读过的数据。
* 任何未读的数据都被移到缓冲区的起始处,新写入的数据将放到缓冲区未读数据的后面。
*/
buffer.compact();
} else {
buffer.clear();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Future方式实现多客户端并发
public class ServerOnFuture {
static final int PORT = 10000;
static final String IP = "localhost";
//无界线程池
static ExecutorService taskExecutorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()) {
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP, PORT));
while (true) {
Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> socketChannelFuture = serverSocketChannel.accept();
try {
final AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = socketChannelFuture.get();
/**
* 创建一个具有回调的线程
*/
Callable<String> worker = new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
while (socketChannel.read(buffer).get() != -1) {
buffer.flip();
ByteBuffer duplicate = buffer.duplicate();
CharBuffer decode = Charset.defaultCharset().decode(duplicate);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
socketChannel.write(buffer).get();
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
buffer.compact();
} else {
buffer.clear();
}
}
socketChannel.close();
return "服务端反馈信息:收到";
}
};
/**
* 将线程提交到线程池
*/
taskExecutorService.submit(worker);
//获取线程数
System.out.println(((ThreadPoolExecutor) taskExecutorService).getActiveCount());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
/**
* 出现异常,关闭线程池
*/
taskExecutorService.shutdown();
/**
* boolean isTerminated()
* 若关闭后所有任务都已完成,则返回true。
* 注意除非首先调用shutdown或shutdownNow,否则isTerminated永不为true。
*/
while (!taskExecutorService.isTerminated()) {
}
//跳出循环,结束程序
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
异步非阻塞和Group
AsynchronousChannelGroup是异步Channel的分组管理器,它可以实现资源共享。
创建AsynchronousChannelGroup时,需要传入一个ExecutorService,也就是绑定一个线程池。
该线程池负责两个任务:处理IO事件和触发CompletionHandler回调接口。
每个异步通道都必须关联一个组,要么是系统默认组,要么是用户创建的组。
如果不使用group参数,java使用一个默认的系统范围的组对象。
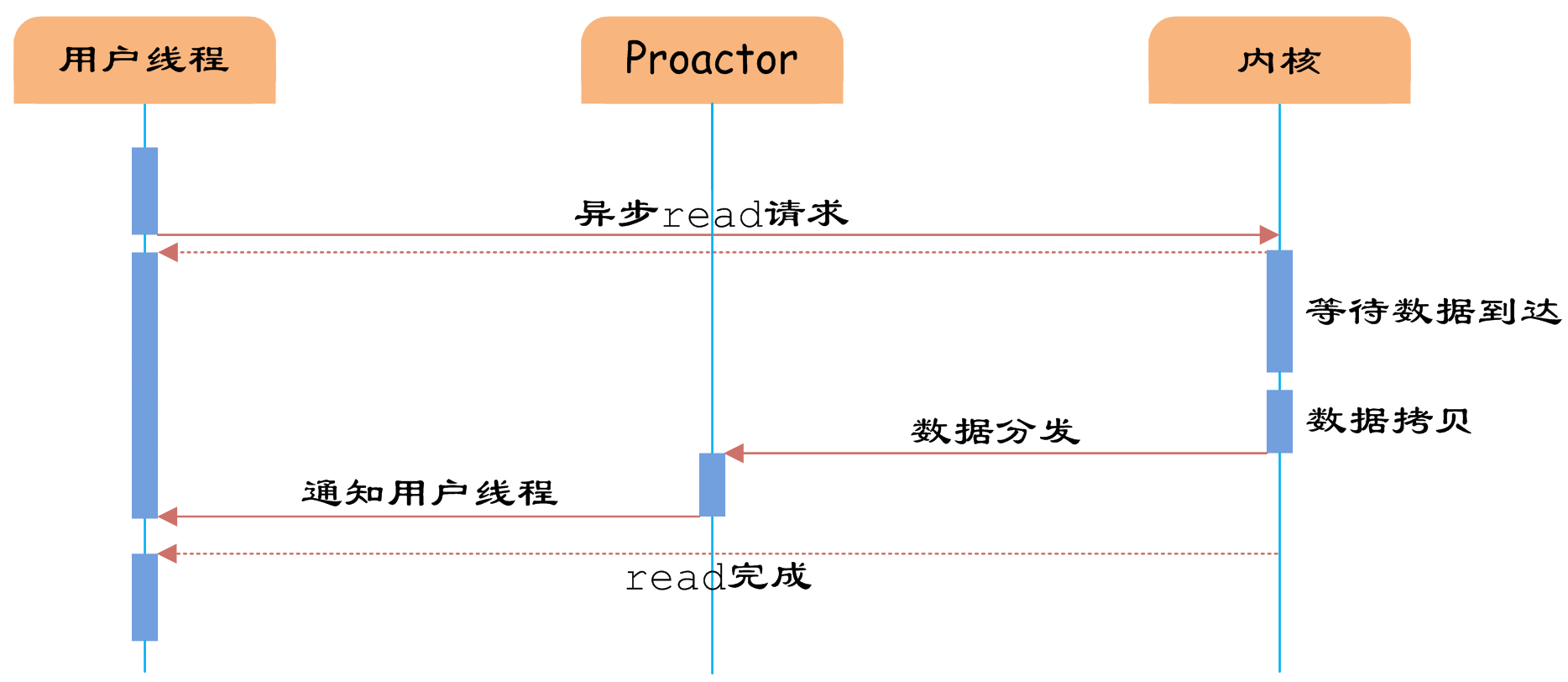
异步IO模型中,用户线程直接使用内核提供的异步IO API发起read请求。
发起后立即返回,继续执行用户线程代码。
此时用户线程已经将调用的AsynchronousOperation和CompletionHandler注册到内核,然后操作系统开启独立的内核线程去处理IO操作。
当read请求的数据到达时,由内核负责读取socket中的数据,并写入用户指定的缓冲区中。
最后内核将read的数据和用户线程注册的CompletionHandler分发给内部Proactor,Proactor将IO完成的信息通知给用户线程(一般通过调用用户线程注册的完成事件处理函数),完成异步IO。
Callback方式客户端(异步非阻塞)
public class ClientOnCompletionHandler {
static final int PORT = 10000;
static final String IP = "localhost";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (final AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open()) {
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(IP, PORT), null, new CompletionHandler<Void, Void>() {
final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
@Override
public void completed(Void result, Void attachment) {
try {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Hello Server!".getBytes())).get();
while (socketChannel.read(buffer).get() != -1) {
buffer.flip();
ByteBuffer duplicate = buffer.duplicate();
CharBuffer decode = Charset.defaultCharset().decode(duplicate);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
buffer.clear();
int r = new Random().nextInt(10);
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("客户端消息:".concat(String.valueOf(r)).getBytes())).get();
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
System.out.println("连接失败!");
}
});
//主要是阻塞作用,因为AIO是异步的,所以此处不阻塞的话,主线程很快执行完毕,并会关闭通道
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Callback方式服务端(异步非阻塞)
public class ServerOnCompletionHandler {
static final int PORT = 10000;
static final String IP = "localhost";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打开通道
try (final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()) {
//创建服务
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP, PORT));
//接收客户端连接
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Void>() {
final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, Void attachment) {
/**
* 注意接收一个连接之后,紧接着可以接收下一个连接,所以必须再次调用accept方法
* AsynchronousSocketChannel就代表该CompletionHandler处理器在处理连接成功时的result(AsynchronousSocketChannel的实例)
*/
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
try {
while (socketChannel.read(buffer).get() != -1) {
buffer.flip();
final ByteBuffer duplicate = buffer.duplicate();
final CharBuffer decode = Charset.defaultCharset().decode(duplicate);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
socketChannel.write(buffer).get(); //get()用于阻塞使IO操作完成
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
buffer.compact();
} else {
buffer.clear();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
/**
* 失败后也需要接收下一个连接
*/
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
System.out.println("连接失败!");
}
});
//主要是阻塞作用,因为AIO是异步的,所以此处不阻塞的话,主线程很快执行完毕,并会关闭通道
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
自定义Group
public class ServerOnReaderAndWriterForMultiClients {
static final int PORT = 10000;
static final String IP = "localhost";
static AsynchronousChannelGroup threadGroup = null;
static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(executorService, 5);
//或者使用指定数量的线程池
//threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withFixedThreadPool(5, Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try (AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup)) {
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP, PORT));
serverSocketChannel.accept(serverSocketChannel, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel>() {
final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel attachment) {
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
try {
while (socketChannel.read(buffer).get() != -1) {
buffer.flip();
final ByteBuffer duplicate = buffer.duplicate();
final CharBuffer decode = Charset.defaultCharset().decode(duplicate);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
socketChannel.write(buffer).get(); //get()用于阻塞使IO操作完成
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
buffer.compact();
} else {
buffer.clear();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel attachment) {
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
System.out.println("连接失败!");
}
});
//此方法一直阻塞,直到组终止、超时或当前线程中断
threadGroup.awaitTermination(Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}