原文地址:http://www.25hoursaday.com/CsharpVsJava.html
6、集合
许多有名的编程语言都会包含一个集合框架,框架一般由各种用于保存数据的数据结构和配套的操作对象的算法构成。集合框架的优势是让开发者可以不用写数据结构和排序算法,把精力放在真正的业务逻辑上。还有就是可以让不同的项目保持一致性,新的开发者也少了很多学习曲线。
C#集合框架大多位于System.Collections和System.Collections.Generic命名空间。Systems.Collections命名空间包含了表示抽象数据类型的接口和抽象类,比如IList, IEnumerable, IDictionary, ICollection, 和 CollectionBase,只要数据结构从抽象数据类型派生,开发者无需关心其内部如何实现。System.Collections命名空间还包含了很多数据结构的具体实现,包括ArrayList, Stack, Queue, HashTable 和SortedList。这四种结构都提供了同步包装,可以在多线程程序中线程安全。System.Collections.Generic命名空间实现了System.Collections空间中主要数据结构的泛型版本,包括泛型的List<T>, Stack<T>,Queue<T>, Dictionary<K,T> 和SortedDictionary<K,T>类。
Java集合框架则在java.util包中包含许多类和接口。java.util包也同样支持泛型,并没有使用新的命名空间来放置泛型类型。Java集合框架和C#相似,不过可以认为是C#集合框架的超集,因为它实现了一些其它特性。
注意:后面作者的话我就不翻译了,因为他提到的Java中有,而C#中没有的集合在.NET 3.5和.NET 4.0中都已经支持
7、goto
和Java不同,C#包含的goto可以用来在代码中进行跳转,尽管goto被嘲笑,但是有的时候还是可以使用goto来减少代码重复并增加可读性。goto语句第二个用处是可以重用异常,因为异常抛出是无法跨越方法边界的。
注意:在C#中goto无法跳转到语句块
C# Code using System; using System.Net.Sockets; class GotoSample{ public static void Main(string[] args){ int num_tries = 0; retry: try{ num_tries++; Console.WriteLine("Attempting to connect to network. Number of tries =" + num_tries); //Attempt to connect to a network times out //or some some other network connection error that //can be recovered from throw new SocketException(); }catch(SocketException){ if(num_tries < 5) goto retry; } }/* Main(string[]) */ }//GotoSample
8、虚方法
面向对象的一个主要特点就是多态。多态可以让我们和继承体系中的泛化类型而不是实际类型打交道。也就是一般在基类中实现的方法在派生类中重写,我们即使持有基类类型的引用,但是其指向派生类型,在运行时而不是编译时动态绑定的方法叫做虚方法。在Java中所有的方法都是虚方法,而在C#中,必须通过virtual关键字显式指定方法为虚方法,默认不是虚方法。同样可以用override关键字在子类中重写虚方法或使用new关键字隐藏基类方法。在Java中可以通过标记方法为final关键字让方法不能被派生类重写,在C#中可以不标记virtual来实现。主要区别是,如果派生类也实现了相同方法,C#的可以通过把引用指向基类调用到基类的方法,而在Java中如果基类实现了final方法,派生类不允许再有同名的方法。
C# Code using System; public class Parent{ public void DoStuff(string str){ Console.WriteLine("In Parent.DoStuff: " + str); } } public class Child: Parent{ public void DoStuff(int n){ Console.WriteLine("In Child.DoStuff: " + n); } public void DoStuff(string str){ Console.WriteLine("In Child.DoStuff: " + str); } } public class VirtualTest{ public static void Main(string[] args){ Child ch = new Child(); ch.DoStuff(100); ch.DoStuff("Test"); ((Parent) ch).DoStuff("Second Test"); } }//VirtualTest OUTPUT: In Child.DoStuff: 100 In Child.DoStuff: Test In Parent.DoStuff: Second Test
Java Code class Parent{ public void DoStuff(String str){ System.out.println("In Parent.DoStuff: " + str); } } class Child extends Parent{ public void DoStuff(int n){ System.out.println("In Child.DoStuff: " + n); } public void DoStuff(String str){ System.out.println("In Child.DoStuff: " + str); } } public class VirtualTest{ public static void main(String[] args){ Child ch = new Child(); ch.DoStuff(100); ch.DoStuff("Test"); ((Parent) ch).DoStuff("Second Test"); } }//VirtualTest OUTPUT: In Child.DoStuff: 100 In Child.DoStuff: Test In Child.DoStuff: Second Test
C#的例子可以通过把基类DoStuff(string) 方法标记为virtual子类方法标记为override关键字来实现和Java相同输出:
# Code using System; public class Parent{ public virtual void DoStuff(string str){ Console.WriteLine("In Parent.DoStuff: " + str); } } public class Child: Parent{ public void DoStuff(int n){ Console.WriteLine("In Child.DoStuff: " + n); } public override void DoStuff(string str){ Console.WriteLine("In Child.DoStuff: " + str); } } public class VirtualTest{ public static void Main(string[] args){ Child ch = new Child(); ch.DoStuff(100); ch.DoStuff("Test"); ((Parent) ch).DoStuff("Second Test"); } }//VirtualTest
如上例子可以修改子类的DoStuff(string)方法为如下以得到之前的结果:
public new void DoStuff(string str)
9、文件IO
两种语言都通过Stream类支持IO操作,如下例子把input.txt的内容复制到output.txt中。
C# Code using System; using System.IO; public class FileIOTest { public static void Main(string[] args){ FileStream inputFile = new FileStream("input.txt", FileMode.Open); FileStream outputFile = new FileStream("output.txt", FileMode.Open); StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(inputFile); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(outputFile); String str; while((str = sr.ReadLine())!= null) sw.Write(str); sr.Close(); sw.Close(); } }//FileIOTest
Java Code import java.io.*; public class FileIO{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File inputFile = new File("input.txt"); File outputFile = new File("output.txt"); FileReader in = new FileReader(inputFile); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in); FileWriter out = new FileWriter(outputFile); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(out); String str; while((str = br.readLine())!= null) bw.write(str); br.close(); bw.close(); } }//FileIOTest
10、对象序列化
对象持久化或叫序列化是通过诸如文件或网络读写对象的能力。如果在使用程序的时候对象的状态必须保存下来,那么对象持久化就很有用。有的时候以简单文本形式保存数据不够,以DBMS保存数据又劳师动众了,那么可以使用序列化直接保存,还有的时候可以使用序列化来传输类型。C#中可序列化类型标记[Serializable]特性。如果C#的类的一些成员不需要在运行时序列化,可以标记[NonSerialized]特性。这些字段通常用于计算或是临时的值,不需要保存下来。C#提供了两种格式来序列化类,XML或二进制格式,前者对于人来说更可读,后者更高效。当然我们也可以通过实现ISerializable接口实现自定义的序列化方式。
在Java中,对象序列化需要实现Serializable接口,而transient关键字用于标记不需要序列化的成员。默认情况下,Java支持序列化对象到二进制格式,但是提供了重写标准序列化过程的方式。需要重写默认序列化的对象需要实现如下方法签名:
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream stream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream stream) throws IOException
由于上面的方法是private的,使用readObject和writeObject来实现自定义序列化的话没有要实现的接口,对于需要公开访问的方法的类实现自定义序列化可以使用java.io.Externalizable接口,指定readExternal() 和writeExternal()。
C# Code using System; using System.IO; using System.Reflection; using System.Runtime.Serialization; using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary; using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Soap; [Serializable] class SerializeTest{ [NonSerialized] private int x; private int y; public SerializeTest(int a, int b){ x = a; y = b; } public override String ToString(){ return "{x=" + x + ", y=" + y + "}"; } public static void Main(String[] args){ SerializeTest st = new SerializeTest(66, 61); Console.WriteLine("Before Binary Write := " + st); Console.WriteLine("\n Writing SerializeTest object to disk"); Stream output = File.Create("serialized.bin"); BinaryFormatter bwrite = new BinaryFormatter(); bwrite.Serialize(output, st); output.Close(); Console.WriteLine("\n Reading SerializeTest object from disk\n"); Stream input = File.OpenRead("serialized.bin"); BinaryFormatter bread = new BinaryFormatter(); SerializeTest fromdisk = (SerializeTest)bread.Deserialize(input); input.Close(); /* x will be 0 because it won't be read from disk since non-serialized */ Console.WriteLine("After Binary Read := " + fromdisk); st = new SerializeTest(19, 99); Console.WriteLine("\n\nBefore SOAP(XML) Serialization := " + st); Console.WriteLine("\n Writing SerializeTest object to disk"); output = File.Create("serialized.xml"); SoapFormatter swrite = new SoapFormatter(); swrite.Serialize(output, st); output.Close(); Console.WriteLine("\n Reading SerializeTest object from disk\n"); input = File.OpenRead("serialized.xml"); SoapFormatter sread = new SoapFormatter(); fromdisk = (SerializeTest)sread.Deserialize(input); input.Close(); /* x will be 0 because it won't be read from disk since non-serialized */ Console.WriteLine("After SOAP(XML) Serialization := " + fromdisk); Console.WriteLine("\n\nPrinting XML Representation of Object"); XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument(); doc.Load("serialized.xml"); Console.WriteLine(doc.OuterXml); } } Java Code import java.io.*; class SerializeTest implements Serializable{ transient int x; private int y; public SerializeTest(int a, int b){ x = a; y = b; } public String toString(){ return "{x=" + x + ", y=" + y + "}"; } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ SerializeTest st = new SerializeTest(66, 61); System.out.println("Before Write := " + st); System.out.println("\n Writing SerializeTest object to disk"); FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("serialized.txt"); ObjectOutputStream so = new ObjectOutputStream(out); so.writeObject(st); so.flush(); System.out.println("\n Reading SerializeTest object from disk\n"); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("serialized.txt"); ObjectInputStream si = new ObjectInputStream(in); SerializeTest fromdisk = (SerializeTest)si.readObject(); /* x will be 0 because it won't be read from disk since transient */ System.out.println("After Read := " + fromdisk); } }
输出结果:
Before Write := {x=66, y=61}
Writing SerializeTest object to disk
Reading SerializeTest object from disk
After Read := {x=0, y=61}
11、文档生成
C#和Java都提供了从源文件提取特殊格式的注释然后集中到一个文档中。这些注释一般是API规范,这是一种非常有用的方式来生成类库文档。生成的文档也可以在设计者、开发者和QA之间分发。Javadoc是一种非常有用的工具用于从源代码提取API文档。Javadoc从源代码注释中提取内容生成HTML文档。可以生成的描述信息包括包、类、成员级别。可以在类或成员变量的描述中提供对其它类或类成员的引用。
Javadoc允许方法有如下信息:
1)描述方法
2)方法抛出的异常
3)方法接收的参数
4)方法的返回值
5)关联的方法和成员
6)API是否被弃用
7)方法首次提供的时间
废弃信息对于编译器也有用,如果在编译的时候编译器发现调用了废弃的方法可以给予警告。
Javadoc自动提供如下信息:
1)继承的API
2)派生类列表
3)实现的类或借口
4)类序列化格式
5)包继承层次
由于Java生成HTML文档,可以在Javadoc注释中使用HTML。如下是一个例子:
Java Code /** * Calculates the square of a number. * @param num the number to calculate. * @return the square of the number. * @exception NumberTooBigException this occurs if the square of the number * is too big to be stored in an int. */ public static int square(int num) throws NumberTooBigException{}
C#使用XML作为文档格式。生成的文档是XML文件,包含了用于提供的元数据以及少量自动生成的信息。C#的XML文档在生成的时候不会包含有关继承API列表、派生类或实现接口等元数据。
XML格式的主要优势是可以以各种方式来用。可以用XSLT样式来吧生成ASCII文本、HTML等。也可以作为一些工具的数据源来生成特殊的文档。
如下是C# XML文档的例子:
C# Code ///<summary>Calculates the square of a number.</summary> ///<param name="num">The number to calculate.</param> ///<return>The square of the number. </return> ///<exception>NumberTooBigException - this occurs if the square of the number ///is too big to be stored in an int. </exception> public static int square(int num){}
12、单个文件中的多个类
两种语言都可以在单个文件中定义多个类,但是有区别。在Java中,一个原文件中只可以有一个public访问的类并且类名需要和不带扩展名的源文件名保持一致。C#则对一个文件有多少个public类以及文件名是否和类名一致都没有限制。
13、导入类库
在应用程序中使用类库有两个步骤,首先需要在源文件中使用using或import关键字来引用空间或包,其次需要告诉编译器哪里有需要的类库。对于Java来说指定类库位置可以使用CLASSPATH环境变量或使用-classpath编译器选项,对于C#则在编译的时候指定/r开关。
14、事件
所谓事件驱动编程就是一个对象可以进行注册使得自己在别的独享状态修改或发生某个事件的时候被通知。事件驱动编程也被称作发布订阅模型或观察者设计模式,并且在图形用户接口GUI编程上特别常见。Java和C#都有自己的机制实现事件。典型的发布订阅模型是一个一对多的关系,也就是一个发布者对应多个订阅者。订阅者在发布者这里注册要调用的方法,订阅者通过内部集合保存订阅者对象。如果订阅者感兴趣的状态改变,发布者会调用一个方法遍历订阅者集合调用回调方法。
在Java中没有通用的机制来实现事件,而是采用了GUI类中使用的设计模式。事件一般是java.util.EventObject类的子类,这个类具有设置或获取事件来源的方法。在Java中订阅者一般实现接口,并且以Listener结尾,比如MouseListener, ActionListener, KeyListener,包含一个回调方法用于在事件发生的时候被发布者调用。发布者一般包含add和Listerner名字组合而成的方法用于添加注册的订阅者,比如addMouseListener, addActionListener, addKeyListener。发布者还包含用于移除订阅者的方法。这些结构构成了Java程序中的事件驱动模型。
C#使用委托来提供发布订阅模型的显式支持,事件一般是System.EventArgs类的子类。发布者具有protected的方法并以On为前缀,比如OnClick, OnClose, OnInit,在某个事件发生的时候调用这个方法,这个方法然后会调用委托并且传入EventArgs对象的实例作为参数。这个方法作为protected的话派生类就可以直接调用,无需注册委托。订阅者的方法接收和事件委托相同的返回类型和参数。事件委托一般接收两个参数,一个Object表示事件的源,一个EventArgs类表示发生的事件,并且委托是void返回值。在C#中event用于自动指定事件驱动中回调的订阅者委托。在编译的时候,编译器会增加+=和-=,等同于Java的注册和移除订阅者的方法。
如下例子演示了一个类生成20个随机数,然后在遇到偶数的时候触发事件。
C# Code using System; class EvenNumberEvent: EventArgs{ /* HACK: fields are typically private, but making this internal so it * can be accessed from other classes. In practice should use properties. */ internal int number; public EvenNumberEvent(int number):base(){ this.number = number; } } class Publisher{ public delegate void EvenNumberSeenHandler(object sender, EventArgs e); public event EvenNumberSeenHandler EvenNumHandler; protected void OnEvenNumberSeen(int num){ if(EvenNumHandler!= null) EvenNumHandler(this, new EvenNumberEvent(num)); } //generates 20 random numbers between 1 and 20 then causes and //event to occur if the current number is even. public void RunNumbers(){ Random r = new Random((int) DateTime.Now.Ticks); for(int i=0; i < 20; i++){ int current = (int) r.Next(20); Console.WriteLine("Current number is:" + current); //check if number is even and if so initiate callback call if((current % 2) == 0) OnEvenNumberSeen(current); }//for } }//Publisher public class EventTest{ //callback function that will be called when even number is seen public static void EventHandler(object sender, EventArgs e){ Console.WriteLine("\t\tEven Number Seen:" + ((EvenNumberEvent)e).number); } public static void Main(string[] args){ Publisher pub = new Publisher(); //register the callback/subscriber pub.EvenNumHandler += new Publisher.EvenNumberSeenHandler(EventHandler); pub.RunNumbers(); //unregister the callback/subscriber pub.EvenNumHandler -= new Publisher.EvenNumberSeenHandler(EventHandler); } }
Java Code import java.util.*; class EvenNumberEvent extends EventObject{ public int number; public EvenNumberEvent(Object source, int number){ super(source); this.number = number; } } interface EvenNumberSeenListener{ void evenNumberSeen(EvenNumberEvent ene); } class Publisher{ Vector subscribers = new Vector(); private void OnEvenNumberSeen(int num){ for(int i=0, size = subscribers.size(); i < size; i++) ((EvenNumberSeenListener)subscribers.get(i)).evenNumberSeen(new EvenNumberEvent(this, num)); } public void addEvenNumberEventListener(EvenNumberSeenListener ensl){ subscribers.add(ensl); } public void removeEvenNumberEventListener(EvenNumberSeenListener ensl){ subscribers.remove(ensl); } //generates 20 random numbers between 1 and 20 then causes and //event to occur if the current number is even. public void RunNumbers(){ Random r = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); for(int i=0; i < 20; i++){ int current = (int) r.nextInt() % 20; System.out.println("Current number is:" + current); //check if number is even and if so initiate callback call if((current % 2) == 0) OnEvenNumberSeen(current); }//for } }//Publisher public class EventTest implements EvenNumberSeenListener{ //callback function that will be called when even number is seen public void evenNumberSeen(EvenNumberEvent e){ System.out.println("\t\tEven Number Seen:" + ((EvenNumberEvent)e).number); } public static void main(String[] args){ EventTest et = new EventTest(); Publisher pub = new Publisher(); //register the callback/subscriber pub.addEvenNumberEventListener(et); pub.RunNumbers(); //unregister the callback/subscriber pub.removeEvenNumberEventListener(et); } }
运行结果
Current number is:19
Current number is:15
Current number is:1
Current number is:1
Current number is:-9
Current number is:-17
Current number is:-1
Current number is:-18
Even Number Seen:-18
Current number is:0
Even Number Seen:0
Current number is:1
Current number is:-2
Even Number Seen:-2
Current number is:-9
Current number is:-4
Even Number Seen:-4
Current number is:17
Current number is:-7
Current number is:1
Current number is:0
Even Number Seen:0
Current number is:15
Current number is:-10
Even Number Seen:-10
Current number is:-9
15、跨语言互操作
跨语言互操作是在一个语言中访问另一个语言构造的能力。在Java中有很多跨语言互操作的方式。首先JNI机制允许Java程序调用C或C++甚至汇编语言写的本机方法。本机方法可以使用JNI来访问Java的特性,比如调用Java语言方法,初始化和修改Java类,抛出和捕获异常,进行运行时类型检查,动态加载Java类。要创建JNI程序可以进行如下步骤:
1)创建Java程序,把包含本机方法的声明标记为native方法
2)写一个main方法加载步骤6的类库,然后使用本机方法
3)使用javac编译器编译包含native方法和main的类
4)使用javah编译器和-jni开关来生产头文件和本地方法
5) 使用你选择的语言写本机方法
6) 把头文件和本机源文件编译到共享类库中,比如Windows的dll或UNIX的.so
Java还可以通过Java IDL来和CORBA的分布式对象交互。CORBA应用程序一般由对象请求代理ORB、客户端和服务端构成。ORB负责匹配请求客户端到服务端,使用对象引用来定位目标对象。ORB检查对象引用的时候会检查目标对象是否是远程的。如果对象时本地的ORB进行进程内调用IPC,否则ORB封送参数并且把调用通过网络路由到远程ORB。远程ORB然后在本地调用方法,通过网络把结果发送回客户端。CORBA有语言无关的接口定义语言IDL,各种语言都可以支持CORBA映射。Java IDL支持从Java对象到CORBA IDL对象的映射,各种ORB提供各种语言的CORBA语言绑定,包括C, C++, Java, Python, Lisp, Perl, 和Scheme。
在Java中最无缝方式进行跨语言交互的方式是直接把Java编译成字节码。Jython脚本语言是Python编程语言整合到Java平台的一个版本。如下例子演示了Jython如何创建一个Java的随机数类型(java.util.Random)并且和这个类型的实例进行交互。
C:\jython>jython Jython 2.0 on java1.2.1 Type "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> from java.util import Random >>> r = Random() >>> r.nextInt() -790940041 >>> for i in range(5): ... print r.nextDouble() ... 0.23347681506123852 0.8526595592189546 0.3647833839988137 0.3384865260567278 0.5514469740469587 >>>
C#和.NET运行时本来的一个设计目标就是无缝的跨语言交互。任何.NET公共语言运行时的语言都可以基于公共类型系统CTS互相交互。公共类型系统定义了类型如何声明,确保各种语言可以共享类型信息。元数据是描述程序集、类型和应用程序定义的特性的二进制信息,它保存在CLR PE中,或者在程序集加载后保存在内存中。当前.NET运行时支持的语言包括APL, C#, C++, COBOL, Component Pascal, Eiffel, Haskel#/Mondrian, Java, Mercury, Oberon, Perl, Python, Scheme, Smalltalk, ML, 和Visual Basic。由于一种语言中具有的特性很可能在另外一种语言中没有,.NET框架提供了CLS描述一组基本的语言特性和定义如何使用这些特性的规则。CLS规则是公共类型系统的子集,并且通过定义一组编程语言最常见的特性集合来确保跨语言互操作。C#编译器是CLS兼容的编译器,也就是说可以用于编译符合CLS的代码。C#编译器可以检查CLS规范并且在代码使用了不符合CLS功能的时候给出错误。要让C#编译器检查CLS规范可以使用[CLSCompliantAttribute(true)]特性。C#支持的另一种跨语言交互是基于COM的对象,这个机制允许开发者在C#中使用COM,反之亦然。在创建了包装类后,C#对象可以使用COM对象,包装类可以当做普通的C#对象来使用,.NET运行时会处理复杂的参数封送操作。可以使用tlbimp工具来自动创建包装类。对于COM对象使用C#对象,必须创建描述C#对象的类型库,可以使用tlbexp创建类型库以COM的形式来描述C#对象。还可以使用regasm工具来注册程序集。COM对象和C#对象交互的时候,运行时会负责COM和.NET之间数据的封送。C#程序还可以使用extern关键字和DllImport特性来使用任何DLL的功能,这么做的优势是不需要针对C#的调用为方法作特殊处理,并且也不需要有包装来调用既有的代码。
第四部分:C#有但Java没有的地方
1、对象清理
为了提供完全控制类使用的资源,C#提供了System.IDisposable接口,它包含Dispose()方法可以让类的使用者在使用类之后释放必要的资源。管理诸如数据库或文件句柄的类可以从这种模式中收益。Dispose提供了一种确定的方式在类不使用的时候释放资源,这和Java或C#的终结器不同。一般会在Dispose方法的实现中调用GC类的SupressFinalize 方法,因为我们一般通过Dispose方法显式释放资源而不需要运行时的终结器。C#还提供了诸如using关键字之类的语法糖通过Dispose方法释放资源。如果类是Disposable的话,最好让Dispose()方法是幂等的(也就是可以多次调用Dispose()),可以在Dispose()方法中设置一个标志位来检查是否已经Dispose。如下例子演示了类保持打开文件,直到Dispose()方法调用后来表示文件不需要打开了。
C# Code using System; using System.IO; public class MyClass : IDisposable { bool disposed = false; FileStream f; StreamWriter sw; private String name; private int numShowNameCalls = 0; MyClass(string name){ f = new FileStream("logfile.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate); sw = new StreamWriter(f); this.name = name; Console.WriteLine("Created " + name); } ~MyClass(){ Dispose(false); } public void Dispose(){ if(!disposed){ Dispose(true); } } private void Dispose(bool disposing){ lock(this){ /* prevents multiple threads from disposing simultaneously */ /* disposing variable is used to indicate if this method was called from a * Dispose() call or during finalization. Since finalization order is not * deterministic, the StreamWriter may be finalized before this object in * which case, calling Close() on it would be inappropriate so we try to * avoid that. */ if(disposing){ Console.WriteLine("Finalizing " + name); sw.Close(); /* close file since object is done with */ GC.SuppressFinalize(this); disposed = true; } } } public string ShowName(){ if(disposed) throw new ObjectDisposedException("MyClass"); numShowNameCalls++; sw.Write("ShowName() Call #" + numShowNameCalls.ToString() + "\n"); return "I am " + name; } public static void Main(string[] args){ using (MyClass mc = new MyClass("A MyClass Object")){ for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ Console.WriteLine(mc.ShowName()); } //for }/* runtime calls Dispose on MyClass object once "using" code block is exited, even if exception thrown */ }//Main }
如上的模式和C++方式的析构器很像,只不过不需要考虑内存分配。终结器这种不精确的特性一致被Java开发者诟病,有了Dispose后这不再是问题了。
注意:调用Dispose()方法不等同于要求对象被垃圾回收,只不过由于不需要终结器之后可以加速被回收。
2、委托
委托是提供回调函数的机制,委托和C或C++的函数指针相似。委托的一个用途就是根据算法使用的类型传入操作到泛型算法。另一个用途就是为事件注册处理程序。在Java中要使用C#委托中相同的功能,可以创建接口然后指定回调方法,比如Comparable接口,的缺点是方法只能是实例方法,其实一般是当做静态方法来使用的。
要使用委托,首先声明和要调用的回调方法返回值和相同参数的委托。然后定义接收以委托作为参数的方法。完成后,使用符合委托的方法来初始化委托的实例,然后把委托传入接收委托作为参数的方法。委托可以接受静态方法和实例方法,甚至同一时刻接收两种,因为委托是多播的。如下演示了创建和使用实例委托的例子。
C# Code using System; /* Mammal class hierarchy used to show return type covariance */ public class Mammal { public Mammal(){;} public virtual void Speak(){;} } public class Cat : Mammal{ public Cat(){;} public override void Speak(){ Console.WriteLine("Meow"); } } public class Dog : Mammal{ public Dog(){;} public override void Speak(){ Console.WriteLine("Woof"); } } public class Test { // delegate declaration, similar to a function pointer declaration public delegate Mammal CallbackFunction(Dog d); public static Cat BarkAndScareCat(Dog d) { d.Speak(); Cat c = new Cat(); c.Speak(); return c; } public static Mammal BarkAndReturnHome(Dog d) { d.Speak(); return d; } public static void Main(string[] args){ Dog dog = new Dog(); //create delegate using delegate object (old way) CallbackFunction myCallback = new CallbackFunction(BarkAndReturnHome); myCallback(dog); //create delegate using delegate inference (new way) CallbackFunction myCallback2 = BarkAndScareCat; myCallback2(dog); } }
委托可以作为参数传入方法,和C或C++的函数指针有点相似:
C# Code using System; //delegate base public class HasDelegates { // delegate declaration, similar to a function pointer declaration public delegate bool CallbackFunction(string a, int b); //method that uses the delegate public bool execCallback(CallbackFunction doCallback, string x, int y) { Console.WriteLine("Executing Callback function..."); return doCallback(x, y); } } public class FunctionDelegates { public static readonly HasDelegates.CallbackFunction BarFuncCallback = new HasDelegates.CallbackFunction(FunctionBar); public static bool FunctionBar(string a, int b) { Console.WriteLine("Bar: {0} {1}", b, a); return true; } } public class DelegateTest { public static void Main(string[] args){ HasDelegates MyDel = new HasDelegates(); // with static delegate, no need to know how to create delegate MyDel.execCallback(FunctionDelegates.BarFuncCallback, "Thirty Three", 33); } } // DelegateTest
3、值类型(结构)
在Java和C#中,堆上的东西只能等垃圾回收来收集而在栈上的对象会自动被系统回收。一般在栈上分配的内存会比在堆上略快。
在Java中,所有的类都在堆上创建而基元类型在栈上创建。如果对象很小并且很常用的话只能在堆上分配的话会造成一定的性能负担,C#提供了一种机制可以让某种类是基于栈分配的,叫做结构,其实C#内建的诸如int的基元类型就是使用结构来分配的。和类不同,值类型一般按值传递并且不会被垃圾收集。要使用基于栈的类,可以使用struct来替代class关键字。要创建C#结构可以使用和类一样的new关键字。如果结构使用默认构造方法语法创建,那么结构的字段都会使用0初始化。但是,不可以为结构定义默认构造方法。
C# Code using System; struct Point { public int x; public int y; public Point( int x, int y){ this.x = x; this.y = y; } public override string ToString(){ return String.Format("({0}, {1})", x, y); } public static void Main(string[] args){ Point start = new Point(5, 9); Console.WriteLine("Start: " + start); /* The line below wouldn't compile if Point was a class */ Point end = new Point(); Console.WriteLine("End: " + end); } } // Point
4、运行时类型标识(as运算符)
C#的as运算符和C++的dynamic_cast结构一样。as运算符的作用是尝试把类型转换为某种类型,如果不成功的话返回null。
C# Code MyClass mc = o as MyClass; if(mc != null) //check if cast successful mc.doStuff();注意:as不能用于值类型。
5、属性
属性可以避免直接访问类的成员和Java的getters以及setters很像。可以使用属性来访问类的字段或成员属性,但又避免使用方法。可以创建只读、只写或读写属性,此外还可以创建属性让getter和setter具有不同的访问性(比如public的getter和private的setter),如下是使用属性的例子:
C# Code using System; public class User { public User(string name){ this.name = name; } private string name; //property with public getter and private setter public string Name{ get{ return name; } private set { name = value; } } private static int minimum_age = 13; //read-write property for class member, minimum_age public static int MinimumAge{ get{ return minimum_age; } set{ if(value > 0 && value < 100) minimum_age = value; else Console.WriteLine("{0} is an invalid age, so minimum age remains at {1}", value, minimum_age); } } public static void Main(string[] args){ User newuser = new User("Bob Hope"); User.MinimumAge = -5; /* prints error to screen since value invalid */ User.MinimumAge = 18; //newuser.Name = "Kevin Nash"; Causes compiler error since Name property is read-only Console.WriteLine("Minimum Age: " + User.MinimumAge); Console.WriteLine("Name: {0}", newuser.Name); } } // User
6、多维度数组
如下代码演示了多维数组和交错数组的区别
C# Code using System; public class ArrayTest { public static void Main(string[] args){ int[,] multi = { {0, 1}, {2, 3}, {4, 5}, {6, 7} }; for(int i=0, size = multi.GetLength(0); i < size; i++){ for(int j=0, size2 = multi.GetLength(1); j < size2; j++){ Console.WriteLine("multi[" + i + "," + j + "] = " + multi[i,j]); } } int[][] jagged = new int[4][]; jagged[0] = new int[2]{0, 1}; jagged[1] = new int[2]{2, 3}; jagged[2] = new int[2]{4, 5}; jagged[3] = new int[2]{6, 7}; for(int i=0, size = jagged.Length; i < size; i++){ for(int j=0, size2 = jagged[1].Length; j < size2; j++){ Console.WriteLine("jagged[" + i + "][" + j + "] = " + jagged[i][j]); } } } } // ArrayTest
7、索引器
索引器是重写类[]运算符的语法。如果类包含另外一种对象的话,索引器就很有用。索引器的灵活之处在于支持任何类型,比如整数或字符串、还可以创建索引器允许多维数组语法,可以在索引器中混合和匹配不同的类型,最后,索引器可以重载。
C# Code using System; using System.Collections; public class IndexerTest: IEnumerable, IEnumerator { private Hashtable list; public IndexerTest (){ index = -1; list = new Hashtable(); } //indexer that indexes by number public object this[int column]{ get{ return list[column]; } set{ list[column] = value; } } /* indexer that indexes by name */ public object this[string name]{ get{ return this[ConvertToInt(name)]; } set{ this[ConvertToInt(name)] = value; } } /* Convert strings to integer equivalents */ private int ConvertToInt(string value){ string loVal = value.ToLower(); switch(loVal){ case "zero": return 0; case "one": return 1; case "two": return 2; case "three": return 3; case "four": return 4; case "five": return 5; default: return 0; } return 0; } /** * Needed to implement IEnumerable interface. */ public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){ return (IEnumerator) this; } /** * Needed for IEnumerator. */ private int index; /** * Needed for IEnumerator. */ public bool MoveNext(){ index++; if(index >= list.Count) return false; else return true; } /** * Needed for IEnumerator. */ public void Reset(){ index = -1; } /** * Needed for IEnumerator. */ public object Current{ get{ return list[index]; } } public static void Main(string[] args){ IndexerTest it = new IndexerTest(); it[0] = "A"; it[1] = "B"; it[2] = "C"; it[3] = "D"; it[4] = "E"; Console.WriteLine("Integer Indexing: it[0] = " + it[0]); Console.WriteLine("String Indexing: it[\"Three\"] = " + it["Three"]); Console.WriteLine("Printing entire contents of object via enumerating through indexer :"); foreach( string str in it){ Console.WriteLine(str); } } } // IndexerTest
8、预处理指令
C#包含预处理器,相当于C/C++预处理器的有限子集。C#预处理器没有#include文件的能力也没有使用#define进行文本替换的能力。主要的能力在于使用#define和#undef标识符以及通过#if和#elif以及#else选择编译某段代码的能力。#error和#warning指示器可以在编译的时候让指示器之后的错误或警告消息显示出来。#pragma指示器用于处理屏蔽编译器警告消息。最后,#line指示器可以用于编译器发现错误的时候指定源文件行号。
C# Code #define DEBUG /* #define must be first token in file */ using System; #pragma warning disable 169 /* Disable 'field never used' warning */ class PreprocessorTest{ int unused_field; public static void Main(string[] args){ #if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("DEBUG Mode := On"); #else Console.WriteLine("DEBUG Mode := Off"); #endif } }
9、别名
using关键字可以用于为完全限定名设置别名,和C/C++的typedef相似。如果类的完全限定名需要解决命名空间冲突的话,这就很有用了。
C# Code using Terminal = System.Console; class Test{ public static void Main(string[] args){ Terminal.WriteLine("Terminal.WriteLine is equivalent to System.Console.Writeline"); } }
10、运行时代码生成
Reflection.Emit命名空间包含了一些类可以用于生成.NET中间语言,以及在运行时在内存中构建类甚至把PE文件写到磁盘上。这类似Java的那些通过生成Java字节码写入磁盘,用于在运行时创建Java类然后被程序使用的类库。Reflection.Enmit命名空间主要的用户是编译器或脚本引擎的作者。比如,System.Text.RegularExpressions使用Reflection.Emit类库来为每一个编译后的表达式生成自定义匹配引擎。
11、指针和不安全的代码
尽管C#和Java一样,不能使用指针类型,但是如果C#代码在unsafe上下文中执行的话就可以使用指针类型。如果C#代码在unsafe上下文中执行,那么就会禁止许多运行时检查,程序也必须在所运行的机器上有完全信任权限。写unsafe代码的语法和语义和在C和C++中使用指针的语法和语义相似。写unsafe代码时,必须使用unsafe关键字把代码块指定为unsafe的,并且程序必须使用/unsafe编译器开关编译。由于垃圾回收期可能会在程序执行的过程中重新分配托管变量,所以在fixed代码块中使用托管变量的时候需要使用fixed关键字来固定变量地址。如果没有fixed关键字的话,标记和压缩垃圾回收期可能会在回收的过程中移动变量的地址。
C# Code using System; class UnsafeTest{ public static unsafe void Swap(int* a, int*b){ int temp = *a; *a = *b; *b = temp; } public static unsafe void Sort(int* array, int size){ for(int i= 0; i < size - 1; i++) for(int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) if(array[i] > array[j]) Swap(&array[i], &array[j]); } public static unsafe void Main(string[] args){ int[] array = {9, 1, 3, 6, 11, 99, 37, 17, 0, 12}; Console.WriteLine("Unsorted Array:"); foreach(int x in array) Console.Write(x + " "); fixed( int* iptr = array ){ // must use fixed to get address of array Sort(iptr, array.Length); }//fixed Console.WriteLine("\nSorted Array:"); foreach(int x in array) Console.Write(x + " "); } }
12、按引用传递
在Java中,传给方法的参数是按值传递的,方法操作的是复制的数据而不是原来的数据。在C#中,可以指定参数按照引用传递而不是数据拷贝。有的时候如果希望方法返回超过一个对象的时候就有用。指定参数按引用传递的关键字是ref和out。区别是使用ref的话传入参数必须初始化,而out则不需要。
Java Code class PassByRefTest{ public static void changeMe(String s){ s = "Changed"; } public static void swap(int x, int y){ int z = x; x = y; y = z; } public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 5, b = 10; String s = "Unchanged"; swap(a, b); changeMe(s); System.out.println("a := " + a + ", b := " + b + ", s = " + s); } } OUTPUT a := 5, b := 10, s = Unchanged C# Code using System; class PassByRefTest{ public static void ChangeMe(out string s){ s = "Changed"; } public static void Swap(ref int x, ref int y){ int z = x; x = y; y = z; } public static void Main(string[] args){ int a = 5, b = 10; string s; Swap(ref a, ref b); ChangeMe(out s); Console.WriteLine("a := " + a + ", b := " + b + ", s = " + s); } } OUTPUT a := 10, b := 5, s = Changed
13、逐字字符串
C#提供了一种方式来避免在字符串常量中使用转移序列。唯一的例外是双引号需要使用两个双引号,可以在字符串声明的时候使用@来声明逐字字符串。
C# Code using System; class VerbatimTest{ public static void Main(){ //verbatim string string filename = @"C:\My Documents\My Files\File.html"; Console.WriteLine("Filename 1: " + filename); //regular string string filename2 = "C:\\My Documents\\My Files\\File.html"; Console.WriteLine("Filename 2: " + filename2); string snl_celebrity_jeopardy_skit = @" Darrell Hammond (Sean Connery) : I'll take ""Swords"" for $400 Will Farrell (Alex Trebek) : That's S-Words, Mr Connery. "; Console.WriteLine(snl_celebrity_jeopardy_skit); } }
14、溢出检查
C#提供了显式检测或忽略溢出条件的选项。溢出条件检测到之后会抛出System.OverflowException。由于溢出检查会带来性能损失,所以需要通过/checked+编译选项显式启用。可以通过在代码块声明checked来表示代码总是进行溢出检查,或是使用unchecked表示总是取消溢出检查。
C# Code using System; class CheckedTest{ public static void Main(){ int num = 5000; /* OVERFLOW I */ byte a = (byte) num; /* overflow detected only if /checked compiler option on */ /* OVERFLOW II */ checked{ byte b = (byte) num; /* overflow ALWAYS detected */ } /* OVERFLOW III */ unchecked{ byte c = (byte) num; /* overflow NEVER detected */ } }//Main }
15、显式接口实现
有的时候在实现接口的时候可能会遇到冲突,比如FileRepresentation类可能会实现IWindow和IFileHandler接口,他妈两个接口都有Close方法,IWindow的Close方法表示关闭GUI窗口,而IFileHandler 的Close方法表示关闭文件。在Java中除了只写一个Close方法之外别无他法,而在C#中可以为每一个接口写一个实现。比如对于之前提到的例子,FileRepresentation类可以有两个不同的Close方法。注意,显式接口方法是private的,并且只有转换成相应类型之后才能进行方法调用。
C# Code using System; interface IVehicle{ //identify vehicle by model, make, year void IdentifySelf(); } interface IRobot{ //identify robot by name void IdentifySelf(); } class TransformingRobot : IRobot, IVehicle{ string model; string make; short year; string name; TransformingRobot(String name, String model, String make, short year){ this.name = name; this.model = model; this.make = make; this.year = year; } void IRobot.IdentifySelf(){ Console.WriteLine("My name is " + this.name); } void IVehicle.IdentifySelf(){ Console.WriteLine("Model:" + this.model + " Make:" + this.make + " Year:" + this.year); } public static void Main(){ TransformingRobot tr = new TransformingRobot("SedanBot", "Toyota", "Corolla", 2001); // tr.IdentifySelf(); ERROR IVehicle v = (IVehicle) tr; IRobot r = (IRobot) tr; v.IdentifySelf(); r.IdentifySelf(); } } OUTPUT Model:Toyota Make:Corolla Year:2001 My name is SedanBot
16、友元程序集
友元程序集特性允许内部类型或内部方法被其它程序集访问。可以使用[InternalsVisibleToAttribute]特性来实现友元程序集。如下代码演示了2个源文件编译成2个程序集来使用友元程序集特性。
C# Code // friend_assembly_test.cs // compile with: /target:library using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; using System; [assembly:InternalsVisibleTo("friend_assembly_test_2")] // internal by default class Friend { public void Hello() { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); } } // public type with internal member public class Friend2 { internal string secret = "I like jelly doughnuts"; } C# Code 2 // friend_assembliy_test_2.cs // compile with: /reference:friend_assembly_test.dll /out:friend_assembly_test_2.exe using System; public class FriendFinder { static void Main() { // access an internal type Friend f = new Friend(); f.Hello(); Friend2 f2 = new Friend2(); // access an internal member of a public type Console.WriteLine(f2.secret); } }
17、命名空间限定符
项目越大越有可能发生命名空间冲突。C#有::运算符来指定命名空间的作用域。运算符左边的操作数表示的是解决冲突的作用域,右边的操作数表示的是要解决冲突的名字。左操作数可以是关键字global指代全局作用域或是命名空间的别名。
C# Code using System; using sys = System; namespace TestLib{ class Test{ public class System {} static DateTime Console = DateTime.Now; public static void Main(){ //Console.WriteLine("Hello world"); doesn't work due to static member variable named 'Console' //System.Console.WriteLine("Hello world"); doesn't work due to nested class named 'System' global::System.Console.WriteLine("The time is " + Console); sys::Console.WriteLine("Hello again"); } }
18、迭代器
对于支持foreach循环的数据结构,必须实现或返回System.Collections.IEnumerable的实例。枚举器写起来还是有点麻烦的,yield关键字可以把任何方法或属性转换为枚举器。可以使用yield return语句来一个一个返回内容,可以使用yield break来表示结束了序列。方法或属性必须返回IEnumerable, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerator 或IEnumerator<T>中的一个。
C# Code using System; using System.Collections; class Test{ public static string[] fruit = {"banana", "apple", "orange", "pear", "grape"}; public static string[] vegetables = {"lettuce", "cucumber", "peas", "carrots"}; public static IEnumerable FruitAndVeg{ get{ foreach(string f in fruit){ yield return f; } foreach(string v in vegetables){ yield return v; } yield break; //optional } } public static void Main(){ foreach (string produce in Test.FruitAndVeg){ Console.WriteLine(produce); } } }
19、部分类
部分类特性使得我们可以在多个源文件中定义单个类、接口或接口。对于自动生成的代码特别有用。在这个特性出现之前,我们可能会修改自动生成的代码,因为手写代码和自动生成的代码位于一个文件中。而有了这个特性,就减少了出现这种情况的可能。可以通过在类声明中使用partial关键字来启动部分类,如下代码演示了定义在两个源文件中的部分类。注意,一个源文件中的方法和属性可以引用另一个源文件中定义的方法和属性。
C# Code using System; partial class Test{ public static string[] fruit = {"banana", "apple", "orange", "pear", "grape"}; public static string[] vegetables = {"lettuce", "cucumber", "peas", "carrots"}; public static void Main(){ foreach (string produce in Test.FruitAndVeg){ Console.WriteLine(produce); } } } C# Code 2 using System; using System.Collections; partial class Test{ public static IEnumerable FruitAndVeg{ get{ foreach(string f in fruit){ yield return f; } foreach(string v in vegetables){ yield return v; } } }
需要注意的是类上的特性会进行合并,因此矛盾的特性是不允许的,比如一个文件中类声明的是private另一个文件声明的是public的。
20、可空类型
可空类型System.Nullable类型的实例。可空类型可以表示底层值类型的值也可以表示空值。例如,Nullable<bool>可以表示值true、false和null。可空类型的变量可以使用值的类型加上?运算符来声明。bool?等价于Nullable<bool>。每一个可空类型都有HasValue属性来表示是否具有有效的值或是null。可空类型真实的值保存在其Value属性中。GetValueOrDefault()方法可以返回可空类型的值或如果是null的话返回底层值类型的默认值。
可空类型在用于把C#对象映射到关系型数据库的时候很有用,因为在SQL数据库中可以存在null的有效值。
C# Code using System; public class Test{ public static void Main(string[] args){ int? x = 5; if(x.HasValue){ Console.WriteLine("The value of x is " + x.Value); } x = null; //prints 0 Console.WriteLine(x.GetValueOrDefault()); } }
??运算符叫做空结合运算符,用于测试可空类型的值,并且在值是空的情况下返回另外一个值。因为x??y等价于x==(nulll ? y : x)。
C# Code using System; public class Test{ public static void Main(string[] args){ int? x = null; int y = x ?? 5; //prints 5 Console.WriteLine(y); } }
21、匿名方法
匿名方法是和委托相关的一个特性。匿名方法是用于以匿名形式声明委托的方法,而不需要一个独立的方法。如下代码比较了使用匿名方法和具名方法的委托:
C# Code using System; public class Test { // delegate declaration, similar to a function pointer declaration public delegate void CallbackFunction(string a, int b); public static void PrintString(string a, int b){ for(int i = 0; i < b ; i++) Console.WriteLine("{0}.) {1}", i + 1, a); } public static void Main(string[] args){ /* anonymous code block */ CallbackFunction cf = delegate (string a, int b){ for(int i = 0; i < b ; i++) Console.WriteLine("{0}.) {1}", i + 1, a); }; cf("Thirty Three", 10); /* using a named delegate function */ CallbackFunction cf2 = new CallbackFunction(Test.PrintString); cf2("Twenty Two", 5); } }
在使用的时候要记住匿名方法有一些限制,比如诸如break、goto和contiune之类的跳转语句不能用于从匿名方法跳转到外部。匿名方法也不能引用定义在外部方法的ref或out参数。
(其实还有很多,感叹C#的伟大)
第五部分:Java有但C#没有的地方
1、受检查的异常
在异常这个概念出现之前,大多数异常处理都是通过返回代码进行。异常对于返回值来说有很多优势:
1)提供了一致的模型来处理错误和其它非预期的情况
2)如果没有在当前上下文中处理异常的话可以向上传播
3)开发者可以把处理错误的代码和普通业务逻辑分离
Java创建了额外的机制来处理受检查的异常和不受检查的异常。对于受检查的异常,调用的方法必须捕获异常,或通过throws声明异常必须被其调用方法处理。从另外一方面来说,不受检查的异常不需要catch也或用throws子句声明,不受检查的异常和返回代码一样不会让编译器出警告或错误,但是如果在运行时忽略异常的话同样会终止程序。受检查的异常一般用于告诉调用者如何和为什么会发生调用失败。不受检查的异常是一般程序中大部分地方都会发生的异常,如果都要进行显式检查的话开销比价值大。比如空对象引用的异常或是数组越界的异常,如果是收检查的异常话,就需要在每一个访问对象或访问数组的时候都进行try catch,因此比较适合不受检查的异常。
在C#中所有异常都是未收检查的异常,也没有throws子句。这么做的主要劣势是API只能通过文档来告诉调用者自己会抛出哪些异常。比如对于如下的代码,唯一知道下面方法会出现哪些异常的方法是查看所有调用方法的源代码或这些方法的源代码。
public string GetMessageFromServer(string server) { //Set up variables and String to write to the server Encoding ASCII = Encoding.ASCII; string Get = "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: " + server + "\r\nConnection: Close\r\n\r\n"; Byte[] ByteGet = ASCII.GetBytes(Get); Byte[] RecvBytes = new Byte[256]; String strRetPage = null; // IPAddress and IPEndPoint represent the endpoint that will // receive the request // Get first IPAddress in list return by DNS IPAddress hostadd = Dns.Resolve(server).AddressList[0]; IPEndPoint EPhost = new IPEndPoint(hostadd, 80); //Create the Socket for sending data over TCP Socket s = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp ); // Connect to host using IPEndPoint s.Connect(EPhost); if (!s.Connected) { strRetPage = "Unable to connect to host"; return strRetPage; } // Sent the GET text to the host s.Send(ByteGet, ByteGet.Length, 0); // Receive the page, loop until all bytes are received Int32 bytes = s.Receive(RecvBytes, RecvBytes.Length, 0); strRetPage = "Default HTML page on " + server + ":\r\n"; strRetPage = strRetPage + ASCII.GetString(RecvBytes, 0, bytes); while (bytes > 0) { bytes = s.Receive(RecvBytes, RecvBytes.Length, 0); strRetPage = strRetPage + ASCII.GetString(RecvBytes, 0, bytes); } return strRetPage; }
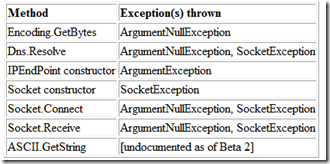
上面的代码取自.NET框架Beta2文档的Socket类。注意到,在这段代码中没有捕获异常。如下是根据文档得出的这个方法可能抛出的异常:
(后面关于有无这个特性好坏的争论就不翻译了)
2、跨平台移植
Java技术一个很大的卖点就是Java写的应用程序一次编写到处运行。Sun官方支持Linux、Solaris 和 Windows,其它一些公司也实现了OS/2, AIX 和MacOS平台的Java。.NET也通过Mono项目和Ximian提供了移植性的支持。
3、扩展
Java扩展机制允许开发者扩展核心Java平台。开发者可以创建让Java运行时当做认为是核心Java类的类和包,比如java.lang, java.util, java.net等。
4、strictfp
在Java中strictfp是可以用于类、方法或借口声明的修饰符,用于确保符合IEEE 754的精确浮点数算术。当对一个类或接口使用 strictfp 关键字时,该类中的所有代码,包括嵌套类型中的初始设定值和代码,都将严格地进行计算。严格约束意味着所有表达式的结果都必须是 IEEE 754 算法对操作数预期的结果,以单精度和双精度格式表示。
Java Code public class FPTest { static strictfp double halfOfSquareFP(double n){ return n * 4.0 * 0.5; } static double halfOfSquareNFP(double n){ return n * 4.0 * 0.5; } public static void main(String[] args) { double d = 6.6e+307; System.out.println(halfOfSquareFP(d)); System.out.println(halfOfSquareNFP(d)); } }//FPTest
5、动态类加载
Java中在运行时动态加载类的能力非常强大,动态类加载使得Java应用程序可以下载目标机器上没有的class文件。在一个机器上的对象类型可以无缝传输到其它机器。新的类型可以引入远程机器,可以在运行时扩展远程应用程序的行为。如下例子演示了远程应用程序接收类型实现某个接口:
Java Code public class MyRMIServer extends UnicastRemoteObject implements SomeInterface { public MyRMIServer() throws RemoteException{ super();} public String obtainName(IStockTicker ticker){ String stock_ticker = ticker.getTicker(); if(stock_ticker.equalsIgnoreCase("MSFT")) return "Microsoft Corporation"; else if(stock_ticker.equalsIgnoreCase("SUNW")) return "Sun Microsystems"; else return "Unknown Stock Ticker"; }/* obtainName(IStockTicker) */ }
obtainName() 远程方法接收实现IStockTicker接口的类型,远程客户端可以调用这个方法然后传入实现IStockTicker的类型,例如NASDAQStock,如果MyRMIServer 所谓远程机器没有类的话,整个NASDAQStock 需要的类都会自动传输到远程机器。
6、包含字段的接口
在Java中,接口中可以声明常量,在实现的类中可以使用这个常量,这在C#中是没有的。这其实无关紧要,因为原先要这么这么用的主要原因是模拟枚举。
7、匿名内部类
匿名内部类是类的声明位于类创建实例内的类。匿名内部类一般用于在应用程序中只会有一个类的实例,最常用的就是在GUI类库中指定回调。如下是使用匿名内部类来实现状态设计模式的例子:
Java Code /* An instance of this class represents the current state of a ClientView GUI. */ public abstract class ClientState{ // This instance of the class is used to signify that the user is not logged in. // The only thing a user can do in this state is login and exit. public static ClientState NOT_LOGGED_IN = new ClientState() { public void setMenuState(ClientView cv) { cv.setMenuEnabledState(false); /* disable all menus */ cv.menuLogin.setEnabled(true); cv.menuExit.setEnabled(true); //can't type cv.textArea.setEnabled(false); } public String toString(){ return "ClientState: NOT_LOGGED_IN"; } }; // This instance of the class is used to signify that the user is logged in // but has not yet created a document to work with. The user cannot type or save // anything in this mode. public static ClientState NO_OPEN_DOCUMENT = new ClientState() { public void setMenuState(ClientView cv) { cv.setMenuEnabledState(false); /* disable all menus */ cv.menuLogin.setEnabled(true); cv.menuExit.setEnabled(true); cv.menuOpenFile.setEnabled(true); cv.menuNewFile.setEnabled(true); //can't type cv.textArea.setEnabled(false); } public String toString(){ return "ClientState: NO_OPEN_DOCUMENT"; } }; // This instance of the class is used to signify that the user is editting a file. // In this mode the user can use any functionality he/she sees fit. public static ClientState EDITTING_DOCUMENT = new ClientState() { public void setMenuState(ClientView cv) { cv.setMenuEnabledState(true); /* enable all menus cv.textArea.setEnabled(true); } public String toString(){ return "ClientState:EDITTING_DOCUMENT"; } }; // Default constructor private to stop people from directly creating instances // of the class. private ClientState() {;} // This disables various elements of the ClientView's menu dependent on which // ClientState object this is. public abstract void setMenuState(ClientView cv); } // ClientState
如下是使用ClientState类的例子
bool loginUser(String username, String passwd) { //check if already logged in if(myGUI.state == ClientState.NOT_LOGGED_IN) return true; //enable parts of the GUI if the user authenticates if(userAuthenticated(username, passwd)){ myGUI.state = ClientState.NO_OPEN_DOCUMENT; myGUI.state.setMenuState(myView); return true; } return false; }/* loginUser(String, String) */
8、静态导入
静态导入特性使我们可以访问类静态成员的时候不需要指定类名,这个特性可以让我们减少代码的冗余,特别对于某些帮助类型来说很方便。静态导入和普通的import语句很像,只不过多了static关键字,导入的是类而不是包名。
Java Code import static java.awt.Color.*; public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //constants not qualified thanks to static import System.out.println(RED + " plus " + YELLOW + " is " + ORANGE); } }
输出:
java.awt.Color[r=255,g=0,b=0] plus java.awt.Color[r=255,g=255,b=0] is java.awt.Color[r=255,g=200,b=0]
参考
- Eckel, Bruce. Thinking In Java. Prentice Hall, 2000.
- Gunnerson, Eric. A Programmer's Introduction To C#. Apress, 2001.
- Sun Microsystems. The Java™ Tutorial.<http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/>
- Microsoft Corporation. .NET Framework Programming. < http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms229284(VS.80).aspx>
- Microsoft Corporation. C# Language Reference. < http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/618ayhy6(VS.80).aspx>