Scrapy 框架介绍
-
Scrapy是用纯Python实现一个为了爬取网站数据、提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架。
-
Srapy框架,用户只需要定制开发几个模块就可以轻松的实现一个爬虫,用来抓取网页内容以及各种图片,非常方便。
-
Scrapy 使用了Twisted异步网络框架来处理网络通讯,可加快下载速度,不用自己去实现异步框架,并且包含各种中间件接口,可灵活完成各种需求。
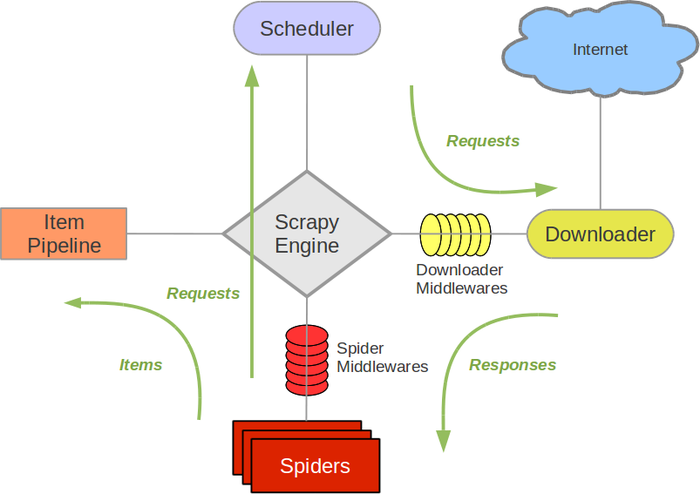
1.Scrapy架构图(绿线是数据流向)
-
Scrapy Engine(引擎): 负责Spider(爬虫)、ItemPipeline、Downloader、Scheduler(调度器)中间的通讯,信号、数据传递等。 -
Scheduler(调度器): 负责接受引擎发来的Request请求,并按一定的方式进行整理排列,入队,当引擎需要时,交还给引擎。 Downloader(下载器):负责下载Scrapy Engine(引擎)发送的所有Requests请求,并将Scrapy Engine(引擎)获取到的Responses交还给Scrapy Engine(引擎),由Scrapy Engine(引擎)交给Spider(爬虫)来处理,-
Spider(爬虫):负责处理所有Responses,从中分析提取数据,获取Item字段需要的数据,并将需要跟进的URL提交给引擎,再次进入Scheduler(调度器), -
Item Pipeline(管道):它负责处理Spider(爬虫)中获取到的Item,并进行进行后期处理(详细分析、过滤、存储等)的地方. -
Downloader Middlewares(下载中间件):一个可以自定义扩展下载功能的组件。 -
Spider Middlewares(Spider中间件):一个可以自定扩展和操作引擎和Spider中间通信的功能组件(如进入Spider的Responses;和从Spider出去的Requests)
2.Scrapy运作流程:
- Scrapy Engine(引擎)从Scheduler(调度器)中取出一个链接(URL)用于接下来的抓取
- Scrapy Engine(引擎)把URL封装成一个请求(Request)传给Downloader(下载器)
- Downloader(下载器)把资源下载下来,并封装成应答包(Response)
- 爬虫解析Response
- 解析出实体(Item),则交给实体管道进行进一步的处理
- 解析出的是链接(URL),则把URL交给Scheduler(调度器)等待抓取
3.Scrapy 爬虫制作步骤:
- 新建项目 (scrapy startproject xxx):新建一个新的爬虫项目
- 明确目标 (编写items.py):明确你想要抓取的目标
- 制作爬虫 (spiders/xxspider.py):制作爬虫开始爬取网页
- 存储内容 (pipelines.py):设计管道存储爬取内容
Scrapy 配置安装
Scrapy框架官方网址:http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest
Scrapy中文维护站点:http://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/index.html
1.Windows 安装方式
- Python 2 / 3
- 升级pip版本:
pip install --upgrade pip - 通过pip 安装 Scrapy 框架
pip install Scrapy
2.Ubuntu 需要9.10或以上版本安装方式
- Python 2 / 3
- 安装非Python的依赖
sudo apt-get install python-dev python-pip libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev zlib1g-dev libffi-dev libssl-dev - 通过pip 安装 Scrapy 框架
sudo pip install scrapy
具体Scrapy安装流程参考:http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/intro/install.html#intro-install-platform-notes
Scrapy爬虫入门
抓取地址:http://www.itcast.cn/channel/teacher.shtml
抓取目标:抓取网站里的所有讲师的姓名、职称和个人信息
抓取步骤:
- 打开mySpider目录下的items.py
- Item 定义结构化数据字段,用来保存爬取到的数据
- 创建一个 scrapy.Item 类, 并且定义类型为 scrapy.Field的类属性来定义一个Item
- 创建一个ItcastItem 类,和构建item模型(model)
import scrapy
class ItcastItem(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field()
level = scrapy.Field()
info = scrapy.Field()
制作爬虫 (spiders/itcastSpider.py)
1.爬取数据
import scrapy
# 创建一个爬虫类
class ItcastSpider(scrapy.Spider):
# 爬虫名
name = "itcast"
# 允许爬虫作用的范围
allowed_domains = ["itcast.cn"]
# 爬虫真实的url
start_urls = ('http://www.itcast.cn/')
def parse(self, response):
pass
要建立一个Spider,需用scrapy.Spider类创建一个子类,并确定三个强制的属性和 一个方法:
-
name = "":爬虫的识别名称,必须是唯一的,在不同的爬虫必须定义不同的名字。 -
allow_domains = []是搜索的域名范围,也就是爬虫的约束区域,规定爬虫只爬取这个域名下的网页。 -
start_urls = ():爬取的URL元组/列表。爬虫从这里开始抓取数据,第一次下载的数据将会从这些urls开始。其他子URL将会从这些起始URL中继承性生成。 -
parse(self, response):解析的方法,每个初始URL完成下载后将被调用,调用的时候传入从每一个URL传回的Response对象来作为唯一参数,作用如下:
-
- 负责解析返回的网页数据(response.body),提取结构化数据(生成item)
- 生成需要下一页的URL请求
在mySpider目录下执行:
scrapy crawl itcast
爬取网页源代码信息
2.取数据
爬取整个网页完毕,接下来的就是的取过程(根据网页源码虚则合理的爬取工具)
from mySpider.items import ItcastItem
def parse(self, response):
#open("teacher.html","wb").write(response.body).close()
# 存放老师信息的集合
items = []
for each in response.xpath("//div[@class='li_txt']"):
# 将我们得到的数据封装到一个 `ItcastItem` 对象
item = ItcastItem()
#extract()方法返回的都是unicode字符串
name = each.xpath("h3/text()").extract()
title = each.xpath("h4/text()").extract()
info = each.xpath("p/text()").extract()
#xpath返回的是包含一个元素的列表
item['name'] = name[0]
item['title'] = title[0]
item['info'] = info[0]
items.append(item)
# 直接返回最后数据
return items
3.保存数据
scrapy保存信息的最简单的方法主要有四种,-o 输出指定格式的文件,,命令如下:
# json格式,默认为Unicode编码 scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.json # json lines格式,默认为Unicode编码 scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.jsonl # csv 逗号表达式,可用Excel打开 scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.csv # xml格式 scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.xml
Scrapy Shell
Scrapy终端是一个交互终端,可在未启动spider的情况下尝试及调试代码,也可用来测试XPath或CSS表达式,查看他们的工作方式,方便从爬取的网页中提取数据。
官方文档:http://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/topics/shell.html
1.启动Scrapy Shell
进入项目的根目录,执行下列命令来启动shell:
scrapy shell "http://www.itcast.cn/channel/teacher.shtml"
Scrapy Shell根据下载的页面会自动创建一些方便使用的对象,例如 Response 对象,以及 Selector 对象 (对HTML及XML内容)。
-
当shell载入后,将得到一个包含response数据的本地 response变量,输入
response.body将输出response的包体,输出response.headers可以看到response的包头。 -
输入
response.selector时, 将获取到一个response 初始化的类 Selector 的对象,此时可以通过使用response.selector.xpath()或response.selector.css()来对 response 进行查询。 -
Scrapy也提供了一些快捷方式, 例如
response.xpath()或response.css()同样可以生效(如之前的案例)。
2.Selectors选择器
Scrapy Selectors 内置 XPath 和 CSS Selector 表达式机制
Selector有四个基本的方法,最常用的还是xpath:
- xpath(): 传入xpath表达式,返回该表达式所对应的所有节点的selector list列表
- extract(): 序列化该节点为Unicode字符串并返回list
- css(): 传入CSS表达式,返回该表达式所对应的所有节点的selector list列表,语法同 BeautifulSoup4
- re(): 根据传入的正则表达式对数据进行提取,返回Unicode字符串list列表
3.案例
爬取地址:http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a
# 启动
scrapy shell "http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
# 返回 xpath选择器对象列表
response.xpath('//title')
[<Selector xpath='//title' data=u'<title>u804cu4f4du641cu7d22 | u793eu4f1au62dbu8058 | Tencent u817eu8bafu62dbu8058</title'>]
# 使用 extract()方法返回 Unicode字符串列表
response.xpath('//title').extract()
[u'<title>u804cu4f4du641cu7d22 | u793eu4f1au62dbu8058 | Tencent u817eu8bafu62dbu8058</title>']
# 打印列表第一个元素,终端编码格式显示
print response.xpath('//title').extract()[0]
<title>职位搜索 | 社会招聘 | Tencent 腾讯招聘</title>
# 返回 xpath选择器对象列表
response.xpath('//title/text()')
<Selector xpath='//title/text()' data=u'u804cu4f4du641cu7d22 | u793eu4f1au62dbu8058 | Tencent u817eu8bafu62dbu8058'>
# 返回列表第一个元素的Unicode字符串
response.xpath('//title/text()')[0].extract()
u'u804cu4f4du641cu7d22 | u793eu4f1au62dbu8058 | Tencent u817eu8bafu62dbu8058'
# 按终端编码格式显示
print response.xpath('//title/text()')[0].extract()
职位搜索 | 社会招聘 | Tencent 腾讯招聘
response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]')
职位名称:
print site[0].xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
TEG15-运营开发工程师(深圳)
职位名称详情页:
print site[0].xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
position_detail.php?id=20744&keywords=&tid=0&lid=0
职位类别:
print site[0].xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
技术类
3.Item Pipeline
当Item在Spider中被收集之后,它将会被传递到Item Pipeline,这些Item Pipeline组件按定义的顺序处理Item。
item pipeline的一些典型应用:
- 验证爬取的数据(检查item包含某些字段,比如说name字段)
- 查重(并丢弃)
- 将爬取结果保存到文件或者数据库中
①.item pipeline编写:
import something
class SomethingPipeline(object):
def __init__(self):
# 可选实现,做参数初始化等
# doing something
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# item (Item 对象) – 被爬取的item
# spider (Spider 对象) – 爬取该item的spider
# 这个方法必须实现,每个item pipeline组件都需要调用该方法,
# 这个方法必须返回一个 Item 对象,被丢弃的item将不会被之后的pipeline组件所处理。
return item
def open_spider(self, spider):
# spider (Spider 对象) – 被开启的spider
# 可选实现,当spider被开启时,这个方法被调用。
def close_spider(self, spider):
# spider (Spider 对象) – 被关闭的spider
# 可选实现,当spider被关闭时,这个方法被调用
②.Item Pipeline组件启用
为了启用Item Pipeline组件,必须将它的类添加到 settings.py文件ITEM_PIPELINES 配置
# Configure item pipelines
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
#'mySpider.pipelines.SomePipeline': 300,
"mySpider.pipelines.ItcastJsonPipeline":300
}
分配给每个类的整型值,确定了他们运行的顺序,item按数字从低到高的顺序,通过pipeline,通常将这些数字定义在0-1000范围内(0-1000随意设置,数值越低,组件的优先级越高)
③.重新启动爬虫
from mySpider.items import ItcastItem
def parse(self, response):
#open("teacher.html","wb").write(response.body).close()
# 存放老师信息的集合
#items = []
for each in response.xpath("//div[@class='li_txt']"):
# 将我们得到的数据封装到一个 `ItcastItem` 对象
item = ItcastItem()
#extract()方法返回的都是unicode字符串
name = each.xpath("h3/text()").extract()
title = each.xpath("h4/text()").extract()
info = each.xpath("p/text()").extract()
#xpath返回的是包含一个元素的列表
item['name'] = name[0]
item['title'] = title[0]
item['info'] = info[0]
#items.append(item)
#将获取的数据交给pipelines
yield item
# 返回数据,不经过pipeline
#return items
执行命令:
scrapy crawl itcast
Spider
Spider类定义了如何爬取某个网站,包括:爬取的动作(例如:是否跟进链接)以及如何从网页的内容中提取结构化数据(爬取item)。
class scrapy.Spider是最基本的类,所有编写的爬虫必须继承这个类。
主要用到的函数及调用顺序为:
__init__(): 初始化爬虫名字和start_urls列表start_requests() 调用make_requests_from url():生成Requests对象交给Scrapy下载并返回responseparse(): 解析response,并返回Item或Requests(需指定回调函数)。Item传给Item pipline持久化 , 而Requests交由Scrapy下载,并由指定的回调函数处理(默认parse()),一直进行循环,直到处理完所有的数据为止。
#所有爬虫的基类,用户定义的爬虫必须从这个类继承
class Spider(object_ref):
#定义spider名字的字符串(string)。spider的名字定义了Scrapy如何定位(并初始化)spider,所以其必须是唯一的。
#name是spider最重要的属性,而且是必须的。
#一般做法是以该网站(domain)(加或不加 后缀 )来命名spider。 例如,如果spider爬取 mywebsite.com ,该spider通常会被命名为 mywebsite
name = None
#初始化,提取爬虫名字,start_ruls
def __init__(self, name=None, **kwargs):
if name is not None:
self.name = name
# 如果爬虫没有名字,中断后续操作则报错
elif not getattr(self, 'name', None):
raise ValueError("%s must have a name" % type(self).__name__)
# python 对象或类型通过内置成员__dict__来存储成员信息
self.__dict__.update(kwargs)
#URL列表。当没有指定的URL时,spider将从该列表中开始进行爬取。 因此,第一个被获取到的页面的URL将是该列表之一。 后续的URL将会从获取到的数据中提取。
if not hasattr(self, 'start_urls'):
self.start_urls = []
# 打印Scrapy执行后的log信息
def log(self, message, level=log.DEBUG, **kw):
log.msg(message, spider=self, level=level, **kw)
# 判断对象object的属性是否存在,不存在做断言处理
def set_crawler(self, crawler):
assert not hasattr(self, '_crawler'), "Spider already bounded to %s" % crawler
self._crawler = crawler
@property
def crawler(self):
assert hasattr(self, '_crawler'), "Spider not bounded to any crawler"
return self._crawler
@property
def settings(self):
return self.crawler.settings
#该方法将读取start_urls内的地址,并为每一个地址生成一个Request对象,交给Scrapy下载并返回Response
#该方法仅调用一次
def start_requests(self):
for url in self.start_urls:
yield self.make_requests_from_url(url)
#start_requests()中调用,实际生成Request的函数。
#Request对象默认的回调函数为parse(),提交的方式为get
def make_requests_from_url(self, url):
return Request(url, dont_filter=True)
#默认的Request对象回调函数,处理返回的response。
#生成Item或者Request对象。用户必须实现这个类
def parse(self, response):
raise NotImplementedError
@classmethod
def handles_request(cls, request):
return url_is_from_spider(request.url, cls)
def __str__(self):
return "<%s %r at 0x%0x>" % (type(self).__name__, self.name, id(self))
__repr__ = __str__
主要属性和方法
-
name
定义spider名字的字符串。
例如,如果spider爬取 mywebsite.com ,该spider通常会被命名为 mywebsite
-
allowed_domains
包含了spider允许爬取的域名(domain)的列表,可选。
-
start_urls
初始URL元祖/列表。当没有制定特定的URL时,spider将从该列表中开始进行爬取。
-
start_requests(self)
该方法必须返回一个可迭代对象(iterable)。该对象包含了spider用于爬取(默认实现是使用 start_urls 的url)的第一个Request。
当spider启动爬取并且未指定start_urls时,该方法被调用。
-
parse(self, response)
当请求url返回网页没有指定回调函数时,默认的Request对象回调函数。用来处理网页返回的response,以及生成Item或者Request对象。
-
log(self, message[, level, component])
使用 scrapy.log.msg() 方法记录(log)message。 更多数据请参见 logging
案例:腾讯招聘网自动翻页采集
1.创建一个新的爬虫:
scrapy genspider tencent "tencent.com"
2.编写items.py
获取职位名称、详细信息、
class TencentItem(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field()
detailLink = scrapy.Field()
positionInfo = scrapy.Field()
peopleNumber = scrapy.Field()
workLocation = scrapy.Field()
publishTime = scrapy.Field()
3.编写tencent.py
# tencent.py
from mySpider.items import TencentItem
import scrapy
import re
class TencentSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
]
def parse(self, response):
for each in response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]'):
item = TencentItem()
name = each.xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
detailLink = each.xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
positionInfo = each.xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
peopleNumber = each.xpath('./td[3]/text()').extract()[0]
workLocation = each.xpath('./td[4]/text()').extract()[0]
publishTime = each.xpath('./td[5]/text()').extract()[0]
#print name, detailLink, catalog, peopleNumber, workLocation,publishTime
item['name'] = name.encode('utf-8')
item['detailLink'] = detailLink.encode('utf-8')
item['positionInfo'] = positionInfo.encode('utf-8')
item['peopleNumber'] = peopleNumber.encode('utf-8')
item['workLocation'] = workLocation.encode('utf-8')
item['publishTime'] = publishTime.encode('utf-8')
curpage = re.search('(d+)',response.url).group(1)
page = int(curpage) + 10
url = re.sub('d+', str(page), response.url)
# 发送新的url请求加入待爬队列,并调用回调函数 self.parse
yield scrapy.Request(url, callback = self.parse)
# 将获取的数据交给pipeline
yield item
4.编写pipeline.py文件
import json
#class ItcastJsonPipeline(object):
class TencentJsonPipeline(object):
def __init__(self):
#self.file = open('teacher.json', 'wb')
self.file = open('tencent.json', 'wb')
def process_item(self, item, spider):
content = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + "
"
self.file.write(content)
return item
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.file.close()
5.在 setting.py 里设置ITEM_PIPELINES
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
#'mySpider.pipelines.SomePipeline': 300,
#"mySpider.pipelines.ItcastJsonPipeline":300
"mySpider.pipelines.TencentJsonPipeline":300
}
执行爬虫:scrapy crawl tencent
CrawlSpiders
快速创建 CrawlSpider模板 的代码:
scrapy genspider -t crawl tencent tencent.com
crawspiders是Spider的派生类,Spider类的设计原则是只爬取start_url列表中的网页,而CrawlSpider类定义了一些规则(rule)来提供跟进link的方便的机制,从爬取的网页中获取link并继续爬取的工作更适合。
源码介绍:
class CrawlSpider(Spider):
rules = ()
def __init__(self, *a, **kw):
super(CrawlSpider, self).__init__(*a, **kw)
self._compile_rules()
#首先调用parse()来处理start_urls中返回的response对象
#parse()则将这些response对象传递给了_parse_response()函数处理,并设置回调函数为parse_start_url()
#设置了跟进标志位True
#parse将返回item和跟进了的Request对象
def parse(self, response):
return self._parse_response(response, self.parse_start_url, cb_kwargs={}, follow=True)
#处理start_url中返回的response,需要重写
def parse_start_url(self, response):
return []
def process_results(self, response, results):
return results
#从response中抽取符合任一用户定义'规则'的链接,并构造成Resquest对象返回
def _requests_to_follow(self, response):
if not isinstance(response, HtmlResponse):
return
seen = set()
#抽取之内的所有链接,只要通过任意一个'规则',即表示合法
for n, rule in enumerate(self._rules):
links = [l for l in rule.link_extractor.extract_links(response) if l not in seen]
#使用用户指定的process_links处理每个连接
if links and rule.process_links:
links = rule.process_links(links)
#将链接加入seen集合,为每个链接生成Request对象,并设置回调函数为_repsonse_downloaded()
for link in links:
seen.add(link)
#构造Request对象,并将Rule规则中定义的回调函数作为这个Request对象的回调函数
r = Request(url=link.url, callback=self._response_downloaded)
r.meta.update(rule=n, link_text=link.text)
#对每个Request调用process_request()函数。该函数默认为indentify,即不做任何处理,直接返回该Request.
yield rule.process_request(r)
#处理通过rule提取出的连接,并返回item以及request
def _response_downloaded(self, response):
rule = self._rules[response.meta['rule']]
return self._parse_response(response, rule.callback, rule.cb_kwargs, rule.follow)
#解析response对象,会用callback解析处理他,并返回request或Item对象
def _parse_response(self, response, callback, cb_kwargs, follow=True):
#首先判断是否设置了回调函数。(该回调函数可能是rule中的解析函数,也可能是 parse_start_url函数)
#如果设置了回调函数(parse_start_url()),那么首先用parse_start_url()处理response对象,
#然后再交给process_results处理。返回cb_res的一个列表
if callback:
#如果是parse调用的,则会解析成Request对象
#如果是rule callback,则会解析成Item
cb_res = callback(response, **cb_kwargs) or ()
cb_res = self.process_results(response, cb_res)
for requests_or_item in iterate_spider_output(cb_res):
yield requests_or_item
#如果需要跟进,那么使用定义的Rule规则提取并返回这些Request对象
if follow and self._follow_links:
#返回每个Request对象
for request_or_item in self._requests_to_follow(response):
yield request_or_item
def _compile_rules(self):
def get_method(method):
if callable(method):
return method
elif isinstance(method, basestring):
return getattr(self, method, None)
self._rules = [copy.copy(r) for r in self.rules]
for rule in self._rules:
rule.callback = get_method(rule.callback)
rule.process_links = get_method(rule.process_links)
rule.process_request = get_method(rule.process_request)
def set_crawler(self, crawler):
super(CrawlSpider, self).set_crawler(crawler)
self._follow_links = crawler.settings.getbool('CRAWLSPIDER_FOLLOW_LINKS', True)
①.LinkExtractors
class scrapy.linkextractors.LinkExtractor
Link Extractors 的目的很简单: 提取链接。
每个LinkExtractor有唯一的公共方法是 extract_links(),它接收一个 Response 对象,并返回一个 scrapy.link.Link 对象。
Link Extractors要实例化一次,并且 extract_links 方法会根据不同的 response 调用多次提取链接。
class scrapy.linkextractors.LinkExtractor(
allow = (),
deny = (),
allow_domains = (),
deny_domains = (),
deny_extensions = None,
restrict_xpaths = (),
tags = ('a','area'),
attrs = ('href'),
canonicalize = True,
unique = True,
process_value = None
)
主要参数:
-
allow:满足括号中“正则表达式”的值会被提取,如果为空,则全部匹配。 -
deny:与这个正则表达式(或正则表达式列表)不匹配的URL一定不提取。 -
allow_domains:会被提取的链接的domains。 -
deny_domains:一定不会被提取链接的domains。 -
restrict_xpaths:使用xpath表达式,和allow共同作用过滤链接。
②.rules
在rules中包含一个或多个Rule对象,每个Rule对爬取网站的动作定义了特定操作。如果多个rule匹配了相同的链接,则根据规则在本集合中被定义的顺序,第一个会被使用。
class scrapy.spiders.Rule(
link_extractor,
callback = None,
cb_kwargs = None,
follow = None,
process_links = None,
process_request = None
)
-
link_extractor:是一个Link Extractor对象,用于定义需要提取的链接。 -
callback: 从link_extractor中每获取到链接时,参数所指定的值作为回调函数,该回调函数接受一个response作为其第一个参数。 -
follow:是一个布尔(boolean)值,指定了根据该规则从response提取的链接是否需要跟进。 如果callback为None,follow 默认设置为True ,否则默认为False。 -
process_links:指定该spider中哪个的函数将会被调用,从link_extractor中获取到链接列表时将会调用该函数。该方法主要用来过滤。 -
process_request:指定该spider中哪个的函数将会被调用, 该规则提取到每个request时都会调用该函数。 (用来过滤request)
③.爬取规则(Crawling rules)
以腾讯招聘为例,
1.首先运行:
scrapy shell "http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
2.导入LinkExtractor,创建LinkExtractor实例对象:
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow=('position.php?&start=d+'))
allow : LinkExtractor对象最重要的参数之一,这是一个正则表达式,必须要匹配这个正则表达式(或正则表达式列表)的URL才会被提取,如果没有给出(或为空), 它会匹配所有的链接。
deny : 用法同allow,只不过与这个正则表达式匹配的URL不会被提取)。它的优先级高于 allow 的参数,如果没有给出(或None), 将不排除任何链接。
3.调用LinkExtractor实例的extract_links()方法查询匹配结果:
page_lx.extract_links(response)
4.没有查到:[]
5.注意转义字符的问题,继续重新匹配:
page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow=('position.php?&start=d+'))
# page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow = ('start=d+'))
page_lx.extract_links(response)
④.CrawlSpider 版本
由于CrawlSpider使用parse方法来实现其逻辑,如果覆盖了 parse方法,crawl spider将会运行失败。
#tencent.py
import scrapy
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
from mySpider.items import TencentItem
class TencentSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
]
page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow=("start=d+"))
rules = [
Rule(page_lx, callback = "parseContent", follow = True)
]
def parseContent(self, response):
for each in response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]'):
name = each.xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
detailLink = each.xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
positionInfo = each.xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
peopleNumber = each.xpath('./td[3]/text()').extract()[0]
workLocation = each.xpath('./td[4]/text()').extract()[0]
publishTime = each.xpath('./td[5]/text()').extract()[0]
#print name, detailLink, catalog,recruitNumber,workLocation,publishTime
item = TencentItem()
item['name']=name.encode('utf-8')
item['detailLink']=detailLink.encode('utf-8')
item['positionInfo']=positionInfo.encode('utf-8')
item['peopleNumber']=peopleNumber.encode('utf-8')
item['workLocation']=workLocation.encode('utf-8')
item['publishTime']=publishTime.encode('utf-8')
yield item
# parse() 方法不需要写
# def parse(self, response):
# pass
运行: scrapy crawl tencent
⑤.Logging
Scrapy提供了log功能,可以通过 logging 模块使用。可以修改配置文件settings.py,任意位置添加下面两行:
LOG_FILE = "TencentSpider.log" LOG_LEVEL = "INFO"
Log levels
-
Scrapy提供5层logging级别:
-
CRITICAL - 严重错误(critical)
- ERROR - 一般错误(regular errors)
- WARNING - 警告信息(warning messages)
- INFO - 一般信息(informational messages)
- DEBUG - 调试信息(debugging messages)
-
logging设置
通过在setting.py中进行以下设置可以被用来配置logging:
LOG_ENABLED默认: True,启用loggingLOG_ENCODING默认: 'utf-8',logging使用的编码LOG_FILE默认: None,在当前目录里创建logging输出文件的文件名LOG_LEVEL默认: 'DEBUG',log的最低级别LOG_STDOUT默认: False 如果为 True,进程所有的标准输出(及错误)将会被重定向到log中。例如,执行 print "hello" ,其将会在Scrapy log中显示。
Request
class Request(object_ref):
def __init__(self, url, callback=None, method='GET', headers=None, body=None,
cookies=None, meta=None, encoding='utf-8', priority=0,
dont_filter=False, errback=None):
self._encoding = encoding # this one has to be set first
self.method = str(method).upper()
self._set_url(url)
self._set_body(body)
assert isinstance(priority, int), "Request priority not an integer: %r" % priority
self.priority = priority
assert callback or not errback, "Cannot use errback without a callback"
self.callback = callback
self.errback = errback
self.cookies = cookies or {}
self.headers = Headers(headers or {}, encoding=encoding)
self.dont_filter = dont_filter
self._meta = dict(meta) if meta else None
@property
def meta(self):
if self._meta is None:
self._meta = {}
return self._meta
常用的参数:
-
url: 就是需要请求,并进行下一步处理的url -
callback: 指定该请求返回的Response,由那个函数来处理。 -
method: 请求一般不需要指定,默认GET方法,可设置为"GET", "POST", "PUT"等,且保证字符串大写 -
headers: 请求时,包含的头文件。一般不需要。 -
encoding: 使用默认的 'utf-8' 就行。 -
dont_filter: 表明该请求不由调度器过滤。这是当你想使用多次执行相同的请求,忽略重复的过滤器。默认为False。 -
errback: 指定错误处理函数 -
meta: 比较常用,在不同的请求之间传递数据使用的。字典dict型:
request_with_cookies = Request(url="http://www.example.com",cookies={'currency': 'USD', 'country': 'UY'},meta={'dont_merge_cookies': True})
Response
class Response(object_ref):
def __init__(self, url, status=200, headers=None, body='', flags=None, request=None):
self.headers = Headers(headers or {})
self.status = int(status)
self._set_body(body)
self._set_url(url)
self.request = request
self.flags = [] if flags is None else list(flags)
@property
def meta(self):
try:
return self.request.meta
except AttributeError:
raise AttributeError("Response.meta not available, this response "
"is not tied to any request")
常见参数:
status: 响应码_set_body(body): 响应体_set_url(url):响应url self.request = request- 其他同request中参数
POST请求
-
可以使用
yield scrapy.FormRequest(url, formdata, callback)方法发送POST请求。 -
如果希望程序执行一开始就发送POST请求,可以重写Spider类的
start_requests(self)方法,并且不再调用start_urls里的url。
class mySpider(scrapy.Spider):
# start_urls = ["http://www.example.com/"]
def start_requests(self):
url = 'http://www.renren.com/PLogin.do'
# FormRequest 是Scrapy发送POST请求的方法
yield scrapy.FormRequest(
url = url,
formdata = {"email" : "mr_mao_hacker@163.com", "password" : "axxxxxxxe"},
callback = self.parse_page
)
def parse_page(self, response):
# do something
模拟登陆
使用FormRequest.from_response()方法模拟用户登录
通常网站通过 实现对某些表单字段(如数据或是登录界面中的认证令牌等)的预填充。
使用Scrapy抓取网页时,如果想要预填充或重写像用户名、用户密码这些表单字段, 可以使用 FormRequest.from_response() 方法实现。
import scrapy
class LoginSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'example.com'
start_urls = ['http://www.example.com/users/login.php']
def parse(self, response):
return scrapy.FormRequest.from_response(
response,
formdata={'username': 'john', 'password': 'secret'},
callback=self.after_login
)
def after_login(self, response):
# check login succeed before going on
if "authentication failed" in response.body:
self.log("Login failed", level=log.ERROR)
return
# continue scraping with authenticated session...
知乎爬虫案例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
from scrapy.selector import Selector
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
from scrapy import Request, FormRequest
from zhihu.items import ZhihuItem
class ZhihuSipder(CrawlSpider) :
name = "zhihu"
allowed_domains = ["www.zhihu.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://www.zhihu.com"
]
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow = ('/question/d+#.*?', )), callback = 'parse_page', follow = True),
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow = ('/question/d+', )), callback = 'parse_page', follow = True),
)
headers = {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip,deflate",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.6,zh;q=0.4",
"Connection": "keep-alive",
"Content-Type":" application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/38.0.2125.111 Safari/537.36",
"Referer": "http://www.zhihu.com/"
}
#重写了爬虫类的方法, 实现了自定义请求, 运行成功后会调用callback回调函数
def start_requests(self):
return [Request("https://www.zhihu.com/login", meta = {'cookiejar' : 1}, callback = self.post_login)]
def post_login(self, response):
print 'Preparing login'
#下面这句话用于抓取请求网页后返回网页中的_xsrf字段的文字, 用于成功提交表单
xsrf = Selector(response).xpath('//input[@name="_xsrf"]/@value').extract()[0]
print xsrf
#FormRequeset.from_response是Scrapy提供的一个函数, 用于post表单
#登陆成功后, 会调用after_login回调函数
return [FormRequest.from_response(response, #"http://www.zhihu.com/login",
meta = {'cookiejar' : response.meta['cookiejar']},
headers = self.headers, #注意此处的headers
formdata = {
'_xsrf': xsrf,
'email': '1095511864@qq.com',
'password': '123456'
},
callback = self.after_login,
dont_filter = True
)]
def after_login(self, response) :
for url in self.start_urls :
yield self.make_requests_from_url(url)
def parse_page(self, response):
problem = Selector(response)
item = ZhihuItem()
item['url'] = response.url
item['name'] = problem.xpath('//span[@class="name"]/text()').extract()
print item['name']
item['title'] = problem.xpath('//h2[@class="zm-item-title zm-editable-content"]/text()').extract()
item['description'] = problem.xpath('//div[@class="zm-editable-content"]/text()').extract()
item['answer']= problem.xpath('//div[@class=" zm-editable-content clearfix"]/text()').extract()
return item
①.Item类设置
from scrapy.item import Item, Field
class ZhihuItem(Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
url = Field() #保存抓取问题的url
title = Field() #抓取问题的标题
description = Field() #抓取问题的描述
answer = Field() #抓取问题的答案
name = Field() #个人用户的名称
②.setting.py 设置抓取间隔
BOT_NAME = 'zhihu' SPIDER_MODULES = ['zhihu.spiders'] NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'zhihu.spiders' DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 0.25 #设置下载间隔为250ms
反反爬虫相关机制
来自于Scrapy官方文档描述:http://doc.scrapy.org/en/master/topics/practices.html#avoiding-getting-banned
通常防止爬虫被反主要有以下几个策略:
-
动态设置User-Agent(随机切换User-Agent,模拟不同用户的浏览器信息)
-
禁用Cookies(也就是不启用cookies middleware,不向Server发送cookies,有些网站通过cookie的使用发现爬虫行为)
- 可以通过
COOKIES_ENABLED控制 CookiesMiddleware 开启或关闭
- 可以通过
-
设置延迟下载(防止访问过于频繁,设置为 2秒 或更高)
-
Google Cache 和 Baidu Cache:如果可能的话,使用谷歌/百度等搜索引擎服务器页面缓存获取页面数据。
-
使用IP地址池:VPN和代理IP,现在大部分网站都是根据IP来ban的。
-
使用 Crawlera(专用于爬虫的代理组件),正确配置和设置下载中间件后,项目所有的request都是通过crawlera发出。
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {'scrapy_crawlera.CrawleraMiddleware': 600} CRAWLERA_ENABLED = True CRAWLERA_USER = '注册/购买的UserKey' CRAWLERA_PASS = '注册/购买的Password'
设置下载中间件(Downloader Middlewares)
下载中间件是处于引擎(crawler.engine)和下载器(crawler.engine.download())之间的一层组件,可以有多个下载中间件被加载运行。
-
当引擎传递请求给下载器的过程中,下载中间件可以对请求进行处理 (例如增加http header信息,增加proxy信息等);
-
在下载器完成http请求,传递响应给引擎的过程中, 下载中间件可以对响应进行处理(例如进行gzip的解压等)
①.process_request(self, request, spider)
-
当每个request通过下载中间件时,该方法被调用。
-
process_request() 必须返回以下其中之一:一个 None 、一个 Response 对象、一个 Request 对象或 raise IgnoreRequest:
-
如果其返回 None ,Scrapy将继续处理该request,执行其他的中间件的相应方法,直到合适的下载器处理函数(download handler)被调用, 该request被执行(其response被下载)。
-
如果其返回 Response 对象,Scrapy将不会调用 任何 其他的 process_request() 或 process_exception() 方法,或相应地下载函数; 其将返回该response。 已安装的中间件的 process_response() 方法则会在每个response返回时被调用。
-
如果其返回 Request 对象,Scrapy则停止调用 process_request方法并重新调度返回的request。当新返回的request被执行后, 相应地中间件链将会根据下载的response被调用。
-
如果其raise一个 IgnoreRequest 异常,则安装的下载中间件的 process_exception() 方法会被调用。如果没有任何一个方法处理该异常, 则request的errback(Request.errback)方法会被调用。如果没有代码处理抛出的异常, 则该异常被忽略且不记录(不同于其他异常那样)。
-
-
参数:
request (Request 对象)– 处理的requestspider (Spider 对象)– 该request对应的spider
②.process_response(self, request, response, spider)
当下载器完成http请求,传递响应给引擎的时候调用
-
process_request() 必须返回以下其中之一: 返回一个 Response 对象、 返回一个 Request 对象或raise一个 IgnoreRequest 异常。
-
如果其返回一个 Response (可以与传入的response相同,也可以是全新的对象), 该response会被在链中的其他中间件的 process_response() 方法处理。
-
如果其返回一个 Request 对象,则中间件链停止, 返回的request会被重新调度下载。处理类似于 process_request() 返回request所做的那样。
-
如果其抛出一个 IgnoreRequest 异常,则调用request的errback(Request.errback)。 如果没有代码处理抛出的异常,则该异常被忽略且不记录(不同于其他异常那样)。
-
-
参数:
request (Request 对象)– response所对应的requestresponse (Response 对象)– 被处理的responsespider (Spider 对象)– response所对应的spider
爬虫案例:
1. 创建middlewares.py文件。
Scrapy代理IP、Uesr-Agent的切换都是通过DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES进行控制,我们在settings.py同级目录下创建middlewares.py文件,包装所有请求。
# middlewares.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import random
import base64
from settings import USER_AGENTS
from settings import PROXIES
# 随机的User-Agent
class RandomUserAgent(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
useragent = random.choice(USER_AGENTS)
request.headers.setdefault("User-Agent", useragent)
class RandomProxy(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
proxy = random.choice(PROXIES)
if proxy['user_passwd'] is None:
# 没有代理账户验证的代理使用方式
request.meta['proxy'] = "http://" + proxy['ip_port']
else:
# 对账户密码进行base64编码转换
base64_userpasswd = base64.b64encode(proxy['user_passwd'])
# 对应到代理服务器的信令格式里
request.headers['Proxy-Authorization'] = 'Basic ' + base64_userpasswd
request.meta['proxy'] = "http://" + proxy['ip_port']
为什么HTTP代理要使用base64编码:
HTTP代理的原理很简单,就是通过HTTP协议与代理服务器建立连接,协议信令中包含要连接到的远程主机的IP和端口号,如果有需要身份验证的话还需要加上授权信息,服务器收到信令后首先进行身份验证,通过后便与远程主机建立连接,连接成功之后会返回给客户端200,表示验证通过。
信令格式:
CONNECT 59.64.128.198:21 HTTP/1.1 Host: 59.64.128.198:21 Proxy-Authorization: Basic bGV2I1TU5OTIz User-Agent: OpenFetion
其中Proxy-Authorization是身份验证信息,Basic后面的字符串是用户名和密码组合后进行base64编码的结果,也就是对username:password进行base64编码。
HTTP/1.0 200 Connection established OK,客户端收到收面的信令后表示成功建立连接,接下来要发送给远程主机的数据就可以发送给代理服务器,代理服务器建立连接后会在根据IP地址和端口号对应的连接放入缓存,收到信令后再根据IP地址和端口号从缓存中找到对应的连接,将数据通过该连接转发出去。
2. 修改settings.py配置USER_AGENTS和PROXIES
①添加USER_AGENTS:
USER_AGENTS = [
"Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; Trident/5.0; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; .NET CLR 3.0.30729; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; Media Center PC 6.0)",
"Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 6.0; Trident/4.0; WOW64; Trident/4.0; SLCC2; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; .NET CLR 3.0.30729; .NET CLR 1.0.3705; .NET CLR 1.1.4322)",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0b; Windows NT 5.2; .NET CLR 1.1.4322; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; InfoPath.2; .NET CLR 3.0.04506.30)",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-CN) AppleWebKit/523.15 (KHTML, like Gecko, Safari/419.3) Arora/0.3 (Change: 287 c9dfb30)",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux; en-US) AppleWebKit/527+ (KHTML, like Gecko, Safari/419.3) Arora/0.6",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.8.1.2pre) Gecko/20070215 K-Ninja/2.1.1",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-CN; rv:1.9) Gecko/20080705 Firefox/3.0 Kapiko/3.0",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux i686; U;) Gecko/20070322 Kazehakase/0.4.5"
]
②添加代理IP设置PROXIES:
PROXIES = [
{'ip_port': '111.8.60.9:8123', 'user_passwd': 'user1:pass1'},
{'ip_port': '101.71.27.120:80', 'user_passwd': 'user2:pass2'},
{'ip_port': '122.96.59.104:80', 'user_passwd': 'user3:pass3'},
{'ip_port': '122.224.249.122:8088', 'user_passwd': 'user4:pass4'},
]
③除非特殊需要,禁用cookies,防止某些网站根据Cookie来封锁爬虫。
COOKIES_ENABLED = False
④设置下载延迟
DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3
⑤最后设置setting.py里的DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES,添加自己编写的下载中间件类。
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
#'mySpider.middlewares.MyCustomDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
'mySpider.middlewares.RandomUserAgent': 1,
'mySpider.middlewares.ProxyMiddleware': 100
}
Settings
Scrapy设置(settings)提供了定制Scrapy组件的方法。可以控制包括核心(core),插件(extension),pipeline及spider组件。比如 设置Json Pipeliine、LOG_LEVEL等。
参考文档:http://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/1.0/topics/settings.html#topics-settings-ref
内置设置参考手册
-
BOT_NAME-
默认: 'scrapybot'
-
当您使用 startproject 命令创建项目时其也被自动赋值。
-
-
CONCURRENT_ITEMS-
默认: 100
-
Item Processor(即 Item Pipeline) 同时处理(每个response的)item的最大值。
-
-
CONCURRENT_REQUESTS-
默认: 16
-
Scrapy downloader 并发请求(concurrent requests)的最大值。
-
-
DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS-
默认: 如下
{ 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8', 'Accept-Language': 'en', }Scrapy HTTP Request使用的默认header。
-
-
DEPTH_LIMIT-
默认: 0
-
爬取网站最大允许的深度(depth)值。如果为0,则没有限制。
-
-
DOWNLOAD_DELAY-
默认: 0
-
下载器在下载同一个网站下一个页面前需要等待的时间。该选项可以用来限制爬取速度, 减轻服务器压力。同时也支持小数:
DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 0.25 # 250 ms of delay- 默认情况下,Scrapy在两个请求间不等待一个固定的值, 而是使用0.5到1.5之间的一个随机值 * DOWNLOAD_DELAY 的结果作为等待间隔。
-
-
DOWNLOAD_TIMEOUT-
默认: 180
-
下载器超时时间(单位: 秒)。
-
-
ITEM_PIPELINES-
默认: {}
-
保存项目中启用的pipeline及其顺序的字典。该字典默认为空,值(value)任意,不过值(value)习惯设置在0-1000范围内,值越小优先级越高。
ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'mySpider.pipelines.SomethingPipeline': 300, 'mySpider.pipelines.ItcastJsonPipeline': 800, }
-
-
LOG_ENABLED-
默认: True
-
是否启用logging。
-
-
LOG_ENCODING-
默认: 'utf-8'
-
logging使用的编码。
-
-
LOG_LEVEL-
默认: 'DEBUG'
-
log的最低级别。可选的级别有: CRITICAL、 ERROR、WARNING、INFO、DEBUG 。
-
-
USER_AGENT-
默认: "Scrapy/VERSION (+http://scrapy.org)"
-
爬取的默认User-Agent,除非被覆盖。
-
-
PROXIES: 代理设置-
示例:
PROXIES = [ {'ip_port': '111.11.228.75:80', 'password': ''}, {'ip_port': '120.198.243.22:80', 'password': ''}, {'ip_port': '111.8.60.9:8123', 'password': ''}, {'ip_port': '101.71.27.120:80', 'password': ''}, {'ip_port': '122.96.59.104:80', 'password': ''}, {'ip_port': '122.224.249.122:8088', 'password':''}, ]
-
-
COOKIES_ENABLED = False- 禁用Cookies