斐波那契数列想必大家都知道吧,如果不知道的话,我就再啰嗦一遍,
斐波那契数列为:1 2 3 5 8 13 ...,也就是除了第一项和第二项为1以外,对于第N项,有f(N)=f(N-1)+f(N-2)。
下面我用三种方法实现这个函数,分别是:递归,循环,矩阵。
递归方法:
public class Feibo { //递归方法 public static int recFeiBo(int n) { if(n<=0) { return 0; } if(n==1 || n==2) { return 1; } return recFeiBo(n-1) + recFeiBo(n-2); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(recFeiBo(6)); } }
循环方法:
public class Feibo{ public static int recFeiBo(int n) { if(n<=0) { return 0; } if(n==1 || n==2) { return 1; } int pre =1; int temp =0; int res =1; for(int i=1; i<=n-2; i++) { temp = res; res+=pre; pre = temp; } return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(recFeiBo(6)); } }
矩阵的方法:
不知道你们有没有发现:
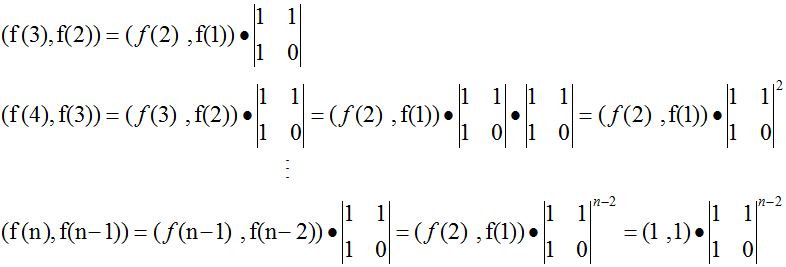
所以,最终求第N项数,就转化为求矩阵的n-2次方。
public class Feibo{ public static int recFeiBo(int n) { if(n<=0) { return 0; } if(n==1 || n==2) { return 1; } int[][] baseMatrix = {{1,1},{1,0}}; int[][] res = matrixPower(baseMatrix, n-2); return res[0][0] + res[1][0]; } public static int[][] matrixPower(int[][] m, int n) { int[][] temp = m; int[][] res = new int[m.length][m[0].length]; for(int i=0; i<m.length; i++) { res[i][i] = 1; } //n左移一位,并赋值给n //下面的for循环是用来快速的求解矩阵的n次方的。可以参考我下一篇关于如何快求解高次方 for(;n!=0; n>>=1) { //判断第0位是不是1 if((n&1)!=0) { res = multiMtrix(res,temp); } temp= multiMtrix(temp, temp); } return res; } private static int[][] multiMtrix(int[][] m1, int[][] m2) { int[][] res = new int[m1.length][m2[0].length]; for(int i=0; i<m1.length; i++) { for(int j=0; j<m2[0].length; j++) { for(int k=0; k<m2.length; k++) { res[i][j] += m1[i][k]*m2[k][j]; } } } return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(recFeiBo(6)); } }
其实斐波那契额数列问题就是可以总结为一类问题,就是让你求的当前值可以用函数表示的,f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2),这类问题你都可以用矩阵的方式去实现,比如爬楼梯问题,有n阶楼梯,每次只能跨1阶或2阶,归结出来就是s(n)=s(n-1)+s(n-2),初始值s(1)=1,s(2)=2.