题目
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:

输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
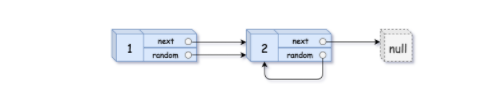
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
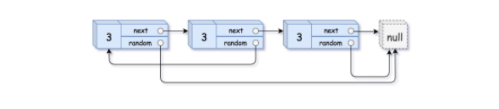
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000
Node.random 为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。
节点数目不超过 1000 。
分析(主要参考Krahets的题解
我们复制一般的链表是这么做的
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
Node dum = new Node(0), pre = dum;
while(cur != null) {
Node node = new Node(cur.val); // 复制节点 cur
pre.next = node; // 新链表的 前驱节点 -> 当前节点
// pre.random = "???"; // 新链表的 「 前驱节点 -> 当前节点 」 无法确定
cur = cur.next; // 遍历下一节点
pre = node; // 保存当前新节点
}
return dum.next;
}
}
出现的问题(即注释掉的语句)主要是,我们的链表节点是一个一个建立起来的,如图
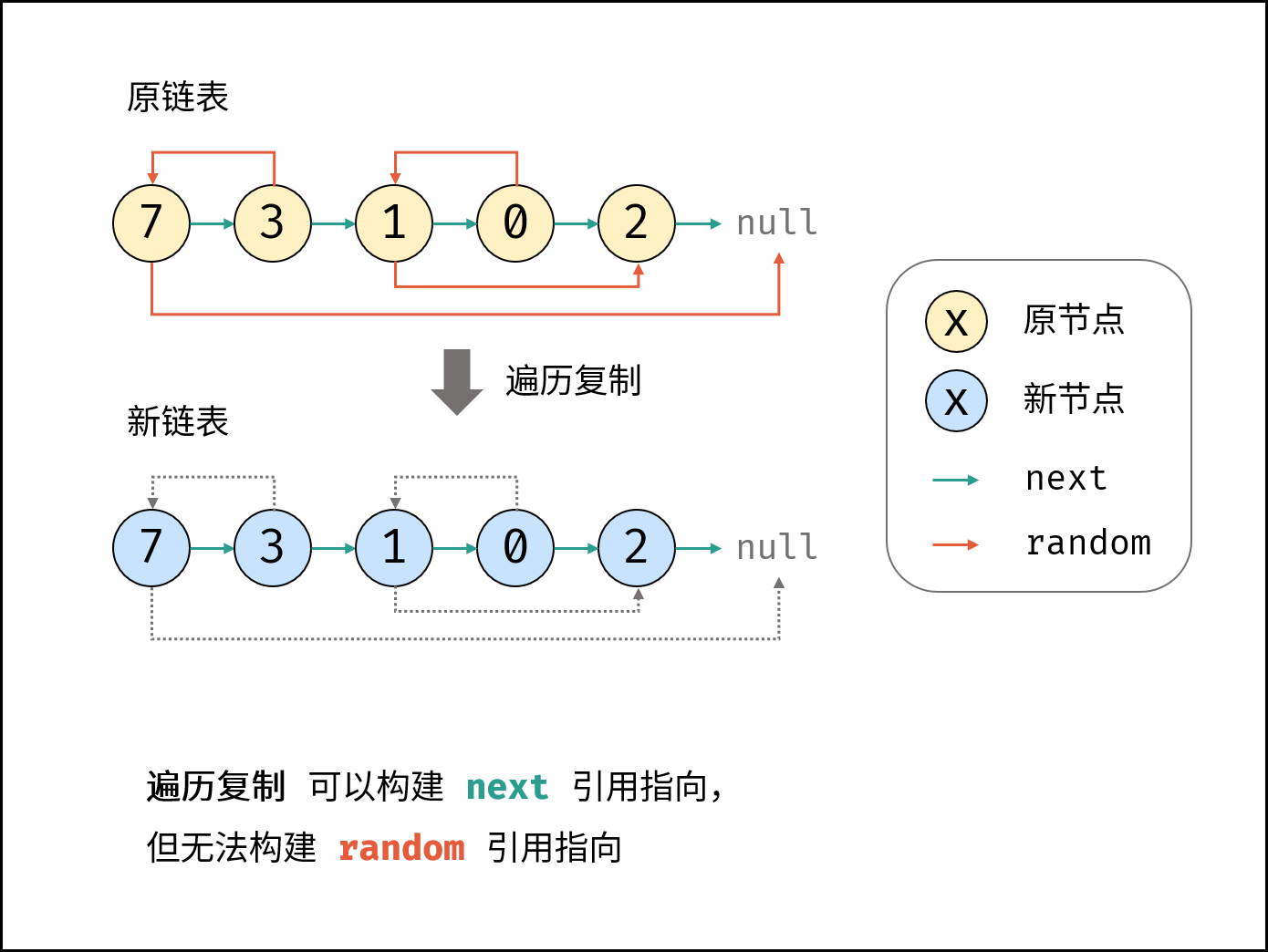
我们建立哨兵节点0后,建立第一个节点7,但是7后面的元素都还没构造出来,所以cur.random实际上是节点7调用Node构造函数的时候默认初始化的null,故输出凡是涉及到random,全是null。
题解1:使用哈希表
先用map建立和原复杂链表一样的链表,遍历新的链表(前后节点都已经建立好了),明确random的指向
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
//从头遍历,将
Node cur = head;
Map<Node, Node> hMap= new HashMap<>();
//复制各节点,建立原节点->新节点的map映射
while(cur != null){
hMap.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
//将cur重新放回头部
cur = head;
//构建新链表的next和random指向
while(cur != null){
hMap.get(cur).next = hMap.get(cur.next);
hMap.get(cur).random = hMap.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
//返回新链表的头结点
return hMap.get(head);
}
}
题解2 拼接+拆分
将新节点拼接在老节点后(eg.1->2->3 变为1->new_1->2-> new_2->3->new_3),明确random指向,返回拆分后的链表
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
//从头遍历,将
Node cur = head;
//1.复制节点,构建拼接链表
while(cur != null){
Node tmp = new Node(cur.val);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
}
//2.构建各节点的random指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.random != null)//防止出现null.next抛出空指针异常,为空的情况不用特殊处理,因为新节点构造时默认初始化的random已经是null了。
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;//cur.random非空的情况,新节点的random应该等于原来random的下一位
cur = cur.next.next;//cur移动两位,指向原链表节点的下一位。
}
//3.拆分两链表
cur = head.next;
Node pre = head, res = head.next;
while(cur.next != null){
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null;//单独处理原链表表尾节点
return res;//返回新链表头节点
}
}