Spring配置
查看配置文件中的标签:
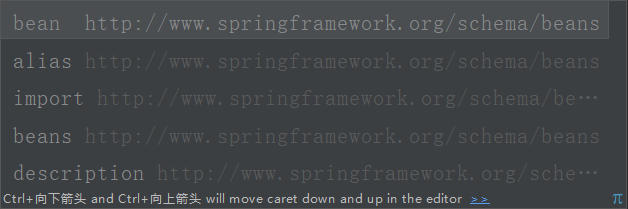
可以看到常用的就只有四个标签!
1、别名(alias)
如果添加了别名,我们也可以使用别名获取到这个对象
<alias name="user" alias="userNew"/>
2、Bean的配置
-
id:bean的唯一标识符,也就是相当于我们学的对象名
-
class:bean 对象对应的全限定名:包名 + 类型
-
name:也是别名,而且可以提示去多个别名
<bean id="user" class="com.star.pojo.User" name="user2 u2,u3;u4">
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"/>
</bean>
3、import
将多个配置文件导入,合并为一个
比如一个项目中有多人开发,这三个人负责不同的类开发,不同的类需要注册再在不同的bean中,我们就可以利用import将所有人的beans.xml合并为一个总的!
<import resource="beans.xml"/>
<import resource="beans2.xml"/>
<import resource="beans3.xml"/>
使用的时候直接使用总的配置!
依赖注入
1、构造器注入
上一篇中IOC创建对象的方式已经说过;
2、Set方式注入
- 依赖注入:Set注入!
- 依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器!
- 注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器来注入!
我们来编写个中数据类型的注入
1、编写实体类
package com.star.pojo;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
import java.util.*;
//导入lombok.jar包
@Setter
@toString
public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;//对象
private String[] books;//数组
private List<String> hobbys;//list
private Map<String,String> card;//map
private Set<String> games;//set
private String wife;//设空值
private Properties info;//Properties
}
其中Address是对象
package com.star.pojo;
public class Address {
private String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
2、注入信息applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.star.pojo.Student">
<property name="name" value="陌星"/>
<property name="address" ref="adr"/>
<property name="books" >
<array>
<value>水浒传</value>
<value>西游记</value>
<value>红楼梦</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
<value>list3</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="key1" value="value1"/>
<entry key="key2" value="value2"/>
<entry key="key3" value="value3"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>set1</value>
<value>set2</value>
<value>set3</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="id">3180</prop>
<prop key="name">wyx</prop>
<prop key="sex">boy</prop>
<prop key="hobby">LOL</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="adr" class="com.star.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3、测试(导入junt.jar包)
@Test
public void studentTest(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
测试结果:

3、拓展方式注入
我们可以使用p命令空间和c命令空间注入!
配置文件
<!--p命名空间注入,可以直接注入属性的值:property-->
<bean id="user" class="com.star.pojo.User" p:name="陌星" p:age="18"/>
<!--c命名空间注入,通过构造器注入:construct-args-->
<bean id="user2" class="com.star.pojo.User" c:age="18" c:name="LenStar"/>
测试
@Test
public void test2(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user2", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
注意:p命令和c命令空间不能直接使用,需要导入xml约束!
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
4、bean的作用域
我们查看bean标签中的scope属性可以看到
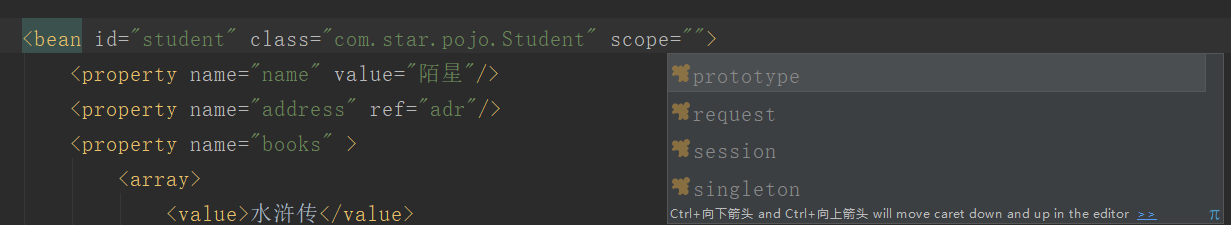
有这四种作用域!
prototype:每次创建新对象
<bean id="student" class="com.star.pojo.Student" scope="prototype"/>
测试
@Test
public void studentTest(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student student1 = (Student) context.getBean("student");
Student student2 = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student1.hashCode());
System.out.println(student2.hashCode());
}
测试结果:
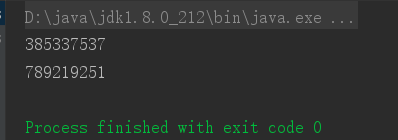
可以看到,hashCode不一样即为两个对象!
singleton:在容器中只有一个对象(默认)
<bean id="student" class="com.star.pojo.Student" scope="singleton"/>
测试结果:
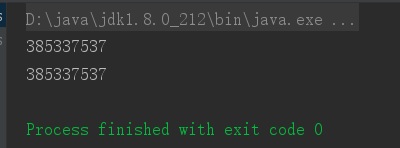
request/session:在web中使用!